4 major classes of biological molecules include:
- Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides)
- Lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids)
- Proteins
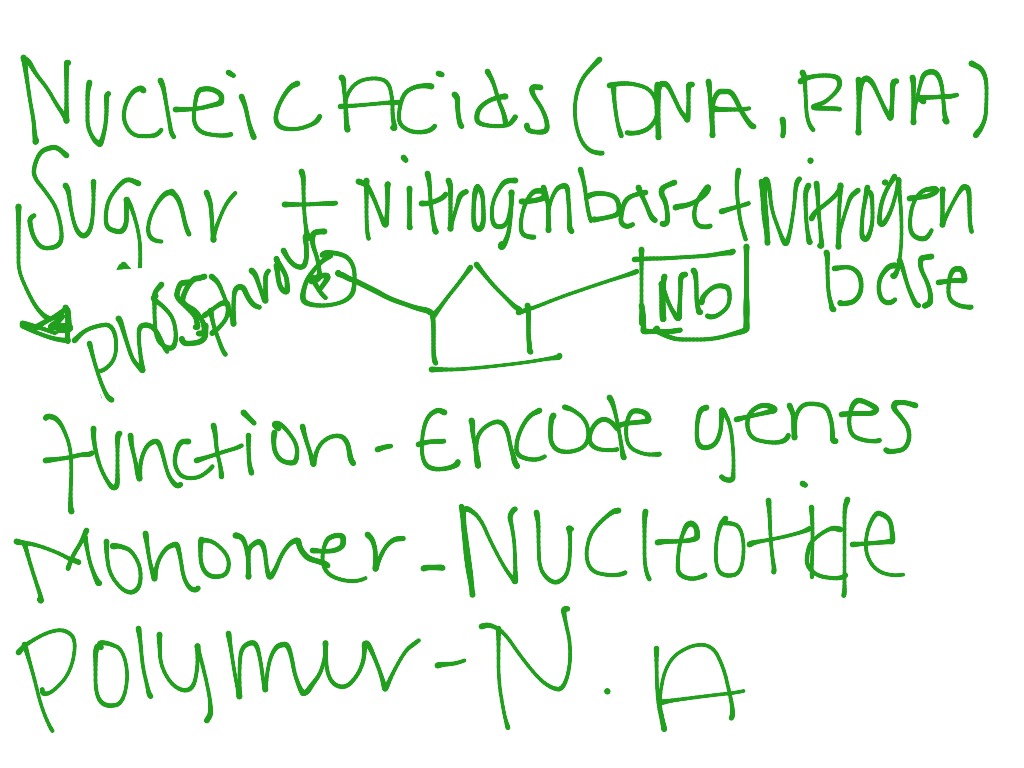
- Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA)
What are the 4 biological molecules and their monomers?
There are four major classes of large biological molecules—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are made up of monomers called monosaccharides that contain carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen.
What are the 4 biological macromolecules and their functions?
The four main macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and lipids. They are an important part of the cell and perform essential functions. Proteins are required for growth and maintenance, immunity and also act as enzymes, hormones, etc. Carbohydrates are the main energy source.
What are the biological molecules?
biomolecule, also called biological molecule, any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living organisms. Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of functions. The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Why are the 4 macromolecules important?
For example, macromolecules provide structural support, a source of stored fuel, the ability to store and retrieve genetic information, and the ability to speed biochemical reactions. Four major types of macromolecules—proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids—play these important roles in the life of a cell.
What are the functions of each group of macromolecules?
Nucleic acids: Stores and transfers info. Carbohydrates; Store energy, provide fuel, and build structure in body, main source of energy, structure of plant cell wall. Lipid: Insulator and stores fat and energy. Protein: Provide structural support,transport, enzymes, movement, defense.
What is the function of protein macromolecules?
Answer and Explanation: A function of a protein macromolecule is to make up the connective tissue in tendons.
What is the main function of a protein?
It helps repair and build your body's tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions. In addition to providing your body with a structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.
What are carbohydrates function?
Carbohydrates, also known as carbs, are vital at every stage of life. They're the body's primary source of energy and the brain's preferred energy source. Carbs are broken down by the body into glucose – a type of sugar. Glucose is used as fuel by your body's cells, tissues, and organs.
What are the four main categories of biomolecules?
The four main categories of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids . While there are some special cases to be found, these four molecules make up the bulk of living bodies, and each plays an essential role in regulating the body's chemistry.
What are the two main types of energy that the body uses?
Carbohydrates are the starches and sugars that bodies use for energy. Brains, for example, consume large amounts of glucose with consumption rising in areas of the brain that are the most active. Lipids help the body store the energy it needs in the form of fats and oils. Wax, of the type secreted by honeybees, is another form of lipid. Proteins are the workhorses of the body's machinery. Proteins carry out specific functions inside cells, and they act as enzymes to catalyze reactions all over the body. Amylase, lactase and pepsin are all proteins used in digestion, for example. Proteins are typically large molecules that can be built up from chains of amino acids called polypeptides. Nucleic acids are central to the function of living cells. Arranged in a linear sequence within DNA, they code for the structure and function of the body's proteins. Nucleic acids also form RNA, which acts to transmit DNA-based instructions to the cellular machinery.
Which molecule contains carbon atoms?
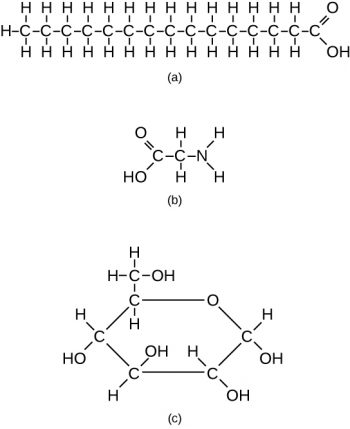
(a) This molecule of stearic acid has a long chain of carbon atoms. (b) Glycine, a component of proteins, contains carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. (c) Glucose, a sugar, has a ring of carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
What are the molecules that make up the majority of the cell's mass?
There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s mass. Biological macromolecules are organic, meaning that they contain carbon (with some exceptions, like carbon dioxide). In addition, they may contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and additional minor elements.
What are carbohydrates in the diet?
Athletes, in contrast, often “carb-load” before important competitions to ensure that they have sufficient energy to compete at a high level. Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet ; grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar. Carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants.
What is the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in a carbohydrate?
In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
How many covalent bonds does carbon have?
Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (CH 4 ), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom ( Figure 1 ).
Where are the sugar and phosphate groups in DNA?
The alternating sugar and phosphate groups lie on the outside of each strand, forming the backbone of the DNA. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior, like the steps of a staircase, and these bases pair; the pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. The bases pair in such a way that the distance between the backbones of the two strands is the same all along the molecule.
Is life a carbon based element?
It is often said that life is “carbon-based.” This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. Other elements play important roles in biological molecules, but carbon certainly qualifies as the “foundation” element for molecules in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role.
How many types of biomolecules are there?
Each of 4 major types of biomolecules is an important cell component and performs a wide variety of functions.
What are the two types of organic compounds?
There are two main types of structures of organic compounds: 1 Structural isomers 2 Stereoisomers
What are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life?
Lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids) Proteins. Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA) Besides their specific roles, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins can serve as a source of energy, while nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life.
How do plants produce carbohydrates?
Plants and algae produce millions of tons of carbohydrates each year through photosynthesis.
What type of structure does carbon form?
Carbon atoms attaching to each other can form straight or branched chains and ringed structures of organic compounds.
Why are stereoisomers different from other types of atoms?
Because of their different structures, they have different properties and are metabolized differently. Stereoisomers have similar placements of their covalent bonds but differ in how these bonds are made to the surrounding atoms. Stereoisomers can be geometrical or optical.
Which functional group of amino acids reacts to each other to form peptide bonds?
Amino and carboxyl functional groups of amino acids react to each other to form peptide bonds of proteins.
What are the large molecules needed for life?
The large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromolecules . There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s mass. Biological macromolecules are organic, meaning that they contain carbon (with some exceptions, like carbon dioxide). In addition, they may contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and additional minor elements.
Which molecule has carbon atoms bonded in various ways to other carbon atoms and the atoms?
(a) This molecule of stearic acid has a long chain of carbon atoms. (b) Glycine, a component of proteins, contains carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. (c) Glucose, a sugar, has a ring of carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
What are carbohydrates in the diet?
Carbohydrates are macromolecules with which most consumers are somewhat familiar. To lose weight, some individuals adhere to “low-carb” diets. Athletes, in contrast, often “carb-load” before important competitions to ensure that they have sufficient energy to compete at a high level. Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet; grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar. Carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants.
How many amino acids are in cytochrome C?
For example, scientists have determined that human cytochrome c contains 104 amino acids. For each cytochrome c molecule that has been sequenced to date from different organisms, 37 of these amino acids appear in the same position in each cytochrome c. This indicates that all of these organisms are descended from a common ancestor. On comparing the human and chimpanzee protein sequences, no sequence difference was found. When human and rhesus monkey sequences were compared, a single difference was found in one amino acid. In contrast, human-to-yeast comparisons show a difference in 44 amino acids, suggesting that humans and chimpanzees have a more recent common ancestor than humans and the rhesus monkey, or humans and yeast.
What is the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in a carbohydrate?
In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
How many covalent bonds does carbon have?
Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (CH 4 ), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom (Figure 2.4. 1 ).
Where are the sugar and phosphate groups in DNA?
The alternating sugar and phosphate groups lie on the outside of each strand, forming the backbone of the DNA. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior, like the steps of a staircase, and these bases pair; the pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. The bases pair in such a way that the distance between the backbones of the two strands is the same all along the molecule.
What are the four types of biomolecules?
The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins . Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely DNA and RNA, have the unique function of storing an organism’s genetic code —the sequence of nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are of critical importance to life on Earth.
What are the most abundant biomolecules?
Proteins also form antibodies and hormones, and they influence gene activity. Likewise, carbohydrates, which are made up primarily of molecules containing atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, are essential energy sources and structural components of all life, and they are among the most abundant biomolecules on Earth.
What are proteins used for in living organisms?
They also serve as transporters, moving nutrients and other molecules in and out of cells, and as enzymes and catalysts for the vast majority of chemical reactions that take place in living organisms. Proteins also form antibodies and hormones, and they influence gene activity.
What is a cell in biology?
cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with…
What are the organelles that separate cells from their environment?
They also form membranes, which separate cells from their environments and compartmentalize the cell interior, giving rise to organelles, such as the nucleus and the mitochondrion, in higher (more complex) organisms. molecular view of the cell membrane.
What are the four types of sugars in lipids?
They are built from four types of sugar units— monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Lipids, another key biomolecule of living organisms, fulfill a variety of roles, including serving as a source of stored energy and acting as chemical messengers.
What is a carbohydrate?
carbohydrate, class of naturally occurring compounds and derivatives formed from them. In the early part of the 19th century, substances such as wood, starch, and linen were found to be composed mainly of molecules containing atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and to have the general formula…
How many different types of molecules are there in life?
A single cell of the bacterium, Escherichia coli contains about 6,000 different organic compounds. It is believed that man may contain about 100,000 different types of molecules although only a few of them have been characterized.
What are the building blocks of complex biomolecules?
Complex biomolecules: ADVERTISEMENTS: The organic compounds such as amino acids, nucleotides and monosaccharide’s serve as the monomeric units or building blocks of complex biomolecules — proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polysaccharides, respectively.
How many monosaccharides are in an oligosaccharide?
Oligosaccharides (Greek: oligo-few) contain 2-10 monosaccharide molecules which are liberated on hydrolysis. Based on the number of monosaccharide units present, the oligosaccharides are further subdivided to disaccharides, tri- saccharides etc.
Where is glycogen found in the body?
Glycogen is the carbohydrate reserve in animals, hence often referred to as animal starch. It is present in high concentration in liver, followed by muscle, brain etc. Glycogen is also found in plants that do not possess chlorophyll (e.g. yeast, fungi). The structure of glycogen is similar to that of amylopectin with more number of branches. Glucose is the repeating unit in glycogen joined together by α (1 → 4) glycosidic bonds, and α (1 → 6) glycosidic bonds at branching points.
When one or more hydroxyl groups of the monosaccharide’s are replaced by amino groups, the?
When one or more hydroxyl groups of the monosaccharide’s are replaced by amino groups, the products formed are amino sugars e.g. D-glucosamine, D-galactosamine. They are present as constituents of heteropoly- saccharides.
How many isomers does glucose have?
Glucose contains 4 asymmetric carbons and thus has 16 isomers.
What are the elements that make up the living matter?
Biomolecules: The living matter is composed of mainly six elements — carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. These elements together constitute about 90% of the dry weight of the human body. Several other functionally important elements are also found in the cells.