The main functions of the skin include:
- Protection of the human body
- Sensation i.e. transmitting to the brain information about surroundings
- Temperature regulation
- Immunity i.e. the role of the skin within the immune system
- Enables movement and growth without injury
- Excretion from the body of certain types of waste materials
- Endocrine function e.g. re. Vitamin D
What are the four protective functions of the skin?
Skin has four main functions, as follows: Protection: As the first line of defense against the external environment, the epidermis is continuously replenishing and shedding tens of thousands ... Mechanical impact: Skin acts as the first physical barrier to withstand any pressure, stress or trauma. ...
What is the primary function of the skin?
Feb 02, 2012 · The skin performs six primary functions which include, protection, absorption, excretion, secretion, regulation and sensation. Protection The skin functions as our first line of defense against toxins, radiation and harmful pollutants.
What is the primary purpose of skin?
Sep 13, 2011 · What are the 4 functions of the skin? The four functions of the skin are 1. Mechanical barrier for infections 2. Sensataion/touch 3. Tempature regulaion 4. Excretion: Waste,Salt,Sweat etc.
What are the components of the skin?
Start studying All four functions of the skin. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

What is the function of skin?
One of the most critical functions of the skin is to act as a protective shield between the external world and the body. At a basic level, we would turn into a mummy under arid conditions without a barrier function. Even small defects in the barrier function appear on the skin as rashes, dryness, or other visible symptoms.
Why is skin important?
The skin plays an important role in immune function. The skin’s defense against antigens like bacteria, fungi, and viruses isn’t just its physical barrier function, though this plays an important role. Once these antigens infiltrate the skin, immune cells like macrophages digest these invaders.
Why do we need moisturizers?
Moisturizers can help to reinforce the barrier function and is a must-have item for those with a compromised barrier function.
How much SPF does a tan have?
While photoprotection is a part of the skin’s function, its protective powers are limited. It’s estimated that a tan provides less than 3 SPF. 3 Staying in the shade, wearing longer clothes, and applying sunscreen can help your skin on the job.
What temperature can humans function at?
Humans have a very narrow range of internal body temperature that they can function at. A mere 2 degree Celcius shift away from 37 is all it takes to fall into hypothermia or hyperthermia, both being very dangerous states. 1 Precise thermoregulation is a necessary adaptation for humans, given the wide ranges of climates that humans have successfully inhabited.
How can I boost my immune system?
Lifestyle factors are relevant as well. Diet, exercise, and living well can help boost your immune system. 1 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566070216300017.
What is the largest organ in the body?
The skin is the largest organ, and also one that is in plain sight. In our everyday lives, the focus is on the outer appearance of our skin , but the skin does much more than look pretty. We look at the important functions of the skin and help you identify when your skin might need a little help from you.
What is the function of skin?
The skin allows us to feel and recognize pain, touch/pressure, and temperature heat and cold. It is covered in somatic sensory receptors which relay these sensations as signals to the brain.
How does skin help the body?
The skin helps release or preservation of heat. Sweat glands within the skin release sweat onto the outer layer of skin, which then evaporates to reduce levels of heat. 4. Immunity. The skin also interacts with the immune system of the body and help destruct microorganism.
What happens when you smoke?
Avoid Smoking. When you smoke, blood vessels within the outer layer of skin begin to narrow, which in turn decreases blood flow. This leads to a depletion of the oxygen and nutrients of the skin, all of which are essential to skin health.
How many layers are there in the human body?
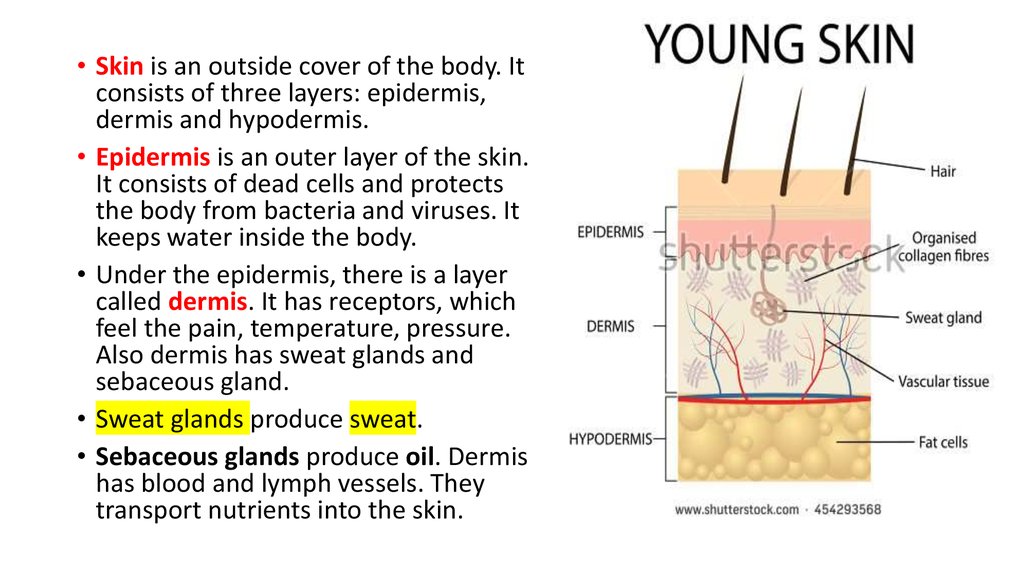
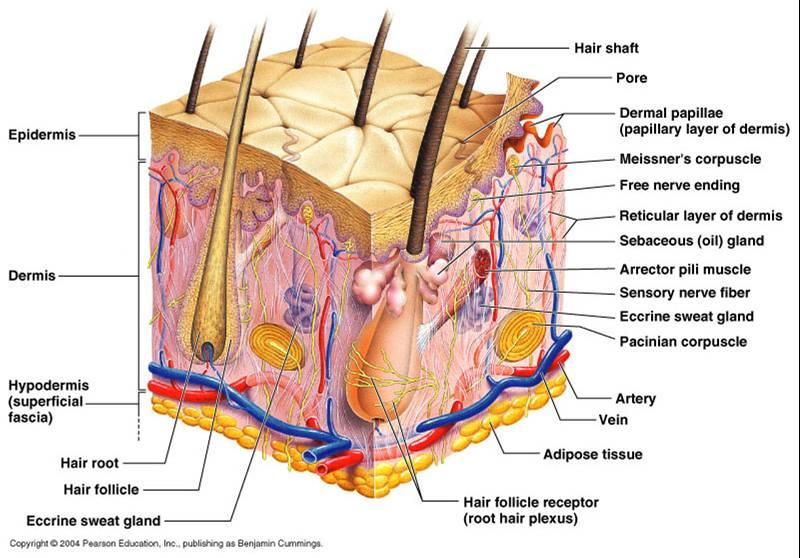
Human skin is made up of three layers, the top layer (epidermis), beneath that you have the subcutaneous layer, and then the dermis. The skin, like most organs, is vital to overall health and it carries out many functions that help us and protect our health. This article will detail the functions of the skin, giving you a clear understanding ...
How to get younger looking skin?
Eat Healthy. Eating plenty of fruit and vegetables will provide you with much needed nutrients, which are beneficial to overall health, as well as skin health. Some research suggests a close correlation between vitamin C and younger looking skin. A healthy diet will ensure optimum functions of the skin.
Why is skin important?
The skin helps to protect us from numerous things, including dehydration, microorganisms/bacteria, injury/trauma, and ultraviolet radiation/sun damage . It acts as a barrier from the outside world, with the tissue being strong enough to protect us. The skin also carries proteins (keratin) and pigments (melanin).
Does skin absorb oxygen?
Absorption: The skin is capable of absorbing necessary substances , such as nitrogen and oxygen. Although we as humans still require lungs to breathe ,some species of animal have such advanced skin that they are capable of absorbing all the oxygen they need through their skin.
What is the function of skin?
Protects the body: The first function of the skin is give protection to the body tissues. The skin protects the tissues of the body from mechanical damage and from bacteria. It also protects the body from losing too much water through evaporation.
What are the different parts of the skin?
The skin is divided into three main parts. These parts are as follow: 1 The epidermis: This is the protective layer of the skin. 2 The dermis: This is a layer that is made up of connective tissues and fibers. 3 Subcutaneous fat: This contains fat cells which store fat.
What is the function of skin?
The skin functions as our first line of defense against toxins, radiation and harmful pollutants. Skin contains cells that provide immune functions to protect against infections. Our skin has the ability to identify and destroy foreign substances that may potentially be harmful to the body.
How many layers are there in the skin?
The skin is a very complex organ. It contains thousands of tiny pores and hair follicles. The skin is broken up into 3 different layers, the epidermis or top layer, dermis, and subcutaneous layer. Each of these layers performs important roles in keeping our body healthy.
How does the skin regulate temperature?
Regulation. The skin regulates the body’s temperature by sweating; when water from sweat on the skin evaporates it gives off heat and cools the body. The body’s temperature increases or by shivering or getting goosebumps when the body is cold. The contraction of muscles releases energy that warms the body. Sensation.
What is the secretion of sebum?
Secretion. The skin secretes sebum, a mixture of oils that keeps the skin soft and supple. The layer of sebum on the outermost layer of the skin is known as the acid mantle. When intact the acid mantle has a PH that ranges from 4.5-5.5. The acid mantle is acidic in nature to protect the skin from outside invasion. Regulation.
Barrier Function
- One of the most critical functions of the skin is to act as a protective shield between the external world and the body. At a basic level, we would turn into a mummy under arid conditions without a barrier function. Even small defects in the barrier function appear on the skin as rashes, dryness, or other visible symptoms. 1. Blocks harmful antigens like viruses, bacteria, and fungus from en…
Thermoregulation
- Humans have a very narrow range of internal body temperature that they can function at. A mere 2 degree Celcius shift away from 37 is all it takes to fall into hypothermia or hyperthermia, both being very dangerous states.1Precise thermoregulation is a necessary adaptation for humans, given the wide ranges of climates that humans have successfully inhabited. 1. Sweat plays an i…
Photoprotection
- Humans are naturally more vulnerable to sun exposure than many animals. We don’t have thick fur, and we don’t wallow in mud regularly. We do have some defense, however, and our skin provides us with melanin, which is the pigment that produces color. 1. UV exposure is a powerful environmental hazard that causes premature aging, skin cancer, and many other skin conditions…
Immunological Protection
- The skin plays an important role in immune function. The skin’s defense against antigens like bacteria, fungi, and viruses isn’t just its physical barrier function, though this plays an important role. Once these antigens infiltrate the skin, immune cells like macrophages digest these invaders. 1. Reactions like inflammation are an important part of the immune system. 2. Several cells in th…