What are the five classes of mollusks?
Classes of Molluscs. Classes of Molluscs. For more than 50 years five classes of living molluscs were recognized: Amphineura, Gastropoda, Scaphopoda, Bivalvia (also called Pelecypoda), and Cephalopoda. Discovery of Neopilina in the 1950s added another class (Monoplacophora), and Hyman* contended that. Figure 16-7.
What animals belong to the phylum Mollusca?
What animals are in the Mollusca phylum?
- Some Kinds of Mollusk.
- Typical mollusk anatomy.
- Typical bivalve shell (this one is a cockle)
- Mussels cling to rocks in tidal waters.
- Many bivalves like these cockles prefer sandy homes where they can burrow.
- Cephalopods have large eyes and brains.
- Camouflaged squid resting near seabed.
- Octopuses.
What is the class and phylum of a mollusk?
Phylum Mollusca is a very diverse (85,000 species ) group of mostly marine species, with a dramatic variety of form. This phylum can be segregated into seven classes: Aplacophora, Monoplacophora, Polyplacophora, Bivalvia, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda, and Scaphopoda.
What are some examples of phylum Mollusca?
Phylum Mollusca
- Phylum Mollusca
- Habit and habitat. Member of this phylum shows a great variety in structural organization, habit and habitat. Most of the members have shells.
- Identifying characters. Body is soft, generally covered by a hard shell. ...
- Example: Pila globosa (Apple snail) lamellidens (Bivalve) Octopus vulgaris (Octopus).

What are the 3 major classes of phylum Mollusca?
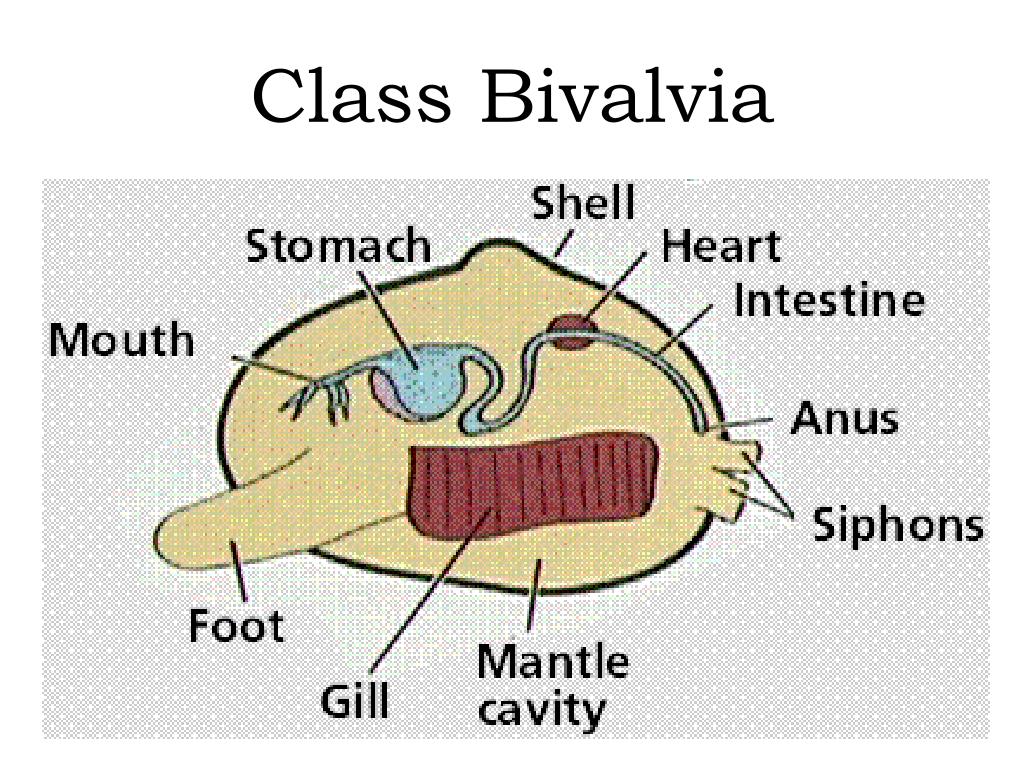
The major classes of living mollusks include gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods (Figure below).Gastropods. Gastropods include snails and slugs. They use their foot to crawl. ... Bivalves. Bivalves include clams, scallops, oysters, and mussels. ... Cephalopods. Cephalopods include the octopus and squid.
What are the classes of the phylum Mollusca?
The Phylum Mollusca consist of 8 classes: 1) the Monoplacophora discovered in 1977; 2) the worm-like Aplacophora or solenogasters of the deep sea; 3) the also worm-like Caudofoveata; 4) the Polyplacophora, or chitons; 5) the Pelecypoda or bivalves; 6) the Gastropoda or snails; 7) the Scaphopoda, or tusk shells; and 8) ...
What are 3 things you know about phylum Mollusca?
Mollusca CharacteristicsThey are mostly found in marine and freshwater. ... They exhibit organ system level of organization.Their body has a cavity.The body is divided into head, visceral mass, muscular foot and mantle.The head comprises of tentacles and compound eyes.The body is covered by a calcareous shell.More items...•
How many classes of Mollusca do we have?
Living mollusks are usually grouped into eight classes: Gastropoda (see gastropod), Bivalvia or Pelecypoda (see bivalve), Cephalopoda (see cephalopod), Scaphopoda (tusk shells), Aplacophora (Solenogasters), Caudofoveata (sometimes included in the Aplacophora order), Polyplacophora (chitons), and Monoplacophora.
What are the four classes of mollusks?
ClassificationClassMajor organismsGastropodaall snails and slugs including abalone, limpets, conch, nudibranchs, sea hares, sea butterfliesBivalviaclams, oysters, scallops, geoducks, mussels, rudists†PolyplacophorachitonsCephalopodasquid, octopuses, cuttlefish, nautiluses, Spirula, belemnites†, ammonites†6 more rows
What are the 4 major molluscs?
The four major groups of mollusks (phyla Mollusca) are: 1) chitons; 2) gastropods, including snails, slugs (mostly marine, but some freshwater), and nudibranches.
What are characteristics of phylum Mollusca?
Molluscs (also know as mollusks) are soft-bodied, bilaterally symmetrical, segmented, coelomate animals; usually shelled having a mantle, ventral foot, anterior head, and a dorsal visceral mass.
What are the 6 molluscs?
Class Gastropoda – snails, slugs, limpets, whelks, conchs, periwinkles, etc.
Which of the following belongs to the phylum Mollusca?
The animals belonging to the phylum Mollusca are apple snail, pearl oyster, devil fish, tusk shell, etc. Hence correct answer is option A.
How many mollusc types are there today?
The molluscs (also called mollusks) compose the large phylum of invertebrate animals known as the Mollusca. Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized.
How do you memorize Mollusca classes?
Mnemonic Device: Some Grownups Can't See Magic Ponies But Children CAN.
What are the two subclasses of the class Amphineura?
Subclass i. Aplacophora or Solenogastres : 1. The body is elongated and worm-like and enveloped by the mantle. 2.
What is an asymmetrical mollusc?
Asymmetrical molluscs with a spirally coiled mantle and a shell of one piece enclosing a corresponding visceral mass. The asymmetry of visceropallium is its fundamental feature. 2. A well-developed head bearing eyes and tentacles are usually present.
What is the body system that consists of two auricles and a ventricle?
8. The rectum pierces the pericardium and the ventricle, and opens in the exhalant siphon. 9. The heart consists of two auricles and a ventricle. 10. The nervous system consists of paired cerebral, pedal and visceral ganglia with their connectives.
How many classes of mollusks are there in the phylum?
The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates —and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species.
How many species of molluscs are there?
Estimates of accepted described living species of molluscs vary from 50,000 to a maximum of 120,000 species. The total number of described species is difficult to estimate because of unresolved synonymy.
What are the most important things that molluscs have done for centuries?
Molluscs have, for centuries, also been the source of important luxury goods, notably pearls, mother of pearl, Tyrian purple dye, and sea silk. Their shells have also been used as money in some preindustrial societies. Mollusc species can also represent hazards or pests for human activities.
What is the shell of a mollusc made of?
This has a single, " limpet -like" shell on top, which is made of proteins and chitin reinforced with calcium carbonate, and is secreted by a mantle covering the whole upper surface. The underside of the animal consists of a single muscular "foot". Although molluscs are coelomates, the coelom tends to be small.
What is the largest phylum of marine organisms?
Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat.
Why are molluscs called archi-molluscs?
Because of the great range of anatomical diversity among molluscs, many textbooks start the subject of molluscan anatomy by describing what is called an archi-mollusc, hypothetical generalized mollusc, or hypothetical ancestral mollusc ( HAM) to illustrate the most common features found within the phylum. The depiction is visually rather similar to modern monoplacophorans.
When did gastropods appear?
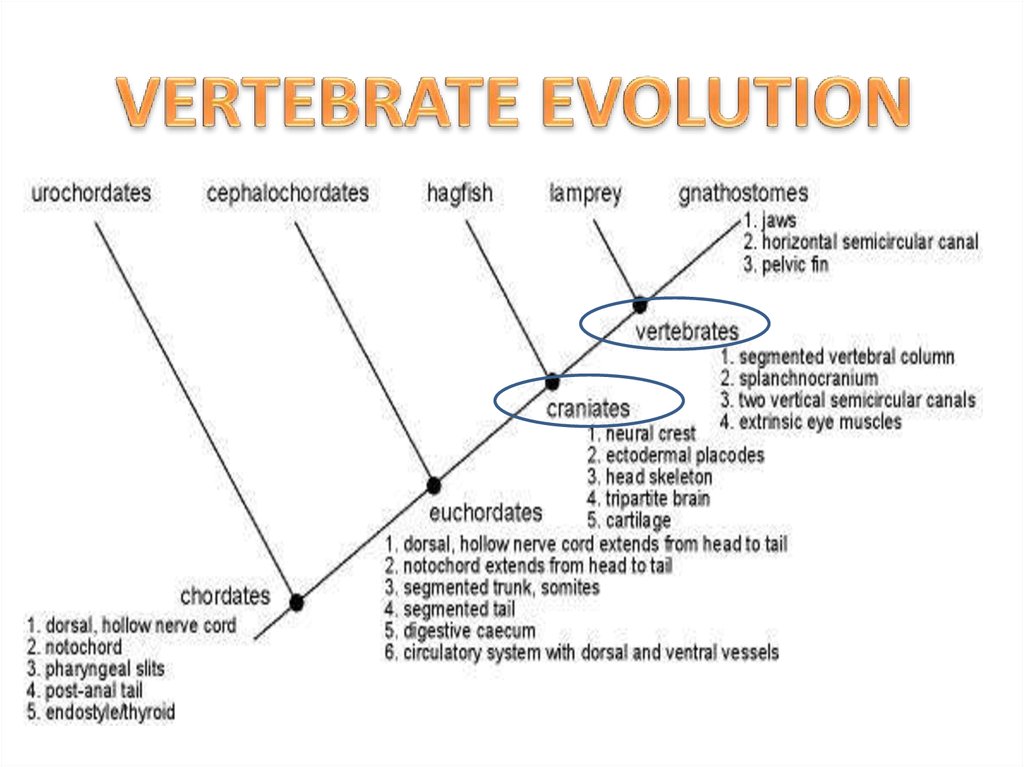
Good evidence exists for the appearance of gastropods (e.g., Aldanella ), cephalopods (e.g., Plectronoceras , ? Nectocaris) and bivalves ( Pojetaia, Fordilla) towards the middle of the Cambrian period, c. 500 million years ago, though arguably each of these may belong only to the stem lineage of their respective classes. However, the evolutionary history both of the emergence of molluscs from the ancestral group Lophotrochozoa, and of their diversification into the well-known living and fossil forms, is still vigorously debated.
What are the characteristics of a mollusc phylum?
Ans: The five characteristics of the phylum Mollusca are as follows: 1.These are mostly marine habitats, and some are freshwater habitats. 2.They are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical with organ system level of organization. 3.The body of molluscs is unsegmented with a distinct head, muscular foot, and visceral hump.
What phylum do snails belong to?
These snails belong to the Phylum Mollusca. Phylum Mollusca is the second most abundant phylum in the Animal Kingdom.
What is the second largest phylum in Animalia?
The phylum Mollusca is the second largest phylum in the Kingdom Animalia. These are soft-bodied animals with an outer covering of calcium shell. They move with the help of a muscular foot. The members are marine forms, and some are freshwater forms.
What is the importance of mollusca?
The economic importance of Phylum Mollusca are as follows: Molluscs like oyster, squid and cuttlefish are used as food in many countries. The shell of many molluscs is of ornamental value, i.e., used in pearl extraction. Dentalium is used as a decorative piece. Sepia ink has medicinal value.
What are the excretory organs of molluscs?
Excretory organs are in the form of structures called organs of Bojanus. Ammonia is the chief excretory matter. The digestive tract is complete with a digestive gland or liver. In some molluscs like Pila, the buccal cavity contains a grasping organ, the radula, with transverse rows of teeth for cutting the grass.
Why do mollusks have osphradium?
Some molluscs have Osphradium for testing the chemical and physical nature of water. The sexes are separate, and fertilization is internal. They are oviparous. The development is either direct or indirect. When the development is indirect, it includes a characteristic larva, veliger, trochophore or glochidium.
Where did the name Mollusca come from?
The name Mollusca came from the Latin, “ mollis ” meaning “ soft ” and this term was first used by the French Zoologist Cuvier in 1798 to describe squids and cuttlefish, an animal whose shell is reduced internal or entirely absent.
Overview
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks . Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied.
Etymology
The words mollusc and mollusk are both derived from the French mollusque, which originated from the Latin molluscus, from mollis, soft. Molluscus was itself an adaptation of Aristotle's τὰ μαλάκια ta malákia (the soft ones; < μαλακός malakós "soft"), which he applied inter alia to cuttlefish. The scientific study of molluscs is accordingly called malacology.
The name Molluscoida was formerly used to denote a division of the animal kingdom containin…
Definition
The most universal features of the body structure of molluscs are a mantle with a significant cavity used for breathing and excretion, and the organization of the nervous system. Many have a calcareous shell.
Molluscs have developed such a varied range of body structures, finding synapomorphies (defining characteristics) to apply to all modern groups is difficult. The most general characteristic of mol…
Diversity
Estimates of accepted described living species of molluscs vary from 50,000 to a maximum of 120,000 species. The total number of described species is difficult to estimate because of unresolved synonymy. In 1969 David Nicol estimated the probable total number of living mollusc species at 107,000 of which were about 12,000 fresh-water gastropods and 35,000 terrestrial. The Biv…
Hypothetical ancestral mollusc
Because of the great range of anatomical diversity among molluscs, many textbooks start the subject of molluscan anatomy by describing what is called an archi-mollusc, hypothetical generalized mollusc, or hypothetical ancestral mollusc (HAM) to illustrate the most common features found within the phylum. The depiction is visually rather similar to modern monoplacophorans.
Ecology
Most molluscs are herbivorous, grazing on algae or filter feeders. For those grazing, two feeding strategies are predominant. Some feed on microscopic, filamentous algae, often using their radula as a 'rake' to comb up filaments from the sea floor. Others feed on macroscopic 'plants' such as kelp, rasping the plant surface with its radula. To employ this strategy, the plant has to be large enough for the mollusc to 'sit' on, so smaller macroscopic plants are not as often eaten as …
Classification
Opinions vary about the number of classes of molluscs; for example, the table below shows seven living classes, and two extinct ones. Although they are unlikely to form a clade, some older works combine the Caudofoveata and Solenogasters into one class, the Aplacophora. Two of the commonly recognized "classes" are known only from fossils.
Classification into higher taxa for these groups has been and remains problematic. A phylogenet…
Evolution
Good evidence exists for the appearance of gastropods (e.g., Aldanella), cephalopods (e.g., Plectronoceras, ?Nectocaris) and bivalves (Pojetaia, Fordilla) towards the middle of the Cambrian period, c. 500 million years ago, though arguably each of these may belong only to the stem lineage of their respective classes. However, the evolutionary history both of the emergence of molluscs …
History of Phylum Mollusca
What Are The Characteristics of Phylum Mollusca?
- Members of this phylum are commonly called soft-bodied animalssince they have a soft body enclosed in a calcareous shell. The characteristics of Phylum Mollusca are listed below: 1. These are mostly marine habitats, and some are freshwater habitats. 2. They are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical with organ system level of organization. 3. The body of molluscs is unsegmented w…
Classification of Phylum Mollusca
- According to the body symmetry and the characteristics of food, shell, gills, mantle, muscles and radula, molluscs are classified into six classes. The classification followed in this article is by Morton and Yonge \(\left( {1964} \right)\) and they classified Mollusca into six classes as they merged class Aplacophora and Poly-placophora into a sin...
Examples of Phylum Mollusca
- Some of the examples of the phylum Mollusca are as follows: 1. Pila Classification of Pila– Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda Order: Architaenioglossa Genus: Pila Fig:Pila 2. Sepia Classification of Sepia Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Cephalopoda Order: Sepiida Family: SepiidaeGenus:Sepia Fig: Sepia 3. Octopus Classification of Octopus– Ki…
Economic Importance of Phylum Mollusca
- The economic importance of Phylum Mollusca are as follows: 1. Molluscs like oyster, squid and cuttlefish are used as food in many countries. 2. The shell of many molluscs is of ornamental value, i.e., used in pearl extraction. 3. Dentaliumis used as a decorative piece. 4. Sepiainkhas medicinal value. 5. Shells of oyster are mixed with tar to make roads. Attempt Mock Tests
Summary
- The phylum Mollusca is the second largest phylum in the Kingdom Animalia. These are soft-bodied animals with an outer covering of calcium shells. Phylum Mollusca’s body is divided into head, visceral mass, and muscular foot. They move with the help of a muscular foot. The members are marine forms, and some are freshwater forms. Molluscs like oysters, squid and cu…
FAQs on Phylum Mollusca
- Q.1. What animals belong to the phylum Mollusca? Ans: The animals that belong to the phylum Mollusca are Pila, Sepia, Octopus, Unio, snail, etc. Q.2. What is the economic importance of snails? Ans:They possess anti-cancer properties and boost the immune system due. They are rich in antioxidants, fatty acids, iron, calcium, etc. Q.3. What are the 6 classes of the phylum Mollusc…