
Three Elements of Nucleotides of DNA
- Nitrogen-Containing Base. The nitrogen-containing base is arguably the most important element in a nucleotide, since the type of base dictates the information that actually makes up the genetic code.
- Deoxyribose Sugar. ...
- Phosphate Group. ...
- Nucleotide Structure. ...
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
- nucleotide. consists of three parts: a five carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- deoxyribose. the five carbon sugar in a DNA nucleotide.
- what does the phosphate group consist of?
- nitrogenous base.
- purines.
- pyrimidines.
- base-pairing rules.
- complementary base pairs.
What are the 3 types of nucleotides?
What are the 3 types of nucleic acids?
- Deoxyribonucleic acid.
- Ribonucleic acid.
- Artificial nucleic acid.
Which nucleotides base pair with each other?
The following abbreviations are commonly used to describe the length of a D/R NA molecule :
- bp = base pair—one bp corresponds to approximately 3.4 Å (340 pm) of length along the strand, and to roughly 618 or 643 daltons for DNA and RNA respectively.
- kb (= kbp) = kilo–base-pair = 1,000 bp
- Mb (= Mbp) = mega–base-pair = 1,000,000 bp
- Gb = giga–base-pair = 1,000,000,000 bp.
What are the names of all the nucleotides?
Three of them are multifunctional:
- GART (reactions 2, 3, and 5)
- PAICS (reactions 6, and 7)
- ATIC (reactions 9, and 10)
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
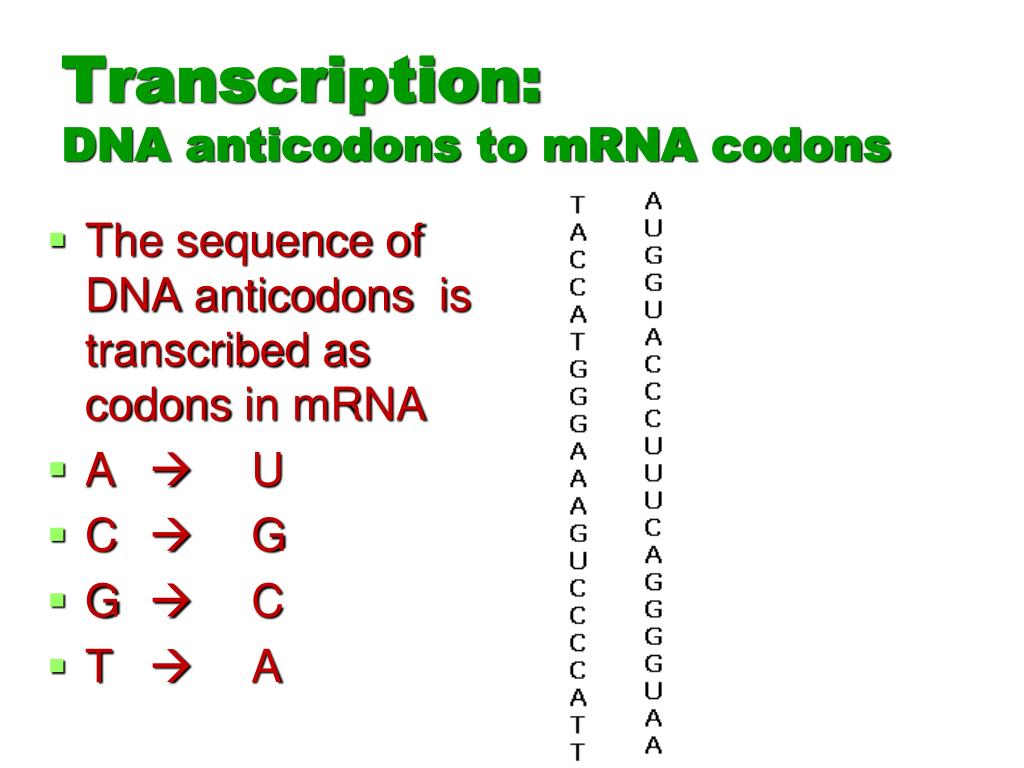
Although DNA and RNA share some similarities, they are built from slightly different sugars, plus there is a base substitution between them. DNA uses thymine (T), while RNA uses uracil (U). Both thymine and uracil bind to adenine (A).
What are the two categories of nitrogenous bases?
Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines.
What are the three parts of DNA?
Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: 1 Nitrogenous Base#N#Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. 2 Pentose Sugar#N#In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. In RNA, the sugar is ribose. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars. The carbons are numbered sequentially, to help keep track of where groups are attached. The only difference between them is that 2'-deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom attached to the second carbon. 3 Phosphate Group#N#A single phosphate group is PO 43-. The phosphorus atom is the central atom. One atom of oxygen is connected to the 5-carbon in the sugar and to the phosphorus atom. When phosphate groups link together to form chains, as in ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the link looks like O-P-O-P-O-P-O, with two additional oxygen atoms attached to each phosphorus, one on either side of the atom.
How many phosphate groups are in a free nucleotide?
The number 5 carbon of the sugar is bonded to the phosphate group. A free nucleotide may have one, two, or three phosphate groups attached as a chain to the 5-carbon of the sugar. When nucleotides connect to form DNA or RNA, the phosphate of one nucleotide attaches via a phosphodiester bond ...
What are the building blocks of DNA and RNA?
Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA and RNA used as genetic material. Nucleotides also are used for cell signaling and to transport energy throughout cells. You may be asked to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded to each other. Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA .
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
The carbons are numbered sequentially, to help keep track of where groups are attached. The only difference between them is that 2'-deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom attached to the second carbon.
What is the link between oxygen and phosphorus?
One atom of oxygen is connected to the 5-carbon in the sugar and to the phosphorus atom. When phosphate groups link together to form chains, as in ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the link looks like O-P-O-P-O-P-O, with two additional oxygen atoms attached to each phosphorus, one on either side of the atom.
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. RNA contains uracil, instead of thymine. A nucleotide within a chain makes up the genetic material of all known living things. They also serve a number of function outside of genetic information storage, as messengers and energy moving molecules.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. RNA contains uracil, instead of thymine. A nucleotide within a chain makes up the genetic material of all known living things. They also serve a number of function outside of genetic information storage, as messengers and energy moving molecules.
What is the central information carrying part of the nucleotide structure?
Nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base is the central information carrying part of the nucleotide structure. These molecules, which have different exposed functional groups, have differing abilities to interact with each other.
Why do some organisms not use uracils?
Most creatures do not use uracil within the DNA because it is short lived, and can degrade into cytosine. However, in RNA uracil is the preferred nucleotide because RNA is also a short lived molecule.
How many phosphate groups are in ATP?
ATP contains three phosphate groups, which can store a lot of energy in their bonds. Unlike ATP, the bonds formed within a nucleotide are known as phosphodiester bonds, because they happen between the phosphate group and the sugar molecule.
What is the idea arrangement of a nucleotide?
As in the image, the idea arrangement is the maximum amount of hydrogen bonds between nucleotides involved. Because of the structure of the nucleotide, only a certain nucleotide can interact with other. The image above shows thymine bonding to adenine, and guanine bonding to cytosine. This is the proper and typical arrangement.
Why are there uneven spots in DNA?
Uneven spots are created when hydrogen bonding does not occur between the opposing nucleotide molecules.
What is the building block of nucleic acids?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids. RNA and DNA are polymers made of long chains of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
There's an A, C, G, and T in DNA, and in RNA there's the same three nucleotides as DNA, and then the T is replaced with a uracil. The nucleotide is the basic building block of these molecules, and is essentially are assembled by the cell one at a time and then strung together by the process of either replication, in the form of DNA, ...
