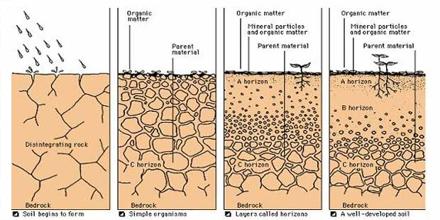
The four main processes in soil formation are:
- additions
- losses
- translocations
- transformations
What are the stages of soil formation?
Types of Soil Formation
- Clay Soil Formation. Clay has a low water drainage rate and shallow air movement. These aspects come from the soil’s structure.
- Sand Soil Formation. Sand formation happens as an effect of rock erosion. ...
- Silt Soil Formation. Silt forms similarly to clay and sand by the erosion of rocks and minerals. ...
What are the steps of soil formation?
Soil formation factors and processes The soil formation is the process of two consecutive stages. 1. The weathering of rock (R) into Regolith 2. The formation of true soil from Regolith The evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of soil forming factors and processes. The first step is accomplished by weathering ...
What process is a cloud to soil?
Types of Clouds
- Stratus Clouds. These are the types of clouds that are low-hanging and cover the sky like a layer. ...
- Cirrus Clouds. These are those super-thin, wispy clouds you see seemingly sitting atop of the sky. ...
- Cumulus Clouds. These are the ones you’re used to seeing, drawing, and taking photos of. ...
What are soil forming factors?
It can be seen from the above analysis that under dry shrinkage and freeze-thaw conditions, the research method used to elucidate the engineering characteristics of earthen soil is relatively singular 26, and the effects of factors such as temperature ...
What are the four 4 main components of soil?
The four components of soil include: mineral matter 45%, organic matter 5%, air 25%, and water 25%.
How many processes of soil formation do we have?
fiveThe evolution of soils and their properties is called soil formation, and pedologists have identified five fundamental soil formation processes that influence soil properties. These five “state factors” are parent material, topography, climate, organisms, and time.
What are the five soil formation?
The whole soil, from the surface to its lowest depths, develops naturally as a result of these five factors. The five factors are: 1) parent material, 2) relief or topography, 3) organisms (including humans), 4) climate, and 5) time.
What are the types of soil formation?
Formation of SoilsMechanical Weathering.Chemical Weathering.
What is the process of soil formation called?
Pedogenesis is defined as the process of soil formation by biogeochemical activities such as weathering. This activity is influenced by climate and organisms present in the soil.
What are the processes of soil formation PDF?
The fundamental processes are accumulation of humus or decayed organic material, eluviation, illuviation and horizonation. Humification is the process of decomposition of organic matter and synthesis of new organic substances. Soil genesis is associated with the origin and development of the biosphere.
What are the four classes of changes to soil horizons?
The four major processes that change parent material into soil and develop soil horizons are additions, losses, translocations, and transformations.
What are the major factors of soil formation class 8?
Climate, , flora and fauna, altitude, and are the five major factors that contribute to soil formation.
What are the factors or processes that make soil Class 9?
Answer: Soil is formed by breaking down of rocks at or near the surface of the Earth through various physical, chemical, and biological processes by various factors such as the sun, water, wind, and living organisms.
What processes play the most important role in soil formation?
Earth ScienceQuestionAnswerWhat processes play the most important role in soil formation?Weathering and biological activityWhich scenario would result in the most erosion?Large agricultural population, abundant rainfall and strong average winds.28 more rows
What are the different weathering process to form a soil?
There are three main types of weathering; physical, chemical and biological. Physical weathering is the influence of processes such as freezing and thawing, wetting and drying, and shrinking and swelling on rocks and other sediments, leading to their breakdown into finer and finer particles.
How does soil form?
The soil formation process depends upon the presence of new soil material which is either acquired by denudation or deposition. Denudation is the abrasion of present rock material by the action of ice, water or wind. Deposition is the accumulation of new materials that have been eroded from another place such as river gravels or blown gravel or the creation of new rocks due to volcanic action or the uplift of the ocean.
How long does it take for soil to form?
Most of the soils of the world have taken more than 10,000 years to form the current state of soils.
How does rain affect soil?
Rainfall leaches away soluble materials and iron-rich minerals from the upper soil horizons into the lower ones and evaporation brings about the accumulation of salt compounds in the surface horizons. Cold winter temperatures give room for frost action which physically disintegrates the rocks into fragments.
How does man's activates affect soil?
This makes the soils more permeable to water and air thus enhancing the soil structure. Man’s activates have as well made tremendous changes to the natural soils. Through cultivation, construction, and addition of fertilizer and lime has altered the physical and chemical properties of the soil.
What is physical weathering?
READ: Physical Weathering - Definition, Processes and Types. The same applies to the alterations in structure, texture, and other mineral compositions. The soil horizons are then cemented by the carbonate, iron, and silica minerals. For instance, sandy soils are normally cemented by iron.
What are the new particles that are leached and eroded away from the soil?
Through the movement of water, wind, ice or the uptake of the accumulated materials by plants, the new particles including clay, organic matter, clay, silt or other chemical compounds are leached and eroded away or taken up from the soil by plants. As a result, the physical and chemical compositions ...
What is podsolisation in soil?
Podsolisation takes place when strong acidic solutions breakdown the clay minerals. Accordingly, aluminum, silica and iron form complex materials together with organic compounds in the soil. These materials and the other accumulations are translocated within the profile and/or between the horizons.
What are some examples of additions to soil?
For example, fallen plant leaves, twigs, dust, animal dung, salts or silica dissolved in groundwater and deposited near or at the soil surface when rising water evaporates.
What is translocation agent?
It involves the movement of inorganic and organic material laterally within a horizon or vertically from one horizon up or down to another. Water, either percolating down with gravity or rising up by capillary action is the most common translocation agent. The material moved within the profile includes dispersed clay particles, dissolved salts and dissolved organic substances.
What organisms transport organic matter from the surface to the surface?
Incorporation of surface organic matter into A and B horizons by certain earth worms, transport of B and C horizon to the surface by termites and rodents .
What is the rhizosphere?
The rhizosphere is the region of soil found close to and influenced by roots. Green water is held in this portion of soil. Photo courtesy of flickr/NRCS Soil Health.
Where is the Institute of Soil and Environmental Sciences?
Institute of Soil and Environmental Sciences, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
What is loss of material from the soil profile?
Loss of material from the soil profile by leaching to groundwater, erosion of surface material, or other forms of removal (often transformation and translocation result in the accumulation of material in a particular horizon). Click the link below to view a video depicting erosion of an Organic soil.
What is the term for the transport of inorganic and organic materials from one horizon to another?
Translocation (transportation) of inorganic and organic materials from one horizon to another, either up or down (material is primarily moved by water but may also be moved by soil organisms). Click the links below to view the video clips:
What are the three stages of soil formation?
Soil formation can vary depending on what type of soil is forming – clay, sand, or silt . But generally, these are the three stages that most soils go through on their way to full formation.
What is the definition of soil formation?
Encyclopedia Britannica defines soil formation as “The evolution of soils and their properties.”
Why do microorganisms play a role in soil formation?
Microorganisms play an even greater role in soil formation because of how they guide the soil nitrogen process, which is essential for the balance of minerals and chemical reactions in the soil. Without the soil nitrogen process, the ocean and other bodies of water would become inhabitable for sea life.
Why is it important to classify soil types?
Classifying soil types helps farmers when conducting a soil survey on their fields, or gardeners when they wish to plant only the best species of plants that will thrive in the soil.
How long does it take for soil to form?
Soil formation happens over hundreds, sometimes thousands, of years, but you can still see evidence of that formation today. You can see the soft, dark topsoil layer and every layer underneath, all the way down to the impenetrable bedrock. These layers are called soil horizons.
What are the horizons of soil?
Deeper horizons usually remain unmoving until someone digs into the ground. The soil horizons are O, A, E, B, C, and R. Many factors go into soil formation, and how the soil turns out in appearance and feel depends entirely upon them.
How big is clay soil?
Clay soil has small clay particles that are no larger than 0.002 mm in diameter and are grouped tightly. As a result of this type of particle structure, there is very little space left over for air and water. The particles in soil come directly from the soil formation process.
How long does it take for a soil to form?
It may take hundreds to thousands of years. It will take longer in colder and drier regions than in warmer and wetter regions. This is due to the soil forming processes such as translocation and transformation being slower in cold and/or dry areas. Essentially, chemical reactions (weathering) occur faster as temperature increases. Since soil formation also requires organisms and organisms require water, reactions (formation) occur faster if there is sufficient water present.
How many layers of soil are there?
Like humans, soils have different properties based on where they are from, and where they “grew up” (formed). Soils have 6 major horizontal layers, or horizons that can be present. These horizons are often present in different types of soil, but each area usually has soils that have similar properties if they are near each other. Soil particles are moved by water, wind, ice, or formed in place from the rocks. Soils form differently for many reasons, and The CLORPT PowerPoint details major soil forming factors: CLimate, Organisms, Relief, Parent material, and Time.
What grade is New England soil?
New England Soil Horizons (Grades 4+, perhaps more towards 8-12) A PowerPoint presentation can be followed from this site. Good overview for upper levels. Focuses on New England profiles but can be used in other areas
What is the process of soil formation?
Pedogenesis can be defined as the process of soil formation or development. The soil formation is a continuous process. The term pedogenesis is derived from the Greek word pedo or pedon meaning a 'soil' or 'earth' and genesis meaning 'origin' or 'birth'.
How many factors are there in soil formation?
This unconsolidated material is acted on by the five soil forming factors and soil is formed.
How is soil formed?
Soil is one of the principal substrate of life on the earth, serving as a reservoir of water and nutrients as a medium for the filtration and breakdown of injurious waste, and as a participant in the cycling of carbon and other elements through the global ecosystem. It has evolved through weathering processes driven by biological, climatic, geologic, and topographic influence. Soil is an outer most of the soft most layer of earth, formed by different process which is generally called soil forming forces or pedogenesis. Pedogenesis can be defined as the process of soil formation or development. The soil formation is a continuous process. The term pedogenesis is derived from the Greek word pedo or pedon meaning a 'soil' or 'earth' and genesis meaning 'origin' or 'birth'. It is the process that involves environment and its component, time and geological history. It takes a several hundred years to form a soil profile. With horizon or layer distinct in composition, texture and structure which depending on various factors which have active involvement in pedogenesis or soil formation process. Soil formation occurs through a series of changes. Soil starts with freshly weathered rock influenced by different organic activities altering its structure and pattern. Biogeochemical process act to create and destroy within soils. These alteration leads to development of layers termed as soil horizons differ from one another depending on how and when they are formed. The soil forming factors continue to effect soils even on 'stable' landscapes. Materials are deposited and also blown or washed away from the surface. The addition, removals and the alterations can be either slow or rapid solely depending on climate, position, landscape and biological activity.
What are the active components of soil ecosystem?
The active components of soil ecosystem are plants, animals, microorganisms and man. The role of microorganisms in soil form ation is related to the humification and m ineralization of. vegetation. The action of animals especially burrow ing animals to dig and mix-up the soil mass and thus di sturb.
What are the major determinants of soil formation?
Organis ms including fungi, bacteria, animals, humans, and vegetations are the major determinants and they im pact on the physical. and chemical environments of the soils.
What was the parent material of soil?
Most soil parent materials were rocks at som e time in their history.
What determines the mineralog ical composition of soil?
The parental material determines the mineralog ical composition and widely contributes to the. chemical and physical characteristics of the soil. The type of parental material also det ermines the rate. at which soil forming processes occurs. Different places have different soils based on the paren t.
What is another process that may be operative in soils?
Another process that may be operative in soils is pedoturbation. It is the process of mixing of the soil.
What is the process of differentiation of soil in different horizons along the depth of the soil body?
The differentiation is due to the fundamental processes, humification, eluviation and illuviation.
What are passive soil forming factors?
The passive soil forming factors are those which represent the source of soil forming mass and conditions affecting it. These provide a base on which the active soil forming factors work or act for the development of soil.
Why is soil on steep slopes shallow?
It is due to accelerated erosion, which removes surface material before it has the time to develop. Reduced percolation of water through soil is because of surface runoff, and lack of water for the growth of plants, which are responsible for checking of erosion and promote soil formation.
Which process is slower, pedogenic or geological?
The pedogenic processes, although slow in terms of human life, yet work faster than the geological processes in changing lifeless parent material into true soil full of life.
Is podzolization a negative process?
It is a process of soil formation resulting in the formation of Podzols and Podzolic soils. In many respects, podzolization is the negative of calcification. The calcification process tends to concentrate calcium in the lower part of the B horizon, whereas podzolization leaches the entire solum of calcium carbonates.