
Cell theory
In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to di…
Full Answer
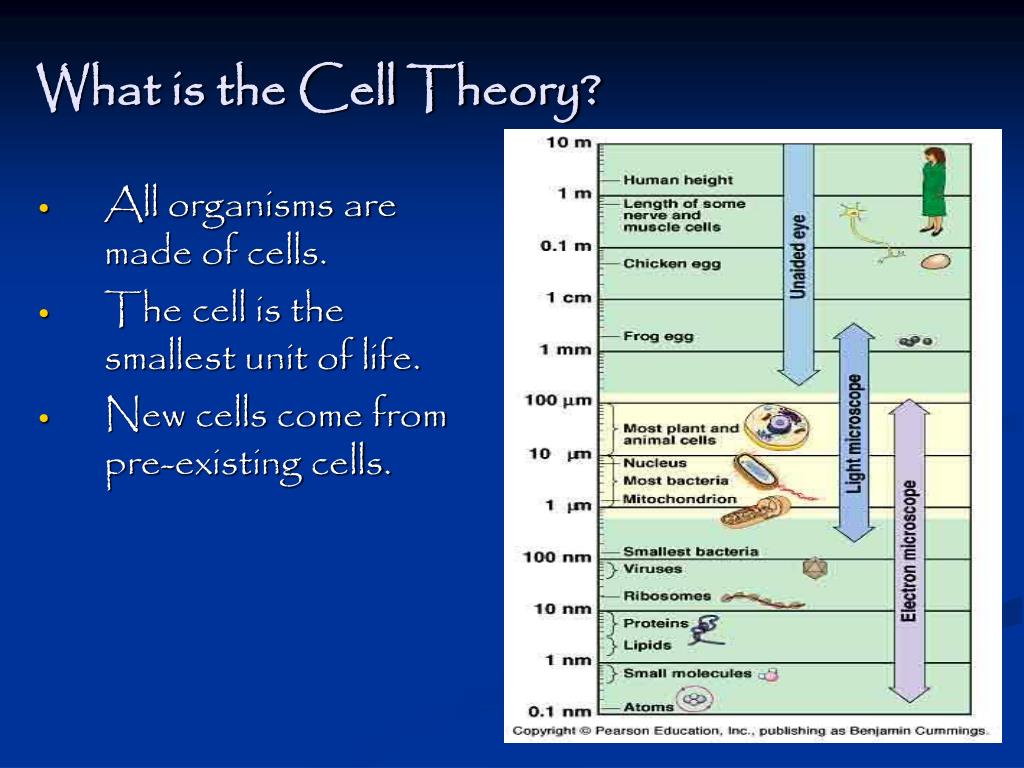
What is the cell theory?
Cell theory 1 All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2 The cell is the most basic unit of life#N#Schleiden's theory of free cell formation through crystallization was refuted... 3 All cells arise only from pre-existing cells More ...
What are the 3 parts of the cell theory?
3 Parts of Cell Theory. Cell theory has three major hypotheses: First, all organisms are made of cells. Second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. The third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells.
What are the main tenants of cell theory?
According to the theory, all organisms are made of cells. Groups of cells create tissues, organs, and organisms. Further, cells can only arise from other cells. These are the main tenants of cell theory. Before the invention of advanced microscopes, microorganisms were unknown, and it was assumed that individuals were the basic units of life.
What is the cell theory 4 parts?
3:504:254 Parts of Cell Theory - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo to sum up we've got a mnemonic a b c d's of cell theory a stands for all all living things areMoreSo to sum up we've got a mnemonic a b c d's of cell theory a stands for all all living things are made of cells b stands for basic cells are the basic unit of life structure and function of life c
What are the 3 main cell theory?
The generally accepted portions of the modern Cell Theory are as follows: The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. Cells arise from other cells through cellular division.
What are the 4 components of the cell theory and who contributed to its development?
Cell theory states that all organisms are made of at least one cell, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells arise from preexisting cells. Major contributors to cell theory are Robert Hooke, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow.
Who are the 4 major scientists who discovered the cell theory?
The ideas of all three scientists — Schwann, Schleiden, and Virchow — led to cell theory, which is one of the fundamental theories unifying all of biology. Cell theory states that: All organisms are made of one or more cells. All the life functions of organisms occur within cells.
What 4 Things do all cells have in common?
All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; 2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; 3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and 4) ribosomes, ...
What is cell theory explain?
Definition of cell theory : a theory in biology that includes one or both of the statements that the cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of living matter and that the organism is composed of autonomous cells with its properties being the sum of those of its cells.
How many cell theories are there?
threeCell theory has three major hypotheses: First, all organisms are made of cells. Second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. The third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells.
Who are the 5 contributors of cell theory?
The observations of Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow, and others led to the development of the cell theory. The cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things.
Who made the cell theory?
First proposed by German scientists Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in 1838, the theory that all plants and animals are made up of cells marked a great conceptual advance in biology and resulted in renewed attention to the living processes that go on in cells.
What are the cell types?
There are two distinct types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Though the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ (see prokaryote, eukaryote), their molecular compositions and activities are very similar. The chief molecules in cells are nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides.
What is modern cell theory?
Modern cell theory states that: The bodies of all living beings are made up of cells and their products. Cells are units of structure in the body of living organisms. Every cell is made up of a mass of protoplasm having a nucleus, organelles and a covering membrane.
What is classical cell theory?
Classical cell theory, as developed through the observations of Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow, and others, holds that: All organisms are made up of one or more cells. Cells are the fundamental functional and structural unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Who came up with the 3 principles of cell theory?
The classical cell theory was proposed by Theodor Schwann in 1839. There are three parts to this theory. The first part states that all organisms are made of cells.
What are the 3 structures that all cells have in common?
It includes features from all cell types. A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
What are the three parts of the cell theory Brainly?
The three parts of the cell theory are as follows: (1) All living things are made up of cells. (2) Cells are the smallest units (or most basic building blocks) of life. (3) All cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division.
What is the 2nd part of the cell theory?
The second part of cell theory was that new cells are formed from preexisting cells. The third part is that all cells are similar. Finally, cells are the most basic units of life. In other words, everything is made up of cells.
What are the parts of cell theory?
The generally accepted parts of modern cell theory include: 1 All known living things are made up of one or more cells 2 All living cells arise from pre-existing cells by division. 3 The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms. 4 The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of independent cells. 5 Energy flow ( metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. 6 Cells contain DNA which is found specifically in the chromosome and RNA found in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. 7 All cells are basically the same in chemical composition in organisms of similar species.
How many different cell types are there in animals?
Animals have evolved a greater diversity of cell types in a multicellular body (100–150 different cell types), compared with 10–20 in plants, fungi, and protoctista.
When was the cell discovered?
The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 using a microscope. The first cell theory is credited to the work of Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in the 1830s. In this theory the internal contents of cells were called protoplasm and described as a jelly-like substance, sometimes called living jelly. At about the same time, colloidal chemistry began its development, and the concepts of bound water emerged. A colloid being something between a solution and a suspension, where Brownian motion is sufficient to prevent sedimentation . The idea of a semipermeable membrane, a barrier that is permeable to solvent but impermeable to solute molecules was developed at about the same time. The term osmosis originated in 1827 and its importance to physiological phenomena realized, but it wasn’t until 1877, when the botanist Pfeffer proposed the membrane theory of cell physiology. In this view, the cell was seen to be enclosed by a thin surface, the plasma membrane, and cell water and solutes such as a potassium ion existed in a physical state like that of a dilute solution. In 1889 Hamburger used hemolysis of erythrocytes to determine the permeability of various solutes. By measuring the time required for the cells to swell past their elastic limit, the rate at which solutes entered the cells could be estimated by the accompanying change in cell volume. He also found that there was an apparent nonsolvent volume of about 50% in red blood cells and later showed that this includes water of hydration in addition to the protein and other nonsolvent components of the cells.
Why are cells in animal tissues observed after plants?
The cells in animal tissues were observed after plants were because the tissues were so fragile and susceptible to tearing, it was difficult for such thin slices to be prepared for studying. Biologists believed that there was a fundamental unit to life, but were unsure what this was. It would not be until over a hundred years later that this fundamental unit was connected to cellular structure and existence of cells in animals or plants. This conclusion was not made until Henri Dutrochet. Besides stating “the cell is the fundamental element of organization”, Dutrochet also claimed that cells were not just a structural unit, but also a physiological unit.
What is the basic unit of structure in all organisms?
Cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
How do all living cells arise?
All living cells arise from pre-existing cells by division. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms. The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of independent cells. Energy flow ( metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells.
What is the cell on the left?
The cell on the left is going through mitosis and its DNA has condensed. In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory first formulated in the mid-nineteenth century, that living organisms are made up of cells, that they are the basic structural/organizational unit of all organisms, and that all cells come from pre-existing cells.
What is cell theory?
Cell theory is a proposed and widely accepted view of how most life on Earth functions. According to the theory, all organisms are made of cells. Groups of cells create tissues, organs, and organisms. Further, cells can only arise from other cells. These are the main tenants of cell theory.
What are the three major hypotheses of cell theory?
Cell theory has three major hypotheses: First, all organisms are made of cells. Second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. The third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells. Thus, all organisms start as single cells.
What is it called when cells separate into two new individuals?
Single-celled organisms divide as well, but when they divide, the cells separate into two new individuals. This is known as asexual reproduction. For more, see our article on the Three Parts of Cell Theory.
How to study cell theory?
Single-celled organisms are a great way to study cell theory. With modern microscopes, the processes behind cell theory can easily be viewed and studied. A great example of watching cell theory in action can be accomplished by putting a drop of pond water under a microscope.
What is the science of testing cells?
None of the above. 3. A scientist in the lab is testing cells. The scientist has various chemicals that are applied to cells, and the reaction observed. The scientist puts some bleach on cells and watches the reaction. The bleach starts to destroy the cell membrane and eats its way to the DNA, which is also destroyed.
Where were cells first discovered?
Cells were first discovered in plants. Plants, unlike the other examples in this article, have large structures called cell walls, which enable the plant to remain rigid. These cell walls are easily visible, even with the first microscope invented in 1665. Robert Hooke, the man who first identified cells, did so using a simple microscope aimed at a thin slice of cork. He drew what he saw, and published it in a book about microscopy. Below is an image from the book:
Do fungi have cell walls?
In fact, fungi are a sort of intermediate between plants and animals. While they lack the sun-harvesting chloroplasts of plants, they do have cell walls. However, there is one form of life which does not strictly adhere to cell theory. Viruses are small DNA or RNA particles, surrounded by a protective protein coating.
What is the chromatin in a cell?
Chromosomes (A) Chromatin consists of nuclear DNA and the proteins associated with it. When the cell is not dividing, the chromatin is dispersed throughout the nucleus. This two-dimensional image was made using a transmission electron microscope. (B) The chromatin in dividing cells becomes highly condensed so that the individual chromosomes can be seen. This three-dimensional image of isolated metaphase chromosomes was produced using a scanning electron microscope. The
How does kinesin move cells?
kinesin moves vesicles or organelles from one part of a cell to another. It binds to a vesicle and “walks” it along by changing shape. Extracellular structures are secreted to the outside of the plasma membrane. Example: The peptidoglycan cell wall of bacteria. In eukaryotes, extracellular structures have a prominent fibrous macromolecule in a gel-like medium. How do plant cells communicate through their thick cell walls? What structure allows animal cells to signal each other, retain their structure, and be held together in tissues? - Plant cell walls : Cellulose fibers are embedded in other complex polysaccharides and proteins. Adjacent plant cells are connected by plasma membrane-lined channels called plasmodesmata . Many animal cells are surrounded by an extracellular matrix , composed of fibrous proteins such as collagen , gel-like proteoglycans (glycoproteins), and other proteins. The extracellular matrix: Holds cells together in tissues Contributes to properties of bone, cartilage, skin, etc. Filters materials passing between different tissues Orients cell movements in development and tissue repair Plays a role in chemical signaling
Do prokaryotes have a cell wall?
protein complexes; sites of protein synthesis. Most prokaryotes have a rigid cell wall outside the plasma membrane. Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan. Some bacteria have an additional outer membrane . Some bacteria have a slimy capsule of polysaccharides. Photosynthetic bacteria have an internal membrane system that contains molecules necessary for photosynthesis. They lack internal compartmentalization…Others have internal membrane folds that are attached to the plasma membrane; they may function in cell division or in energy-releasing reactions.
What are the 3 principles of cell theory?
Q.1. What are the 3 principles of cell theory?#N#Ans: 1. All living organisms are made up of one cell or more than one cell.#N# 2. All the functions of the body are the product of the functions of independent cells .#N#3. All the cells arise from pre-existing cells.
What is a Cell Theory in Science?
Cell theory was given by Schleiden and Schwann in 1839. It states that all organisms are made of cells, i.e. a cell is a structural and functional unit of an organism. Original cell theory had two points. Later, one point was added by Rudolf Virchow, a German Physician, in 1858. He gave a phrase in his own language, “omnis cellula e cellula”, which means all the cells arise from the pre-existing cells. Cell theory states that-
What is the modern interpretation of cell theory?
Modern Interpretation of Cell Theory. All living organisms are made up of one cell or more cells. All the metabolic functions of the organism are the product of the functions of independent and individual cells. All the cells arise from pre-existing cells. Energy flow occurs within cells.
What are the building blocks of every living organism?
Cells are the building blocks of every living organism. All living organisms are made up of one cell or more than one cell. All the functions of the body are the product of the functions of independent cells. All the cells arise from pre-existing cells.
How do cells function?
Each cell functions as a self-contained unit. It can independently carry out nutrition, growth , respiration, reproduction and self-regulation. In multicellular organisms, cells are not totally independent of one another but interact and cooperate with one another.
Why does energy flow in cells?
Energy flow occurs within cells. This is due to various metabolic activities occurring inside the cell. Each cell contains the whole complement of genetic information, not only for itself but for the whole organism. All cells are basically alike in chemical composition and metabolic activities.
What is the concept of cells?
Concept of Cell. Cells are a basic structural and functional unit of life. Every organism is made up of cells. Organisms may be unicellular or multicellular, depending on the number of cells present in the organisation of the body.
When was cell theory first proposed?
When it was first proposed in the early 1830s, the cell theory had two main components; the cell is the basic functional and structural unit of all living things and all living things are made of one or more cells.
Who developed the cell theory?
The image above shows the German scientist Matthias Schleiden who along with Theodore Schwann, developed the first cell theory. The image above is that of Rudolf Virchow whose contributions to the cell theory are often overlooked in history.
Who came up with the idea that cells only come from other cells?
In 1855, Rudolf Virchow was recognized for his idea that became the third component of the cell theory at the time, Omnis cellula e cellula which is Latin for “cells only come from other cells.”
Who coined the term "cell"?
But even before Leeuwenhoek’s lens improvements, the British scientist Robert Hooke had already coined the term “cell” in 1665 after looking at thin slices of cork under his microscope.
Overview
Cell theory
Credit for developing cell theory is usually given to two scientists: Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden. While Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory, he is not as credited for his attributions toward it. In 1839, Schleiden suggested that every structural part of a plant was made up of cells or the result of cells. He also suggested that cells were made by a crystallization process ei…
History
With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, known as cell biology. When observing a piece of cork under the scope he was able to see pores. This was shocking at the time because it was believed no one else had seen these. To further support his theory, Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann both studied …
Microscopes
Robert Hooke's microscope was a recreation of Anton van Leeuwenhoek's microscope in the 17th century, except his was 300x magnification. The discovery of the cell was made possible through the invention of the microscope. In the first century BC, Romans were able to make glass. They discovered that objects appeared to be larger under the glass. In Italy during th…
Discovery of cells
The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, which can be found to be described in his book Micrographia. In this book, he gave 60 'observations' in detail of various objects under a coarse, compound microscope. One observation was from very thin slices of bottle cork. Hooke discovered a multitude of tiny pores that he named "cells". This came from the Latin word C…
Modern interpretation
The generally accepted parts of modern cell theory include:
1. All known living things are made up of one or more cells
2. All living cells arise from pre-existing cells by division.
3. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms.
Modern version
The modern version of the cell theory includes the ideas that:
• Energy flow occurs within cells.
• Heredity information (DNA) is passed on from cell to cell.
• All cells have the same basic chemical composition.
Opposing concepts in cell theory: history and background
The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 using a microscope. The first cell theory is credited to the work of Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in the 1830s. In this theory the internal contents of cells were called protoplasm and described as a jelly-like substance, sometimes called living jelly. At about the same time, colloidal chemistry began its development, and the concepts of bound water emerged. A colloid being something between a solution and a sus…
Overview
3 Parts of Cell Theory
- Cell theory has three major hypotheses: 1. First, all organisms are made of cells. 2. Second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. 3. The third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells. Thus, all organisms start as single cell...
Cell Theory Examples
- Single-Celled Organisms
Single-celled organisms are a great way to study cell theory. With modern microscopes, the processes behind cell theory can easily be viewed and studied.A great example of watching cell theory in action can be accomplished by putting a drop of pond water under a microscope. Belo… - In Plants
Cells were first discovered in plants. Plants, unlike the other examples in this article, have large structures called cell walls, which enable the plant to remain rigid. These cell walls are easily visible, even with the first microscope invented in 1665.Robert Hooke, the man who first identifie…
Contributions to Cell Theory
- Besides Robert Hooke and Theodor Schwann, a number of scientists have made significant contributions to cell theory. In fact, cell theory has been growing and changing since the first cells were observed, and many fantastic experiments have been devised to show various parts of cell theory.See our article on the Cell Theory Timelinefor more on these events.