Myriapoda types
- Chilopoda Chilopoda is the first class under the subphylum Myriapoda. The class chilopoda contains nearly 8,000 species under this. ...
- Diplopoda Diplopoda is the second class under the subphylum Myriapoda. ...
- Pauropoda Pauropoda is the third class under the subphylum Myriapoda. ...
- Symphyla Symphyla is the fourth class under the subphylum Myriapoda. ...
What are the 4 classes of Arthropoda?
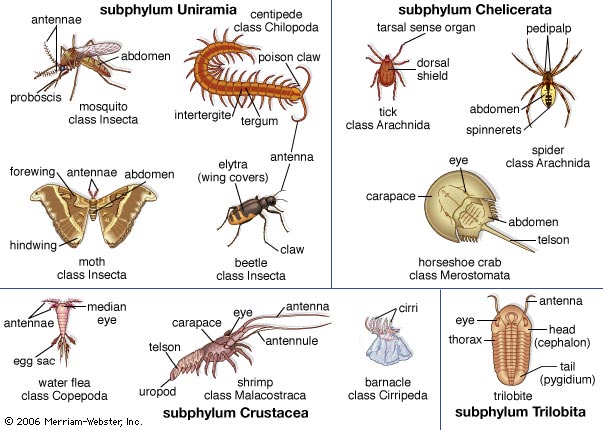
The phylum Arthropoda is commonly divided into four subphyla of extant forms: Chelicerata (arachnids), Crustacea (crustaceans), Hexapoda (insects and springtails), and Myriapoda (millipedes and centipedes).
How many Tagmata does subphylum Myriapoda have?
two tagmataMyriapods' bodies are divided into two tagmata, or body sections—a head and a trunk. The trunk is further divided into multiple segments, each having a pair of appendages, or legs.
What are the two main classes of myriapods?
There are four groups of myriapods; how they are related to each other is not yet well understood. Two of them, the Symphyla and Pauropoda, consist of tiny arthropods living in leaf litter and soil; both superficially resemble centipedes.
What animals are included in the subphylum Myriapoda?
Myriapoda is a subphylum of arthropods containing millipedes, centipedes, and others. The group contains over 16,000 species, most of which are terrestrial.
What are the order of Myriapoda?
There are four extant classes within the Myriapoda: Chilopoda (centipedes), Diplopoda (millipedes), Pauropoda (pauropods) and Symphyla (symphylans).
What are the 7 classes of arthropods?
Arthropod ClassesArachnid. the Class of Arthropods that includes spiders, mites, ticks, scorpions, pseudoscorpions and harvestmen.Chilopoda. ... Collembola. ... Crustaceans. ... Diplopoda. ... Diplura. ... the largest Class of arthropods and the most diverse group of animals in the world.Myriapoda.More items...
What defines Myriapoda?
: any of a group (Myriapoda) of arthropods having the body made up of numerous similar segments nearly all of which bear true jointed legs and including the millipedes and centipedes.
What is phylum Myriapoda?
ArthropodMyriapoda / PhylumArthropods are invertebrate animals having an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. Wikipedia
What are the three classes of Chelicerates?
There are three classes of chelicerates (Merostomata, Arachnida, and Pycnogoida). The class Merostomata includes the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, which has been the subject of extensive neurobiological studies.
What are the 5 major classes of arthropods?
Arthropods are traditionally divided into 5 subphyla: Trilobitomorpha (Trilobites), Chelicerata, Crustacea, Myriapoda, and Hexapoda.
Which group of animals do myriapods belong?
All myriapods belong to a larger groups of animals called arthropods. This means they have a segmented body covered in an exoskeleton and pairs of jointed limbs. There are over a million known arthropod species. Arthropods include insects, arachnids, myriapods and crustaceans.
What are the 4 subphyla of the arthropod phylum?
The Phylum Arthropoda includes a wide range of species divided into the subphyla: Hexapoda, Crustacea, Myriapoda, and Chelicerata.
Do insects have 3 tagmata?
The Hexapoda, including insects, also have three tagmata, usually termed the head, thorax, and abdomen.
How many tagmata are there?
3 main tagmata. Insect bodies are divided into three main parts: head, thorax, and abdomen. The thorax is where all the legs and wings are attached.
Does hexapoda have 3 tagmata?
Hexapods exhibit metameric, or repeated, segmentation and have one pair of appendages per segment. These segments are organized into three tagmata, or specialized segments: the head, thorax, and abdomen.
How many pairs of Antennaes does myriapods have?
Like insects, myriapods have one pair of antennae, but they have many more legs than insects do.
What is a myriapod?
Myriapods. Myriapoda: Myriapods are any invertebrate belonging to the subphylum Myriapoda. This subphylum contains 4 classes, with the two most well-known being Chilopoda (centipedes) and Diplopoda (millipedes). Myriapods have one pair of antennae and mandibles like insects do; however, unlike insects, Myriapods do not have compound eyes.
How are centipedes different from millipedes?
Centipedes are easily distinguishable from millipedes by only having one pair of legs per body segment on their trunk. They are primarily nocturnal predators, utilizing their first pair of legs which have been modified into claws with attached venom glands.
How many legs does a stone centipede have?
In stone centipedes, tergites 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12, and 14 are longer than the others. They also only reach 15 pairs of legs at maturity. Millipedes are the gentler, distant cousins of centipedes. They lack the modified prehensor front legs and venom glands, instead they are primarily detritivores.
How old do desert millipedes live?
Desert millipedes are typically brown or black with a cylindrical body and can live up to 10+ years old. On rare occasions they have been known to form large groups and “march” across roads at our sister park, Big Bend.
How do centipedes live?
They live in the soil, moving about by expanding and contracting their body, where they feed on insect larvae and worms found within. They can be identified by their slow movement, lack of eyes, and having 14 segmented antennae.
How big do centipedes get?
This is the largest species of centipede found in the U.S., growing up to 8 inches in the wild and even longer in captivity. This centipede exhibits aposematism, or warning coloration, to warn potential predators of its venom.
What is the name of the tiger centipede?
The common desert centipede has extremely varied coloration; hence the species name polymorpha, which means “many forms”. Despite the many variations in coloration, the common desert centipede always has one dark, lateral stripe on each body segment. This is where it’s other common name, the tiger centipede, comes from. Like most Chilopods, this centipede is a nocturnal predator and avoids the desert heat by hiding under rocks or in moist environments during the day.
What are the four classes of myriapods?
1.20.2.2 Myriapoda. The Myriapoda consists of four classes of terrestrial arthropods (Chilopoda, Diplopoda, Symphyla, and Pauropoda) that share a number of morphological features. However, the status of the Myriapoda as a monophyletic group is controversial. The traditional view of monophyly, based on morphology (Ax, 1987; Boudreaux, 1987 ), ...
What are the two groups of myriapods?
Myriapods have long been treated as a natural class (Myriapoda) of the phylum Arthropoda, but many doubts have been raised regarding the close affinity between the four main groups of terrestrial, tracheate, and multilegged arthropods traditionally classified as myriapods: the centipedes or Chilopoda, the millipedes or Diplopoda , and the two smaller groups of the Symphyla and Pauropoda. The term Myriapoda, however, is still universally used as vernacular to contrast these arthropods to the insects, also terrestrial and tracheate, with these latter being easily identified by their smaller number of legs (three pairs), the strong differentiation of the trunk into thorax and abdomen, and the generalized presence of wings.
What is the name of the taxon that groups the Myriapoda and the Hexapoda?
Until recently, the favored view ( Figure 2a) was to group the Myriapoda and the Hexapoda in a taxon known as the Antennata ( Kristensen, 1991). Morphological characters supporting this division include absence of second antennas and presence of Malpighian tubules, organs of Tömösvary and tracheae in Myriapoda and Hexapoda.
What are the phylogenetic relationships between myriapods?
The phylogenetic relationships of the various clades among the Myriapoda are not completely known, and active research programs are conducted on the subject. Molecular studies are being used together with morpho-anatomical approaches to show relationships within the subphylum, and the systematics are progressively supported by genomic studies. The present understanding of myriapod phylogeny, and more precisely diplopod phylogeny, strongly support the monophyly of the Myriapoda and the phylogenetic relationships among the Arthropoda or between clades in the Myriapoda (Koch, 2003; Edgecombe, 2004, 2010; Gai et al., 2006; Regier et al., 2010; Giribet and Edgecombe, 2012) and particularly the Diplopoda (Enghoff, 2001; Sierwald et al., 2003; Sierwald and Bond, 2007 ).
What are the two classes of millipedes?
Diplopoda, Chilopoda, Pauropoda and Symphyla were once combined as one class, the Myriapoda, and are still known as the myriapodan classes. All millipedes (Diplopoda) are phytophagous, but most species do not seriously injure plants. The centipedes (Chilopoda) are predaceous and possess a pair of strong, poison-supplied fangs called toxicognaths used to hold and kill their prey. Toxicognaths are modified legs, and the venom they inject can be painful. Centipedes are fast moving, in contrast to the slow-moving millipedes. The minute Pauropoda are of little direct agricultural importance. One member of the Symphyla, Scutigerella immaculata (Newport), is sometimes a pest in greenhouses; the species is whitish, about 8 mm long, and may become very abundant.
What is the sister group of the Antennata?
In recent years the concept of an Antennata taxon has come under attack and an increasing amount of morphological, developmental, and molecular evidence now points to the malacostracan crustaceans, rather than the Myriapoda, as being the sister group to the Hexapoda ( Figures 2b and 2c ). Several of the characters supporting this case involve the structure and development of the nervous system. Some of this evidence is detailed below and has been reviewed elsewhere ( Strausfeld, 1998; Dohle, 2001; Whitington, 2004; Harzsch et al., 2005 ). In brief, several aspects of the organization of the compound eyes, the brain, and the ventral nerve cord (VNC) in adult insects show much closer affinities to malacostracan crustaceans than to myriapods. The mode of generation of neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) and the pattern of early axonogenesis in insect embryos are more closely related to malacostracans than to myriapods.
Which arthropod is the sister group of the hexapoda?
Part a has the Myriapoda as the sister group to the Hexapoda, while (b) and (c) depict the more widely held recent view that Crustacea is the sister group to the Hexapoda. Part b has Chelicerata and Myriapoda as sister groups, while (c) has the Myriapoda basal to the other arthropods.
How many legs does a myriapod have?
Although their name suggests they have myriad (10,000) legs, myriapods range from having over 750 legs to having fewer than ten legs.
Where do myriapods live?
Habitat and Diet: Myriapods are most abundant in moist forests, where they fulfill an important role in breaking down decaying plant material, although a few live in grasslands, semi-arid habitats or even deserts . A very small percentage of species are littoral (found along the sea shore).
What are the only arthropods that have poison claws?
1. Centipedes are the only arthropods known to have 'poison claws'. 2. All centipedes are predators. 3.When they hatch millipe des only have three pairs of legs. 4. Male millipedes court females with songs and backrubs. 5. Male millipedes have 'sex' legs called gonopods.
What is the difference between a chilopod and a millipede?
Chilopods (centipedes) have their first pair of walking legs modified into clawlike appendages; diplopods (millipedes) have each pair of segments fused together , resulting in two pairs of leg s per segment. In other groups, some legs may be modified into gonopods, serving a reproductive function. Having numerous legs requires a degree ...
Why are some legs modified into gonopods?
In other groups, some legs may be modified into gonopods, serving a reproductive function. Having numerous legs requires a degree of rhythmic movement in order to achieve good coordination. Segment and leg length determine the basic gaits, which may be modified to allow rapid escape or slow soil penetration.
Do centipedes have legs?
In most cases, the hatchlings and immature centipedes closely resemble adults; others, however, have only a few pair of legs. Depending on species, the immature centipedes may or may not grow new body segments and legs as they molt.
Do centipedes and millipedes have separate sexes?
Reproduction and Life Cycle: Both Centipedes and Millipedes have separate sexes, the females lay the eggs that have been fertilized by the males. Some species lay eggs in a 'nest' where they are guarded by the female, others lay eggs one at a time and leave them .

Overview
Classification
There has been much debate as to which arthropod group is most closely related to the Myriapoda. Under the Mandibulata hypothesis, Myriapoda is the sister taxon to Pancrustacea, a group comprising the Crustacea and Hexapoda (insects and their close relatives). Under the Atelocerata hypothesis, Hexapoda is the closest, whereas under the Paradoxopoda hypothesis, Chelicerata is the closest. This last hypothesis, although supported by few, if any, morphological …
Anatomy
Myriapods have a single pair of antennae and, in most cases, simple eyes. Exceptions include the large and well-developed compound eyes of Scutigera The mouthparts lie on the underside of the head, with an "epistome" and labrum forming the upper lip, and a pair of maxillae forming the lower lip. A pair of mandibles lie inside the mouth. Myriapods breathe through spiracles that connect to a tracheal system similar to that of insects. There is a long tubular heart that extends through muc…
Ecology
Myriapods are most abundant in moist forests, where they fulfill an important role in breaking down decaying plant material, although a few live in grasslands, semi-arid habitats or even deserts. A very small percentage of species are littoral (found along the sea shore). The majority are detritivorous, with the exception of centipedes, which are chiefly nocturnal predators. A few species of centipedes and millipedes are able to produce light and are therefore bioluminescent Pauropod…
See also
• Euthycarcinoidea, a group of enigmatic arthropods that may be ancestral to myriapods
• Colonization of land, major evolutionary stages leading to terrestrial organisms
• Metamerism, the condition of multiple linearly repeated body segments
External links
• Myriapod Fossil Record - University of Bristol
• International Journal of Myriapodology
• International Society of Myriapodology
• British Myriapod and Isopod Group