A, C, G and T. adenine cytosine Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached. The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrog…Cytosine
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid are nucleic aci…
What are the 4 different bases in DNA?
What are the names of the 4 nitrogen bases in DNA?
- Adenine, abbreviated 'A,' has a 2-ring structure, so that makes it a purine.
- Thymine, abbreviated 'T,' is a pyrimidine, which means it has a 1-ring structure.
- Uracil, abbreviated 'U,' is found in RNA.
- Guanine, abbreviated 'G,' is part of both DNA and RNA, where it bonds with cytosine.
What are 4 bases does DNA contain?
There are four nucleotides, or bases, in DNA:
- adenine (A),
- cytosine (C),
- guanine (G), and
- thymine (T).
What are the 4 main parts of DNA?
The molecular structure of DNA
- DNA molecules are polymers. Polymers are large molecules that are built up by repeatedly linking together smaller molecules, called monomers.
- DNA monomers are called nucleotides. ...
- There are four nucleotide monomers. ...
- The sugar and acid in all four monomers are the same. ...
What are the 4 types DNA?
DNA is made up of molecules called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order of these bases is what determines DNA's instructions, or genetic code.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These building blocks are made of three parts: a phos phate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases. To form a strand of DNA, nucleotides are linked into chains, with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating.
What are the four nitrogen bases found in nucleotides?
The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. For example, the sequence ATCGTT might instruct for blue eyes, while ATCGCT might instruct for brown.
How does DNA make proteins?
First, enzymes read the information in a DNA molecule and transcribe it into an intermediary molecule called messenger ribonucleic acid, or mRNA.
Why is DNA a chromosome?
Because the cell is very small, and because organisms have many DNA molecules per cell, each DNA molecule must be tightly packaged. This packaged form of the DNA is called a chromosome. During DNA replication, DNA unwinds so it can be copied.
Why is DNA in its compact chromosome form?
But during cell division, DNA is in its compact chromosome form to enable transfer to new cells. Researchers refer to DNA found in the cell's nucleus as nuclear DNA.
How much of the DNA is made up of genes?
The size of a gene may vary greatly, ranging from about 1,000 bases to 1 million bases in humans. Genes only make up about 1 percent of the DNA sequence. DNA sequences outside this 1 percent are involved in regulating when, how and how much of a protein is made.
How many genes are in the DNA instruction book?
The complete DNA instruction book, or genome, for a human contains about 3 billion bases and about 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Which chemical base bonds with guanine?
In the DNA double helix, the four chemical bases always bond with the same partner to form "base pairs.". Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T); cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G).
What is DNA sequencing?
Sequencing DNA means determining the order of the four chemical building blocks - called "bases" - that make up the DNA molecule. The sequence tells scientists the kind of genetic information that is carried in a particular DNA segment. For example, scientists can use sequence information to determine which stretches of DNA contain genes and which stretches carry regulatory instructions, turning genes on or off. In addition, and importantly, sequence data can highlight changes in a gene that may cause disease.
What new sequencing methods have been developed?
Since the completion of the Human Genome Project, technological improvements and automation have increased speed and lowered costs to the point where individual genes can be sequenced routinely, and some labs can sequence well over 100,000 billion bases per year, and an entire genome can be sequenced for just a few thousand dollars.Many of these new technologies were developed with support from the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) Genome Technology Program and its Advanced DNA Sequencing Technology awards. One of NHGRI's goals is to promote new technologies that could eventually reduce the cost of sequencing a human genome of even higher quality than is possible today and for less than $1,000.
Why is DNA sequencing important?
In addition, the ability to sequence the genome more rapidly and cost-effectively creates vast potential for diagnostics and therapies. Although routine DNA sequencing in the doctor's office is still many years away, some large medical centers have begun to use sequencing to detect and treat some diseases.
How does nanopore sequencing work?
Nanopore-based DNA sequencing involves threading single DNA strands through extremely tiny pores in a membrane. DNA bases are read one at a time as they squeeze through the nanopore.
What is the purpose of sequencing DNA?
Sequencing DNA means determining the order of the four chemical building blocks - called "bases" - that make up the DNA molecule. The sequence tells scientists the kind of genetic information that is carried in a particular DNA segment.
How much can a human genome be sequenced?
Since the completion of the Human Genome Project, technological improvements and automation have increased speed and lowered costs to the point where individual genes can be sequenced routinely, and some labs can sequence well over 100,000 billion bases per year, and an entire genome can be sequenced for just a few thousand dollars.
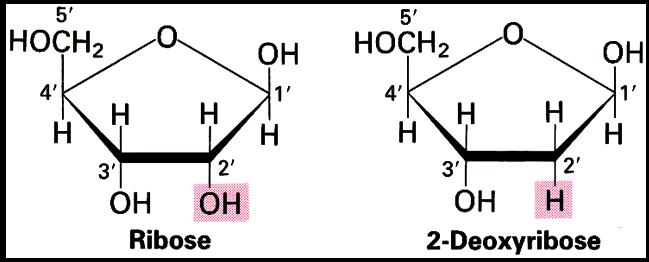
How many carbons are in a nucleic acid?
A nucleic acid, then, is simply a chain of five-carbon sugars linked together...
What is the framework of a biological molecule?
The framework of biological molecules consists predominantly of carbon atoms bonded to other carbon atoms or to atoms of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, or hydrogen.
How are macromolecules formed?
Biological macromolecules are polymers formed by linking monomers together through dehydration reactions. Breaking the bond between subunits involves hydrolysis, which reverses the loss of a water molecule by dehydration.
What is a polysaccharide made of?
Polysaccharides are longer polymers made up of monosaccharides that have been joined through dehydration reactions.
What are the three groups of macromolecules?
Remember that biological macromolecules are traditionally grouped into carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids .
How do cells disassemble macromolecules?
Cells disassemble macromolecules into their constituent subunits through reactions that are the reverse of dehydration-a molecule of water is added instead of removed.
How are transport forms of sugars made?
Transport forms of sugars are commonly made by linking two monosaccharides together...