Steps in Hemostasis
- Vascular Phase Constriction of the blood vessel that is torn starts almost immediately after the injury. ...
- Platelet Phase Platelet aggregation and activation forms a plug before the blood clot. ...
- Clotting Phase The formation of a blood clot provides a more long lasting plug. ...
- Fibrosis and Fibrinolysis Once a clot forms, the blood vessel wall will slowly heal. ...
What are the steps in the hemostasis process?
Steps in Hemostasis 1 Vascular phase – vascular constriction 2 Platelet phase – formation of a platelet plug 3 Coagulation phase – blood clot formation 4 Fibrosis and fibrinolysis – fibrous tissue growth or clot dissolution
What is the second stage of hemostasis?
The second stage of hemostasis involves platelets that move throughout the blood. When the platelets find an exposed area or an injury, they begin to form what is called a platelet plug. The platelet plug formation is activated by a glycoprotein called the Von Willebrand factor (vWF), which are found in the body’s blood plasma.
What is hemostasis in simple words?
Introduction Definition. Hemostasis is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel. It is a process that involves multiple interlinked steps. This cascade culminates into the formation of a “plug” that closes up the damaged site of the blood vessel controlling the bleeding.
What are the steps in the process of coagulation?
Terms in this set (5) Step 1: Vascular Spasms blood vessels constrict to slow blood loss Step 2: Platelet plug formation platelets stick together to plug break Step 3: Coagulation Enzymatic process requiring clotting factors and Ca2+ Step 4: Clot retraction and repair

What are the four steps of hemostasis quizlet?
MatchInitiation and formation of the platelet plug.Extension of the clotting process by the Coagulation Cascade.Termination of clotting by antithrombotic control mechanisms.Removal of the clot by fibrinolysis.
What are the steps of hemostasis quizlet?
Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.It involves three steps: (1) vascular spasm (vasoconstriction); (2) platelet plug formation; and (3) coagulation.
What is a primary hemostasis?
Primary haemostasis is the initial response of the body to vascular injury, and involves interaction between platelets, adhesive proteins located in the subendothelial matrix (including collagen and von Willebrand factor), and circulating fibrinogen.
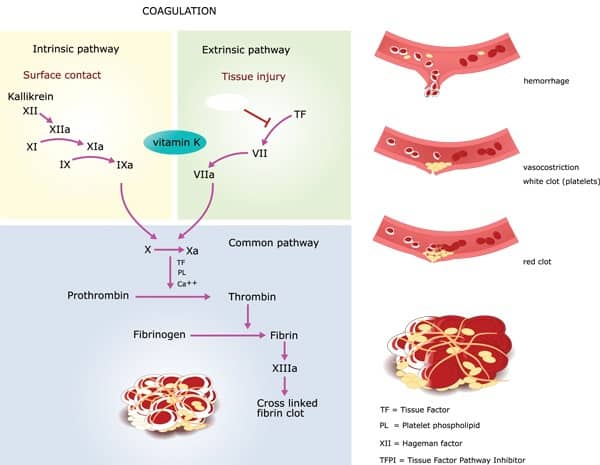
What is the common pathway of hemostasis?
The common pathway consists of factors I, II, V, VIII, X. The factors circulate through the bloodstream as zymogens and are activated into serine proteases. These serine proteases act as a catalyst to cleave the next zymogen into more serine proteases and ultimately activate fibrinogen.
What are the 5 steps of hemostasis?
Terms in this set (16) Vessel Spasm. ... Formation of Platelet Plug. ... Blood Coagulation. ... Clot Retraction. ... Clot Dissolution (Lysis)
What is the last step of hemostasis?
The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting. Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a "molecular glue". Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process.
What is the first stage of hemostasis?
The mechanism of hemostasis can divide into four stages. 1) Constriction of the blood vessel. 2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug." 3) Activation of the coagulation cascade. 4) Formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot.
What are the types of hemostasis?
Hemostasis can be subdivided into three sequential processes: primary hemostasis, secondary hemostasis, and tertiary hemostasis. In primary hemostasis the interaction of the injured endothelium with von Willebrand factor (VWF), and platelets is crucial for the formation of a platelet plug at the injury site.
Which phase of hemostasis is irreversible?
The final phase of platelet activation consists in their aggregation, which is reversible in a first time and irreversible afterwards. On the other hand, the activated platelets can also trigger the process of coagulation, which demonstrates the narrow relationship between the various stages of haemostasis.
What are the 12 blood clotting factors?
What Are The Twelve Blood Clotting Factors?Fibrinogen (Factor 1)Prothrombin (Factor 2)Thromboplastin (Factor 3)Calcium (Factor 4)Proaccelerin or Labile Factor (Factor 5)Stable Factor (Factor 6)Antihemophilic Factor (Factor 8)Christmas Factor (Factor 9)More items...
Which pathway is correct for blood clotting?
Intrinsic pathwayAll the components necessary for the clotting process to proceed are found in the blood. As such, the proteins required for such clotting to take place are part of the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation.
What are the 13 clotting factors?
The following are coagulation factors and their common names:Factor I - fibrinogen.Factor II - prothrombin.Factor III - tissue thromboplastin (tissue factor)Factor IV - ionized calcium ( Ca++ )Factor V - labile factor or proaccelerin.Factor VI - unassigned.Factor VII - stable factor or proconvertin.More items...
What are the steps of homeostasis quizlet?
Terms in this set (4)Stimulus. Produces change in variable, change detected by receptor.Input. Information sent along afferrent pathway to control center.Output. Information sent along efferent pathway to activate effector.Response. Feeds back to influence magnitude of stimulus and returns variable to homeostasis.
What is the first step in hemostasis quizlet?
The first step in hemostasis is: platelet plug formation.
Which of the following lists the steps of hemostasis in the correct sequence?
Hemostasis includes three steps that occur in a rapid sequence: (1) vascular spasm, or vasoconstriction, a brief and intense contraction of blood vessels; (2) formation of a platelet plug; and (3) blood clotting or coagulation, which reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin mesh that acts as a glue to hold the clot ...
What is the final step of the coagulation phase of hemostasis quizlet?
A final interaction for both pathways converts fibrinogen to fibrin, the material that forms the structural matrix of the clot.
What is the process of stopping blood vessels from bleeding?
Hemostasis is a series of overlapping processes intended to stop the bleeding during an injury to the blood vessel. It occurs in 4 stages as
What is the process of breaking down a blood clot?
Fibrinolysis. This is a healing process of the damaged blood vessel. This phase begins with the breakdown of the clot. The clot is broken down by the enzyme plasmin which is an activated form of plasminogen. This plasmin converts insoluble fibrin to soluble form which is removed byphagocytosis.
What happens when a blood clot forms?
Once the clot is formed, the platelets gradually contract and ooze out the serum. This leads to shrinkage of the clot with clear fluid on the surface. As the clot retracts (shrinks) the edges of damaged blood vessel tissue are pulled together leading to the closure of the hole.
How long does it take for a thrombocyte to form a platelet plug?
Many thrombocytes arrive at the injured site due to a positive feedback system to form a platelet plug or seal. This plug formation occurs in 6 minutes and prevents further leakage of blood from the injured site.
Which enzyme converts fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin threads?
This prothrombin activator activates the enzyme thrombin which converts fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin threads.
How many factors are involved in the formation of prothrombin?
This process involves 12 factors that go on to the formation of a prothrombin activator. The factors are termed clotting factors and are listed below.
Which pathway is faster, extrinsic or thromboplastin?
The extrinsic pathway is faster and gets activated within seconds of tissue damage. The thromboplastin is released by damaged tissue which goes on to initiate coagulation.
How long does it take for a hemostasis to take effect?
Steps in Hemostasis. There are broadly four steps in the process of hemostasis. The first step takes effect almost immediately after there has been a break in the blood vessel and may even occur with injury to the blood vessel without a tear. The tear is sealed anywhere within a few minutes to about 20 minutes.
What is the process of stopping blood loss?
Hemostasis Process – Mechanism to Stop Blood Loss. Blood is contained within the cardiovascular system – the heart and blood vessels – with additional amounts stored in the liver and spleen. The quantity of blood in the human body is approximately 5.5 liters. When bleeding, up to 20% of this total blood volume can be lost without a person being ...
What is the clotting phase?
Clotting Phase. The formation of a blood clot provides a more long lasting plug. The clotting process involves the laying down of fibrin which reinforces the platelet plug. Fibrin is a long protein strand which forms from fibrinogen by the action of thrombin.
What is the process of blood clotting?
Simply, hemostasis is the blood clotting process but a number of mechanisms exist before and after the formation of the actual blood clot. Without hemostasis, bleeding would continue unabated and eventually result in death. This process although efficient does have its limitations with severe hemorrhages.
What happens when blood vessels are compromised?
However, the moment the blood vessel wall is compromised, the platelets are strongly attracted to the site of injury. Once attached, the platelet swells and portions of it extend outwards to attached to neighboring platelets or other portions of the torn vessel wall. The platelets can also contract to form a tight and firm plug.
What is the body's series of processes developed to prevent blood loss when a vessel is compromised?
What is hemostasis ? Hemostasis is the body’s series of processes developed to prevent blood loss when a vessel is compromised.
How long does it take for a blood vessel to heal after a break?
The final process that permanently seals the blood vessel may only be completed about 1 to 2 weeks after ...
What is the process of hemostasis?
It begins with trauma to the lining of the blood vessel. Definition. Hemostasis is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel. It is a process that involves multiple interlinked steps. This cascade culminates into the formation of a “plug” that closes up the damaged site of the blood vessel controlling the bleeding.
What is hemostasis in physiology?
Physiology, Hemostasis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. Definition. Hemostasis is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel. It is a process that involves multiple interlinked steps.
What is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel?
Introduction. Definition. Hemostasis is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel. It is a process that involves multiple interlinked steps. This cascade culminates into the formation of a “plug” that closes up the damaged site of the blood vessel controlling the bleeding. It begins with trauma to the lining of the blood ...
What is the hemostatic cascade?
The hemostatic cascade is meant to control hemorrhage and be a protective mechanism. At times, this process is triggered inadvertently while the blood is within the lumen of the blood vessel and without any bleeding.[1]
What to monitor after cardiac stenting?
For patients after cardiac stenting or stroke to monitor the activity of the antiplatelet agents
Which triad of vascular stasis and vascular trauma is a true predictor of thrombo?
General Principle. The Virchow’s triad of hypercoagulability, vascular stasis, and vascular trauma, described in 1856, remains a true predictor of thrombosis.
Which pathway activates factor VII?
Extrinsic Pathway . The tissue factor binds to factor VII and activates it. The activated factor VII (factor VIIa) further activates factor X and factor IX via proteolysis. Activated factor IX (factor IXa) binds with its cofactor – activated factor VIII (factor VIIIa), which leads to the activation of factor X (factor Xa). Factor Xa binds to activated factor V (factor Va) and calcium and generates a prothrombinase complex that cleaves the prothrombin into thrombin. [4]
What are the steps of hemostasis?
Hemostasis has three major steps: 1) vasoconstriction, 2) temporary blockage of a break by a platelet plug, and 3) blood coagulation, or formation of a fibrin clot. These processes seal the hole until tissues are repaired.
How does hemostasis occur?
Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels. It is the instinctive response for the body to stop bleeding and loss of blood. During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting. Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured. Within seconds of a blood vessel’s epithelial wall being disrupted platelets begin to adhere to the sub-endotheliumsurface. It takes approximately sixty seconds until the first fibrin strands begin to intersperse among the wound. After several minutes the platelet plug is completely formed by fibrin. Hemostasis is maintained in the body via three mechanisms:
What is the role of coagulation in hemostatic hemostasis?
Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured.
What is the first response to a vascular spasm?
Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting.
How do platelets help with hemostatic process?
This process is regulated through thromboregulation. Platelets play one of the biggest factors in the hemostatic process. Being the second step in the sequence they stick together (aggregation) to form a plug that temporarily seals the break in the vessel wall.
Why do people develop hemostasis?
Hemostasis disorders can develop for many different reasons. They may be congenital, due to a deficiency or defect in an individual’s platelets or clotting factors. A number of disorders can be acquired as well.
Why does hemostasis not clot?
The body’s hemostasis system requires careful regulation in order to work properly. If the blood does not clot sufficiently, it may be due to bleeding disorders such ashemophilia; this requires careful investigation.
What are the steps of coagulation?
The coagulation process can be described in three major steps: Formation of factor X and prothrombinase. Prothrombinase (prothrombin activator) can form either intrinsically (inside the blood vessels) or extrinsically (outside the blood vessels).
What is the pathway that converts prothrombin to thrombin?
Prothrombin is converted to thrombin. In this common pathway that follows both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways , prothrombinase (with Ca 2+) converts prothrombin to thrombin. Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin. The common pathway continues as thrombin (with Ca 2+) converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
How is a clot strengthened?
Following its formation, a clot is further strengthened by a process called clot retraction. Platelets in the clot contract, pulling on the fibrin strands to which they are attached. The result is a more tightly sealed patch.
What is the breakdown of a clot?
Fibrinolysis is the breakdown of the clot as the damaged blood vessel is repaired. During the formation of a clot, the plasma protein plasminogen is incorporated into the clot. The healthy endothelial tissue that replaces the damaged areas of the blood vessel secretes tissue plasminogen activator (t‐PA), which converts plasminogen into its active form, plasmin (fibrinolysin). Plasmin in turn breaks down fibrin and leads to the dissolution of the clot.
How many factors are involved in coagulation?
Coagulation (blood clotting) is a complex series of reactions that transform liquid blood into a gel (clot), providing a secure patch to the injured blood vessel. Thirteen coagulation factors (numbered I through XIII in order of their discovery) are involved. Most of these factors are proteins released into the blood by the liver.
Which pathway activates factor X?
In the intrinsic pathway, the collagen of the damaged blood vessel initiates a cascade of reactions that activate factor X. In the extrinsic pathway, damaged tissues release thromboplastin (tissue factor, TF), which initiates a shorter and more rapid sequence of reactions to activate factor X.
What is the term for a constriction of a blood vessel?
Hemostasis. A vascular spasm , a constriction of the damaged blood vessel, occurs at the site of injury. Vasoconstriction is initiated by the smooth muscle of the blood vessel in response to the injury and by nerve signals from pain receptors. A platelet plug, consisting of a mass of linked platelets, fills the hole in the damaged blood vessel.
How many components are there in hemostasis?
The actual mechanism of hemostasis can be divided into two main components.
What is primary hemostasis?
Primary Hemostasis. Primary hemostasis involves platelets, which are cellular fragments present in our circulating blood that rush to the site of blood vessel injury to begin plugging the damaged site . Below is explanation of the four stages involved in this process.
What is the process of forming a fibrin clot at the site of blood vessel injury?
The injury itself triggers the processes involved in primary hemostasis ( vasoconstriction, platelet adhesion, platelet activation, and platelet aggregation ) to form a temporary platelet plug, as well as the clotting factors required for the elaborate coagulation cascade in secondary hemostasis that secures a final, stable fibrin clot at the site of injury.
How many clotting factors are involved in fibrin clots?
There are 12 clotting factors.
What is hemostasis in medical terms?
Hemostasis – Part 1 – Primary and Secondary Hemostasis. Dawn Allen Hauser August 11, 2020. Hemostasis is the process that occurs to stop bleeding at the site of an injury. For most people, this may seem like a simple process; hold pressure on the injury for a few minutes and BOOM…no more bleeding. However, a rather complex series ...
What is the factor that converts Prothrombin to Thrombin?
Factor Xa plus activated Factor Va (which is converted from Factor V – Labile Factor) causes the conversion of Prothrombin (Factor II) to Thrombin (Factor IIa). Calcium ions (Ca 2+) are also needed for this process.
What is the cause of vasospasm?
Injury to a blood vessel causes vasospasm, which stimulates vasoconstriction of that vessel. Damaged endothelial cells in the injured blood vessel expose sub-endothelial collagen and something known as von Willebrand factor (vWF).
Where are clotting factors made?
Most Clotting Factors are made in the Liver.
What happens after a clot is formed?
After clot formation actin and myosin (cytoskeletal proteins) contract to pull the clot together and squeeze out any serum/fluid from injured site.

Pathophysiology
- Blood is contained within the cardiovascular system the heart and blood vessels with additional amounts stored in the liver and spleen. The quantity of blood in the human body is approximately 5.5 liters. When bleeding, up to 20% of this total blood volume can be lost without a person being at risk provided that the necessary reflexes take effect. However, this cannot continue unabated …
Definition
- Hemostasis is the bodys series of processes developed to prevent blood loss when a vessel is compromised. It literally means to stop blood and if the hemostatic mechanisms are working as it should it will be able to achieve this goal. Simply, hemostasis is the blood clotting process but a number of mechanisms exist before and after the formation of the actual blood clot. Without hem…
Mechanism
- There are broadly four steps in the process of hemostasis. The first step takes effect almost immediately after there has been a break in the blood vessel and may even occur with injury to the blood vessel without a tear. The tear is sealed anywhere within a few minutes to about 20 minutes. The final process that permanently seals the blood vessel ...
Function
- Platelet aggregation and activation forms a plug before the blood clot. Platelets are tiny disc-shaped components of blood that are in constant circulation. It is formed by the fragmentation of large megakaryocytes and are constantly sealing tiny holes in the blood vessels that occur everyday even without trauma. Despite being a cell fragment and lacking the ability to divide, pla…
Causes
- Under normal circumstances, platelets will not attach to the inner lining of the blood vessel (endothelium). The cell membrane of platelets has specialized glycoproteins that repel it from the endothelium. However, the moment the blood vessel wall is compromised, the platelets are strongly attracted to the site of injury. Once attached, the platelet swells and portions of it exten…
Formation
- The formation of a blood clot provides a more long lasting plug. The clotting process involves the laying down of fibrin which reinforces the platelet plug. Fibrin is a long protein strand which forms from fibrinogen by the action of thrombin. The fibrin then forms a mesh network in which some blood cells and fluid also get trapped along with the platelets.
Prognosis
- Once a clot forms, the blood vessel wall will slowly heal. The clot may either dissolve or form a patch of fibrous tissue (scar). The latter is usually only seen with a severely damaged blood vessel where fibroblasts enter the clot and causes organization. Usually enzymes will dissolve the blood clot in a process known as fibrinolysis once the vessel wall is suitably repaired.