What are the two main phases of glycolysis?
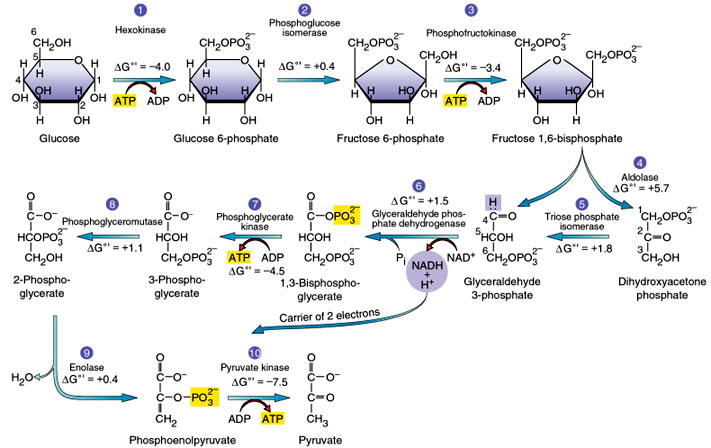
- Hexokinase.
- Phosphoglucose Isomerase.
- Phosphofructokinase.
- Aldolase.
- Triosephosphate isomerase.
- Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase.
- Phosphoglycerate Kinase.
- Phosphoglycerate Mutase.
What is the ultimate end result of glycolysis?
The combined end product of glycolysis is two molecules of pyruvate per molecule of glucose entering the process, plus two molecules of ATP and two of NADH, a so-called high-energy electron carrier. The complete net reaction of glycolysis is: C6H12O6 + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 CH3(C=O)COOH + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+.
What are three things that happen during glycolysis?
Sentences
- __________ is the process by which living cells break down __________ molecules to produce a usable form of energy.
- __________ is synthesized by the body, making it a by-product of cellular respiration.
- __________ is a molecule that is used as energy to drive many processes in living cells.
What are the various steps in glycolysis?
What are the steps of glycolysis simplified?
- Reaction 1: glucose phosphorylation to glucose 6-phosphate.
- Reaction 2: isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate.
- Reaction 3: phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
- Reaction 4: cleavage of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into two three-carbon fragments.
Which phase of meiosis takes the longest to complete?
- G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA. ...
- S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized. ...
- G2 phase: The period after DNA synthesis has occurred but prior to the start of prophase. ...
- In the latter part of interphase, the cell still has nucleoli present.
What happens during the second half of glycolysis?
How many stages are there in the glycolytic pathway?
What is the purpose of glycolysis?

What are two main phases of glycolysis?
MechanismGlycolysis Phases. Glycolysis has two phases: the investment phase and the payoff phase. ... Investment Phase. In this phase, there are two phosphates added to glucose. ... Payoff Phase. It is critical to remember that there are a total of two 3-carbon sugars for every one glucose at the beginning of this phase.
What is the second phase of glycolysis called?
The second half of glycolysis is known as the pay-off phase, characterised by a net gain of the energy-rich molecules ATP and NADH. Since glucose leads to two triose sugars in the preparatory phase, each reaction in the pay-off phase occurs twice per glucose molecule.
What are the stages of glycolysis?
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy StepsStep 1: Hexokinase. ... Step 2: Phosphoglucose Isomerase. ... Step 3: Phosphofructokinase. ... Step 4: Aldolase. ... Step 5: Triosephosphate isomerase. ... Step 6: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase. ... Step 7: Phosphoglycerate Kinase. ... Step 8: Phosphoglycerate Mutase.More items...•
What are the two products of glycolysis called?
Figure 7.2D. 1: Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate molecules: Glycolysis, or the aerobic catabolic breakdown of glucose, produces energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and pyruvate, which itself enters the citric acid cycle to produce more energy.
What is the first phase of glycolysis?
In the first step of glycolysis, the glucose ring is phosphorylated. Phosphorylation is the process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule derived from ATP. As a result, at this point in glycolysis, 1 molecule of ATP has been consumed.
Why is the second half of glycolysis called the payoff phase?
The second half of glycolysis is called the energy payoff phase. In this phase, the cell gains two ATP (from internal ADP + Pi) and 2 NADH (from internal NAD+) molecules. At the end of this phase glucose has become partially oxidized to form pyruvate.
What occurs during the lysis phase 2 of glycolysis?
In the second phase, called the payoff phase, consisting of the remaining 5 steps of the pathway, the two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are converted into two molecules of pyruvate, with the concomitant production of 4 ATP.
What is the payoff phase of glycolysis?
The second half of glycolysis is called the energy payoff phase. In this phase, the cell gains two ATP and two NADH compounds. At the end of this phase, glucose has become partially oxidized to form pyruvate.
What is the correct sequence of glycolysis?
The correct answer is ' G 6-P→ 3-PGAL→3-PGA→3-PEP'.
What is the another name of glycolysis?
EMP pathwayGlycolysis is also called as EMP pathway. It is after the name of the discoverers - Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas.
Why is the third step of glycolysis known as the committed step?
The committed step is the one after which the substrate has only one way to go. Because glycolytic intermediates feed into several other pathways, the regulation of glycolysis occurs at more than one point. This allows the regulation of several pathways to be coordinated.
What is glycolysis and its process?
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms.
Products and Reactants and Krebs Cycle Flashcards | Quizlet
Start studying Products and Reactants and Krebs Cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
BYJUS
BYJUS
Glycolysis Pathway Steps & Summary | What is Glycolysis? - Video ...
Glycolysis Steps. Glycolysis involves: 1. Phosphorylation: Glucose is phosphorylated in the presence of hexokinase to produce Glucose-6-phosphate.In this step, an ATP molecule is converted to ADP ...
What is the purpose of glycolysis?
The main purpose of glycolysis is to provide pyruvate for the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) cycle , not to make adenosine 5′-triphosphate. The glycolytic production of pyruvate reduces the cytosol by increasing the ratio of NADH [a reduced form of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)] to NAD+.
What is the name of the sugar that is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called?
In glycolysis, a six-carbon sugar known as glucose is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate . This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron-carrying molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
How many molecules does glycolysis produce?
Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
How many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis?
A net of two ATP molecules are produced through glycolysis (two are used during the process and four are produced.) Learn more about the 10 steps of glycolysis below.
What is the function of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (?
First, it dehydrogenates GAP by transferring one of its hydrogen (H⁺) molecules to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) to form NADH + H⁺.
What happens to the phosphoglycerokinase in BPG?
The enzyme phosphoglycerokinase transfers a phosphate from BPG to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens to each molecule of BPG. This reaction yields two 3-phosphoglycerate (3 PGA) molecules and two ATP molecules.
How many ATP molecules does pyruvate kinase produce?
This happens for each molecule of PEP. This reaction yields two molecules of pyruvate and two ATP molecules.
How many ATP molecules are in a multistep process?
This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron-carrying molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
What is the process of releasing energy within sugars?
Glycolysis, which translates to "splitting sugars", is the process of releasing energy within sugars. In glycolysis, a six-carbon sugar known as glucose is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, ...
How many steps are involved in glycolysis?
Glycolysis has ten steps, and depending on your interests—and the classes you’re taking—you may want to know the details of all of them. However, you may also be looking for a greatest hits version of glycolysis, something that highlights the key steps and principles without tracing the fate of every single atom. Let’s start with a simplified version of the pathway that does just that.
Where does glycolysis take place?
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: the energy-requiring phase, above the dotted line in the image below, and the energy-releasing phase, below the dotted line. Energy-requiring phase. In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are attached ...
What is the energy-requiring phase of glucose?
Energy-requiring phase. In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are attached to it. The phosphate groups make the modified sugar—now called fructose-1,6-bisphosphate—unstable, allowing it to split in half and form two phosphate-bearing three-carbon sugars.
What is the process of separating glucose into two three-carbon molecules called?
Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today.
Why does glycolysis need electrons?
Glycolysis needs to accept electrons as part of a specific reaction. If there’s no around (because it's all stuck in its form), this reaction can’t happen and glycolysis will come to a halt. So, all cells need a way to turn back into to keep glycolysis going.
What is the first step in the breakdown of glucose?
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
How many ATP and NADH are produced in a series of steps?
In a series of steps that produce one NADH and two ATP, a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate molecule is converted into a pyruvate molecule. This happens twice for each molecule of glucose since glucose is split into two three-carbon molecules, both of which will go through the final steps of the pathway.
What is the energy requiring phase of glycolysis?
During the energy-requiring phase of glycolysis, two ATP molecules are used to split one molecule of glucose into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
How many steps are involved in glycolysis?
There are 10 steps of glycolysis, each involving a different enzyme. Steps 1 – 5 make up the energy-requiring phase of glycolysis and use up two molecules of ATP. Steps 6 – 10 are the energy-releasing phase, which produces four molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH.
What is the reaction of BPG and ATP?
This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase.
How does glycolysis work?
Glycolysis is a 10 step process that releases energy from glucose and converts glucose into pyruvate. These reactions take place in the cytosol of cells and can happen in the presence or absence of oxygen. During glycolysis, a single molecule of glucose is used to produce a net two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, and two molecules of NADH. The pyruvate may then be used in aerobic respiration or, in the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration.
What is the purpose of glycolysis?
During glycolysis, a single molecule of glucose is used to produce a net two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, and two molecules of NADH. The pyruvate may then be used in aerobic respiration or, in the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration. The 10 steps of glycolysis can be divided into two parts.
What is the reaction that transfers phosphate group to ADP?
A phosphate group is transferred from PEP to ADP. This reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate kinase and creates two molecules of ATP and two molecules of pyruvate.
What is the process of releasing energy from glucose?
Glycolysis (AKA the glycolytic pathway) is the metabolic process that releases energy from glucose. During glycolysis, a single molecule of glucose is split into two 3-carbon molecules, called pyruvates. At the same time, energy is extracted from glucose and converted into ATP, which is then used to fuel other cellular processes.
How many steps are involved in glycolysis?
In plants, sucrose breaks down into glucose and fructose with enzyme invertase, and then these two monosaccharides readily enter the glycolytic pathway. This glycolytic pathway consists of ten steps. A specific enzyme catalyzes each step. The ten steps of glycolysis are:
Where does glycolysis take place?
This process occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In addition, glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of all living organisms.
What is the end product of pyruvic acid?
Glycolysis is the pathway that converts glucose into pyruvic acid and yields energy in the form of ATP and N A D H. H +. In this pathway oxygen is not needed and it is a common pathway for aerobic and anaerobic respiration. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of all living cells. The end product is pyruvic acid which is a three-carbon compound.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to form pyruvic acid?
Glycolysis is the series or sequence of reactions or pathways by which glucose is broken down anaerobically to form pyruvic acid. During glycolysis, one glucose molecule makes two molecules of pyruvate.
What are the three enzymes that regulate glycolysis?
Glycolysis is regulated by three regulatory enzymes hexokinase or glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase, and glucose concentration in the blood and by a certain hormone level in the blood.
How is pyruvate formed?
Formation of Pyruvate: In the last step 2 -Phosphoenol pyruvic acid is converted to Pyruvic acid by the removal of phosphorus, thus one molecule of ATP is synthesized from ADP by substrate-level phosphorylation with the action of enzyme pyruvic Kinase. Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis.
What enzyme is involved in phosphorylation of glucose?
Phosphorylation of Glucose: In this step, phosphorylation of glucose by ATP occurs in the presence of Mg 2 + and an enzyme hexokinase to form Glucose- 6 -phosphate.
Where does the glucose pyruvate reaction take place?
It is the process in which a glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cell. Six enzymes are involved in the process. The end products of the reaction include 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
How is a phosphate group added to glucose?
A phosphate group is added to glucose in the cell cytoplasm, by the action of enzyme hexokinase. In this, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose forming glucose,6-phosphate.
What is the substrate of trise phosphate isomerase?
Triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is the substrate in the successive step of glycolysis.
How many molecules of phosphoglycerate are in ATP?
Phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP with the help of phosphoglycerokinase. Thus two molecules of phosphoglycerate and ATP are obtained at the end of this reaction.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
What is Glycolysis? Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytosol of the cell cytoplasm, in the presence or absence of oxygen. Glycolysis is the primary step of cellular respiration.
Which enzyme is responsible for the phosphoglycerate molecule?
The phosphate of both the phosphoglycerate molecules is relocated from the third to the second carbon to yield two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate by the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
Which molecule converts phosphate to fructose?
The other ATP molecule transfers a phosphate group to fructose 6-phosphate and converts it into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by the action of enzyme phosphofructokinase.
What are the phases of the glucose catabolic pathway?
The Glucose catabolic pathway can be divided into two Phases. They are the Preparative Phase and Payoff Phase.
What is the first stage of cellular respiration?
In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration. Without oxygen, glycolysis allows cells to make small amounts of ATP. This process is called fermentation.
What enzyme splits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into two sugars that are isomers?
The enzyme aldolase splits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into two sugars that are isomers of each other. These two sugars are dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde phosphate.
What is the name of the process of splitting sugar?
Glycolysis literally means “ splitting of sugar “. The pathway is also called “ EMP Pathway ” and “ Glucose oxidative pathway “. In glycolysis, Glucose (a six-carbon sugar) is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar. Glycolysis yields two molecules of ATP (free energy-containing molecule), two molecules of pyruvic acid, ...
How many molecules of pyruvic acid are produced in glycolysis?
In summary, a single glucose molecule in glycolysis produces a total of 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, 2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of NADH, and 2 molecules of water.
Which enzyme isomerase rapidly inter-converts the molecules dihydroxyacetone phosphate and gly?
The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase rapidly inter-converts the molecules dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde phosphate. Glyceraldehyde phosphate is removed as soon as it is formed to be used in the next step of glycolysis.
Which enzyme converts glucose 6-phosphate into its isomer fructose 6-phosphate?
The enzyme phosphoglucoisomerase converts glucose 6-phosphate into its isomer fructose 6-phosphate. Isomers have the same molecular formula, but the atoms of each molecule are arranged differently.
What happens during the second half of glycolysis?
Likewise, what occurs during the second half of glycolysis? The second half of glycolysis extracts ATP and high-energy electrons from hydrogen atoms and attaches them to NAD+. Two ATP molecules are invested in the first half and four ATP molecules are formed by substrate phosphorylation during the second half.
How many stages are there in the glycolytic pathway?
The glycolytic pathway can be divided into three stages: (1) glucose is trapped and destabilized; (2) two interconvertible three-carbon molecules are generated by cleavage of six-carbon fructose; and (3) ATP is generated.
What is the purpose of glycolysis?
The main purpose of glycolysis is to provide pyruvate for the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) cycle , not to make adenosine 5′-triphosphate. The glycolytic production of pyruvate reduces the cytosol by increasing the ratio of NADH [a reduced form of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)] to NAD+.
