
The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached. The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrog…Cytosine
What are the 4 bases used to make DNA?
There are four different bases in DNA:
- thymine, T
- adenine, A
- guanine, G
- cytosine, C
What are the 4 main elements that make up DNA?
- Radioactive Carbon: C-14 in place of normal C-12
- Radioactive Hydrogen: H-3 (tritium) instead of normal H-1
- Radioactive Phosphorus: P-32 instead of normal P-31
- Radioactive Sulfur: S-35 instead of normal S-32.
What are 4 base pairs in DNA?
Uracil and modifications Base J Uracil 5-Dihydroxypentauracil 5-Hydroxymethyldeoxyuracil
- Base J
- Uracil
- 5-Dihydroxypentauracil
- 5-Hydroxymethyldeoxyuracil
What are the 4 nitrogenous bases are found in DNA?
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). The nitrogenous bases in RNA are the same, with one exception: adenine (A), guanine (G), uracil (U), and cytosine (C).
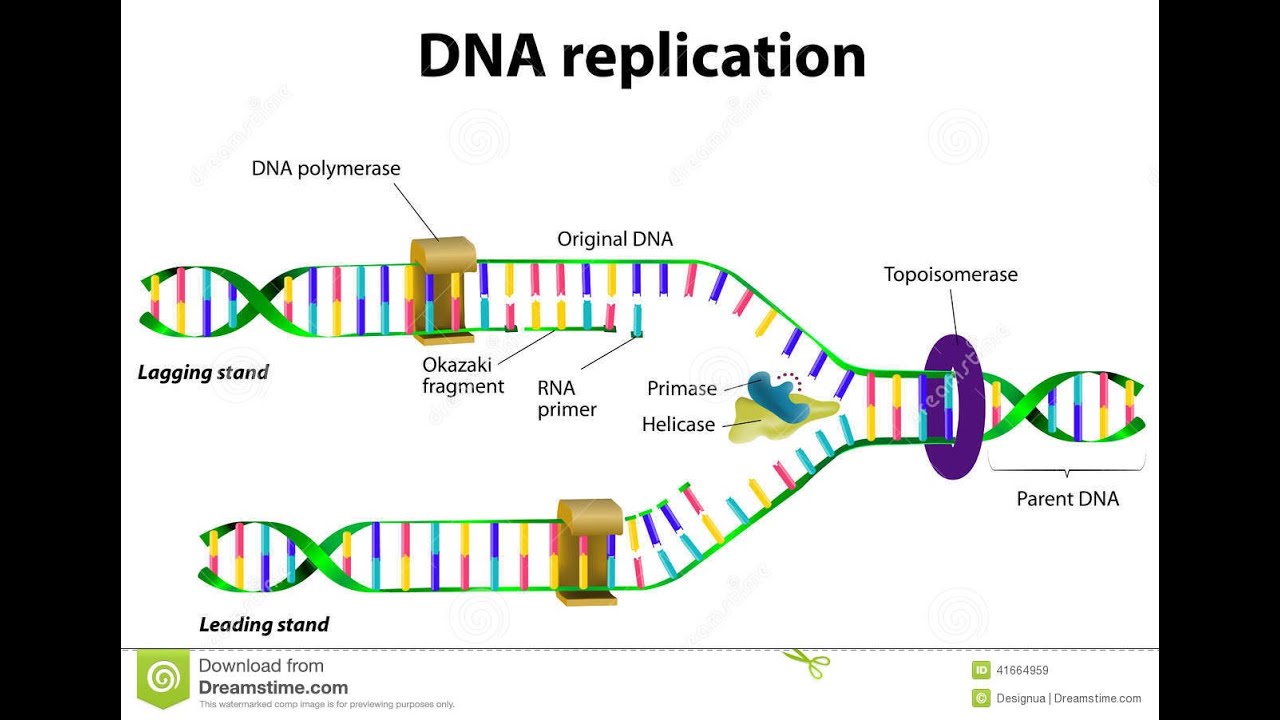
How do the 4 nucleotides in DNA pair up?
Base Pair Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) [GWA-NeeN] or thymine (T). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What are the 4 nucleotides in RNA?
RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine.
What is are the 4 nucleotides in DNA and how do they function?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
What do the 4 nucleotides have in common?
The four types of nucleotides contain four types of nitrogenous bases. Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine are nitrogenous bases present in DNA and uracil instead of thymine in RNA.
What is purine and pyrimidine bases?
Purines (adenine and guanine) are two-carbon nitrogen ring bases while pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) are one-carbon nitrogen ring bases. Also Read: Amino Acids. Given below in a tabular column are the differences between Purines and Pyrimidines.
What are the 5 nucleosides?
The five bases that are found in nucleotides are often represented by their initial letter: adenine, A; guanine, G; cytosine, C; thymine, T; and uracil, U. Note that A, G, C and T occur in DNA; A, G, C and U occur in RNA.
What is adenine thymine guanine and cytosine?
ACGT is an acronym for the four types of bases found in a DNA molecule: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). A DNA molecule consists of two strands wound around each other, with each strand held together by bonds between the bases. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What are the 4 main functions of DNA?
The four roles DNA plays are replication, encoding information, mutation/recombination and gene expression.Replication. DNA exists in a double-helical arrangement, in which each base along one strand binds to a complementary base on the other strand. ... Encoding Information. ... Mutation and Recombination. ... Gene Expression.
Why are there only 4 bases in DNA?
Because four is the minimum possible number. If there is no push to make a system more complex, it will never assemble. One might then argue that a similar system could have been built only using two bases.
What are the 4 types of base pairs?
There are four nucleotides, or bases, in DNA: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C).
How many nucleotides make up a codon?
three nucleotidesA codon is a DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides (a trinucleotide) that forms a unit of genomic information encoding a particular amino acid or signaling the termination of protein synthesis (stop signals). There are 64 different codons: 61 specify amino acids and 3 are used as stop signals.
What are the four nucleotides in the nucleic acid Item 1?
Each nucleotide in DNA contains one of four possible nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G) cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
What 3 things make up A nucleotide of RNA?
Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts:Nitrogenous Base. Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. ... Pentose Sugar. In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. ... Phosphate Group. A single phosphate group is PO43-.
Which nucleotides pair together in RNA?
Transcription: DNA to mRNA DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules. In DNA/RNA base pairing, adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G).
What nucleotides are found in RNA but not DNA?
Uracil is the nitrogenous base present only in RNA, but not in DNA. Thymine is in DNA. DNA have thymine, guanine, adenine and cytosine. Thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA.
How many different types of nucleotides are found in RNA?
four individualRNA is composed of four individual nucleotides. These four nucleotides include adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil, which replaces thymine in DNA.. A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, sugar, and a phosphate group.
What is the order of nucleotides in DNA polymers?
The order of nucleotides along DNA polymers encodes the genetic information carried by DNA. DNA polymers can be tens of millions of nucleotides long. At these lengths, the four-letter nucleotide alphabet can encode nearly unlimited information.
What are the four nitrogen bases?
Nucleotides in DNA contain four different nitrogenous bases: Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine, or Guanine. There are two groups of bases: 1 Pyrimidines: Cytosine and Thymine each have a single six-member ring. 2 Purines: Guanine and Adenine each have a double ring made up of a five-atom ring attached by one side to a six-atom ring.
What is a phosphate molecule?
A phosphate molecule. A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. DNA polymers are strings of nucleotides. Cells build them from individual nucleotides by linking the phosphate of one nucleotide to the #3 carbon of another.
How do cells build nucleotides?
Cells build them from individual nucleotides by linking the phosphate of one nucleotide to the #3 carbon of another. The repeating pattern of phosphate, sugar, then phosphate again is commonly referred to as the backbone of the molecule. The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose.
What is the sugar in DNA?
The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose. Deoxyribose differs from ribose (found in RNA) in that the #2 carbon lacks a hydroxyl group (hence the prefix “Deoxy”). This missing hydroxyl group plays a role in the three-dimensional structure and chemical stability of DNA polymers.
Do nucleosides have phosphates?
Nucleosides are similar to nucleotides, except they do not contain a phosphate group. Without this phosphate group, they are unable to form chains. Test your knowledge of Nucleotides with a quiz. Overview of the illustration. YouTube. SciencePrimer. 3.13K subscribers. Subscribe. Nucleotides in DNA.
What are the four nucleotides of DNA?
The four nucleotides of DNA are :- 1 Adenine 2 Thymine 3 Guanine 4 Cytosine. Adenine pairs with Thymine with 2 Hydrogen bonds. Guanine pairs with Cytosine with three Hydrogen bonds.
What are the four types of nucleotides?
The four types of nucleotides found in DNA are guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine. These are nitrogenous bases and are subdivided into purines and pyrimidines.
What are the nucleotides that make up DNA?
Short answer: Also called DNA monomers, the nucleotides that make up DNA are thymine (T), cytosine (C) ( pyrimidines), a denine (A), guanine (G) ( purines). Cytosine. Adenine pairs with Thymine with 2 Hydrogen bonds. Guanine pairs with Cytosine with three Hydrogen bonds.
How many hydrogen bonds are there between adenine and thymine?
There are two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine, and three hydrogen bonds between cytosine and guanine.The nucleotide in DNA consists of three main structures, which are deoxyribose, a phosphate group and one of four nitrogenous bases.
What are the units of DNA?
DNA Nucleotides are ‘units’ of DNA. They are monomers that, when bonded together, form the polymer for deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. For each nucleotide , you have a Phosphate Group, a Deoxyribose (pentose) Sugar, and a Nitrogenous Base (which is a variable region).
How many nucleotides are in a DNA sequence?
Wikipedia has a great page which outlines the sixty-four different possible combinations of three successive nucleotides in a DNA sequence. Each one has one of four nucleotides on one side, and exactly one that pairs with it on the other side of the double helix.
What are the bonds between nucleotides called?
These nucleotides bind together at the phosphate groups to form a polynucleotide, or DNA strand. These bonds are called phosphodiester bonds — because they are ester bonds, at the phosphate groups, and there are two of them on each phosphate. The Nitrogenous bases have four variations for DNA. They can be.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
There's an A, C, G, and T in DNA, and in RNA there's the same three nucleotides as DNA, and then the T is replaced with a uracil. The nucleotide is the basic building block of these molecules, and is essentially are assembled by the cell one at a time and then strung together by the process of either replication, in the form of DNA, ...
What is the building block of nucleic acids?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids. RNA and DNA are polymers made of long chains of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.
What are the four nucleobases in DNA?
The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level.
What is the name of the nucleotide molecule?
In nucleic acids, nucleotides contain either a purine or a pyrimidine base—i.e., the nucleobase molecule, also known as a nitrogenous base—and are termed ribo nucleotides if the sugar is ribose, or deoxyribo nucleotides if the sugar is deoxyribose. Individual phosphate molecules repetitively connect the sugar-ring molecules in two adjacent ...
What are the two types of organic molecules that make up nucleotides?
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth.
How are signaling nucleotides formed?
Signaling cyclic nucleotides are formed by binding the phosphate group twice to the same sugar molecule, bridging the 5'- and 3'- hydroxyl groups of the sugar. Some signaling nucleotides differ from the standard single-phosphate group configuration, in having multiple phosphate groups attached to different positions on the sugar.
How are nucleotides synthesized?
In vivo, nucleotides can be synthesized de novo or recycled through salvage pathways. The components used in de novo nucleotide synthesis are derived from biosynthetic precursors of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, and from ammonia and carbon dioxide.
What is the name of the nucleotide that contains the five carbon sugar deoxyribose?
This nucleotide contains the five-carbon sugar deoxyribose (at center), a nucleobase called adenine (upper right), and one phosphate group (left). The deoxyribose sugar joined only to the nitrogenous base forms a Deoxyribonucleoside called deoxyadenosine, whereas the whole structure along with the phosphate group is a nucleotide, a constituent of DNA with the name deoxyadenosine monophosphate.
Which nucleotide is the nitrogenous base?
Showing the arrangement of nucleotides within the structure of nucleic acids: At lower left, a monophosphate nucleotide; its nitrogenous base represents one side of a base-pair. At the upper right, four nucleotides form two base-pairs: thymine and adenine (connected by double hydrogen bonds) and guanine and cytosine ...
What are the different types of nucleotides?
Although most people learn only the five main types of nucleotides, there are others, including, for example, cyclic nucleotides (e.g., 3'-5'-cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP.) The bases can also be methylated to form different molecules .
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Each nucleotide is a polymer made up of three parts: A five-carbon sugar (2'-deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA) A phosphate molecule. A nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base.
What is the helix of a nucleotide?
The helix of the molecules forms when two complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each other. Adenine binds with thymine (A-T) in DNA and with uracil in RNA (A-U). Guanine and cytosine complement each other (G-C). To form a nucleotide, a base connects to the first or primary carbon of ribose or deoxyribose.
How are nucleotides named?
Nucleotides are named based on the number of phosphate residues they contain. For example, a nucleotide that has an adenine base and three phosphate residues would be named adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If the nucleotide has two phosphates, it would be adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If there is a single phosphate, ...
What is the chemical formula for pyrimidines?
The pyrimidines are cytosine, thymine, and uracil. The chemical formula of adenine is C 5 H 5 N 5. A denine (A) binds to thymine (T) or uracil (U). It's an important base because it's used not only in DNA and RNA, but also for the energy carrier molecule ATP, the cofactor flavin adenine dinucleotide, and the cofactor nicotinamide adenine ...
How do bases form nucleotides?
To form a nucleotide, a base connects to the first or primary carbon of ribose or deoxyribose. The number 5 carbon of the sugar connects to the oxygen of the phosphate group. In DNA or RNA molecules, a phosphate from one nucleotide forms a phosphodiester bond with the number 3 carbon in the next nucleotide sugar.
How many bases does DNA have?
Both DNA and RNA use four bases, but they don't use all the same ones. DNA uses adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, while RNA uses adenine, guanine, and cytosine but has uracil instead of thymine. The helix of the molecules forms when two complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each other.
