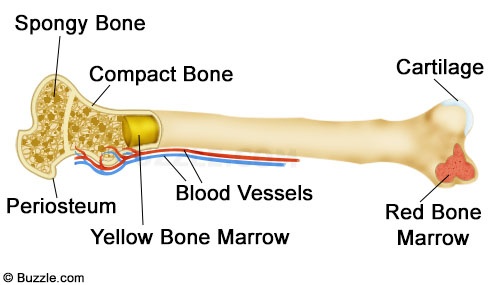
What are the layers of the bone in order?
- Periosteum. The periosteum is a soft outer covering over the bone’s surface.
- Cortical Bone. This layer is hard and thick.
- Cancellous Bone. Cancellous bone is a spongy type of bone inside the cortical bone.
- Bone Marrow.
- A picture of the four bone layers.
- Periosteum – the dense, tough outer shell that contains blood vessels and nerves.
- Compact or dense tissue – the hard, smooth layer that protects the tissue within.
- Spongy or cancellous tissue – the porous, honeycombed material found inside most bones, which allows the bone to be strong yet lightweight.
How many layers are there in a bone?
There are three layers in your bones. The compact bone is the hard, white outer layer. The spongy bone is the hard layer with many holes. The bone marrow is the center layer where blood vessels run through. Furthermore, what are the two layers of bone?
What is between each layer of bone?
The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled internally with spongy bone, another type of osseous tissue. Red bone marrow fills the spaces between the spongy bone in some long bones. Each epiphysis meets the diaphysis at the metaphysis.
What is the tough outer layer of the bone?
The tough, thin outer membrane covering the bones is called the periosteum. Under the hard outer shell of the periosteum are tunnels and canals. Through these, blood and lymphatic vessels carry nourishment for the bone. Muscles, ligaments, and tendons may attach to the periosteum. What type of tissue is bone tissue quizlet?
What is the inner layer of the human bone called?
Bone is living tissue that makes up the body's skeleton. There are 3 types of bone tissue, including the following: Compact tissue. The harder, outer tissue of bones. Cancellous tissue. The sponge-like tissue inside bones. Subchondral tissue. The smooth tissue at the ends of bones, which is covered with another type of tissue called cartilage.

What are layers of bones?
Bones are composed of two layers: a tough outer layer and a spongy inner layer. The outer layer, known as cortical or compact bone, is strong and dense. The inner layer, known as trabecular or cancellous bone, features a light network of connective tissue.
What are the 3 things bones are made of?
Bones are made up of a framework of a protein called collagen, with a mineral called calcium phosphate that makes the framework hard and strong. Bones store calcium and release some into the bloodstream when it's needed by other parts of the body.
What are the 3 major functions of bone?
FunctionAllows movement: Your skeleton supports your body weight to help you stand and move. ... Produces blood cells: Bones contain bone marrow. ... Protects and supports organs: Your skull shields your brain, your ribs protect your heart and lungs, and your backbone protects your spine.More items...•
What are the main components of bone?
The two principal components of bone are collagen and calcium phosphate, which distinguish it from other hard tissues such as chitin, enamel, and shell.
What material are bones made of?
Made mostly of collagen, bone is living, growing tissue. Collagen is a protein that provides a soft framework, and calcium phosphate is a mineral that adds strength and hardens the framework. This combination of collagen and calcium makes bone strong and flexible enough to withstand stress.
Are bones made of cells?
Bone is composed of four different cell types; osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and bone lining cells. Osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteoclasts are present on bone surfaces and are derived from local mesenchymal cells called progenitor cells.
What are the 5 main parts of the skeletal system?
There are five types of bones in the human skeletal system: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid. Long bone: Helps to facilitate movement and support the weight of the body.
What living tissues make up a bone?
Osteoblasts and Osteocytes: these are bone forming cells. Osteoclasts: these are bone resorbing cells. Osteoid: this is the non-mineral, organic part of the bone matrix made of collagen and non-collagenous proteins. Inorganic mineral salts deposited within the matrix.
What are the two parts of a long bone?
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone ( [link] ). A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow marrow. The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone.
What is the anatomical structure of a long bone?
Anatomy of a Long Bone. A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone. Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone.
What is the role of osteoblasts in bone formation?
The osteoblast is the bone cell responsible for forming new bone and is found in the growing portions of bone, including the periosteum and endosteum. Osteoblasts, which do not divide, synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salts. As the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast become trapped within it; as a result, it changes in structure and becomes an osteocyte, the primary cell of mature bone and the most common type of bone cell. Each osteocyte is located in a space called a lacuna and is surrounded by bone tissue. Osteocytes maintain the mineral concentration of the matrix via the secretion of enzymes. Like osteoblasts, osteocytes lack mitotic activity. They can communicate with each other and receive nutrients via long cytoplasmic processes that extend through canaliculi (singular = canaliculus), channels within the bone matrix.
What type of cells are found in bone?
Four types of cells are found within bone tissue. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated and develop into osteoblasts. When osteoblasts get trapped within the calcified matrix, their structure and function changes, and they become osteocytes. Osteoclasts develop from monocytes and macrophages and differ in appearance from other bone cells.
What is the red marrow in the bone?
Red marrow fills the spaces in the spongy bone. Each epiphysis meets the diaphysis at the metaphysis, the narrow area that contains the epiphyseal plate (growth plate), a layer of hyaline (transparent) cartilage in a growing bone.
What is the medullary cavity?
The medullary cavity has a delicate membranous lining called the endosteum (end- = “inside”; oste- = “bone”), where bone growth, repair, and remodeling occur. The outer surface of the bone is covered with a fibrous membrane called the periosteum (peri – = “around” or “surrounding”).
What is the microscopic structure of compact bone called?
The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal, or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. These vessels and nerves branch off at right angles through a perforating canal, also known as Volkmann’s canals, to extend to the periosteum and endosteum.
What are the two types of bone?
Share on Pinterest. Bones are composed of two types of tissue: 1. Compact (cortical) bone: A hard outer layer that is dense, strong, and durable. It makes up around 80 percent of adult bone mass. 2. Cancellous (trabecular or spongy) bone: This consists of a network of trabeculae or rod-like structures.
Which bones are compact?
Short bones: Only a thin layer of compact bone, these include bones of the wrist and ankle.
What are the inactive osteoblasts that have become trapped in the bone that they have created?
Osteocytes : These are inactive osteoblasts that have become trapped in the bone that they have created. They maintain connections to other osteocytes and osteoblasts. They are important for communication within bone tissue.
How do bones raise calcium levels?
Calcium balance: Bones can raise or reduce calcium in the blood by forming bone, or breaking it down in a process called resorption.
Why does osteoporosis occur?
It can be caused by having inadequate calcium, a vitamin D deficiency, consuming excessive alcohol, or smoking tobacco.
What is the largest bone in the human body?
The largest bone in the human body is the thighbone or femur, and the smallest is the stapes in the middle ear, which are just 3 millimeters (mm) long. Bones are mostly made of the protein collagen, which forms a soft framework. The mineral calcium phosphate hardens this framework, giving it strength.
Which cells are responsible for creating bone?
osteoblasts and osteocytes, responsible for creating bone. osteoclasts or bone resorbing cells. osteoid, a mix of collagen and other proteins. inorganic mineral salts within the matrix. nerves and blood vessels. bone marrow. cartilage. membranes, including the endosteum and periosteum.
What are the layers of the hand bone?
x-rays of hand bones. Our bones are made of five main layers. Moving from outside the bone to inside the bone, here are the layers: Periosteum. Cortical, or Hard Bone. Cancellous, or Spongy Bone. Bone Marrow.
What is the outer layer of the bone?
Periosteum. The periosteum is a soft outer covering over the bone’s surface. It provides blood flow to the bone which lets a bone heal, grow, fight infection, and stay healthy. This layer is very thick in children and gets thinner as we get older.
What is the layer of bone that protects the body?
Cortical Bone. This layer is hard and thick. When you see a skeleton, you’re looking at mostly cortical bone. You can think of it like a hard shell, like a turtle has. It’s job is to protect body parts underneath it and hold up muscles around it.
Where is bone marrow located?
Your bone marrow is deep inside your bones – inside the middle of the cortical and spongy bones. It’s job is to make all the blood cells inside your body – red cells, white (infection-fighting) cells, and platelets that help you stop bleeding when you get a cut.
What is cancellous bone?
Cancellous bone is a spongy type of bone inside the cortical bone. It’s not as dense as the outer cortical bone. Some bones have a lot of it, and some bones have less. A broken bone may heal faster if it has more cancellous bone inside.