Assumptions in Ideal Gas Law
- Gas consist of particles which are in constant random motion in straight lines.
- The particles of gas do not exert any force among them. ...
- The particles do not occupy any space relative to its container.
- The molecules of the gas are rigid identical spheres and, all possess the same mass.
- The volume of each molecule is negligible in comparison to the size of the container.
What is the formula for the ideal gas law?
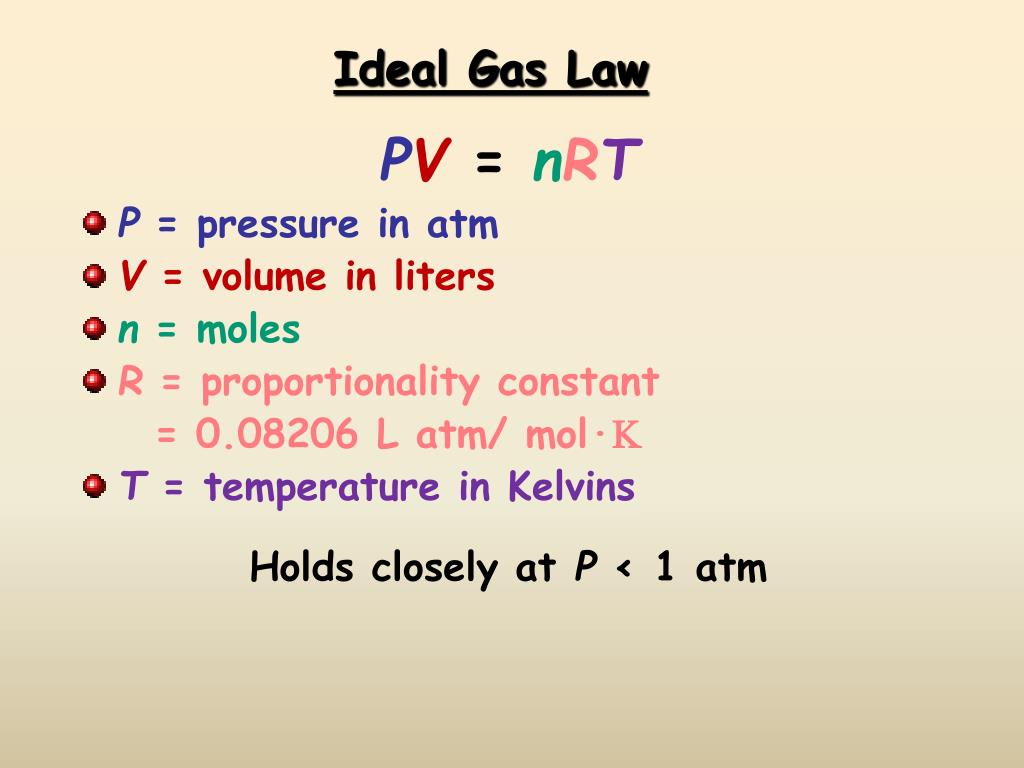
The ideal gas equation is given by PV=nRT P V = n R T . Ideal Gas Law Equation Pressure (P), often measured in atmospheres (atm), kilopascals (kPa), or millimeters mercury/torr (mm Hg, torr)
What are the conditions for ideal gas?
# Assumptions in Ideal Gas Law
- Gas consist of particles which are in constant random motion in straight lines.
- The particles of gas do not exert any force among them. ...
- The particles do not occupy any space relative to its container.
- The molecules of the gas are rigid identical spheres and, all possess the same mass.
What is an ideal gas law?
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations.
What is n in the ideal gas law?
n is the amount of ideal gas measured in terms of moles. R is the gas constant. T is the temperature. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.
.PNG)
What are the 5 characteristics of an ideal gas?
The gas particles have negligible volume. The gas particles are equally sized and do not have intermolecular forces (attraction or repulsion) with other gas particles. The gas particles move randomly in agreement with Newton's Laws of Motion. The gas particles have perfect elastic collisions with no energy loss.
What are the 5 assumptions of the kinetic theory of matter?
The five main postulates of the KMT are as follows: (1) the particles in a gas are in constant, random motion, (2) the combined volume of the particles is negligible, (3) the particles exert no forces on one another, (4) any collisions between the particles are completely elastic, and (5) the average kinetic energy of ...
What are 2 assumptions of an ideal gas?
The ideal gas law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases and relies on the assumptions that (1) the gas consists of a large number of molecules, which are in random motion and obey Newton's laws of motion; (2) the volume of the molecules is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas; and (3) ...
What are the assumptions of gases?
1) All gases are made up of molecules that are constantly and persistently moving in random directions. 2) All the collisions between molecules and even between molecules and walls are considered to be elastic. 3) All the molecules in a certain gas sample obey Newton's laws of motion.
What are the 4 assumptions of kinetic energy?
Explanation: Gas formed by point-like particles ( volume≈0 ); No intermolecualar attractions between the molecules of the gas; Random motion; Elastic collisions.
What are the assumptions of the kinetic model of an ideal gas?
0:191:57Ideal Gas Assumptions - Kinetic Theory - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThere are four main assumptions that we need to make when considering a gas as ideal. Before it canMoreThere are four main assumptions that we need to make when considering a gas as ideal. Before it can obey the gas. Law first the total volume of the individual molecules is negligible compared to the
What are the 4 variables for an ideal gas?
Pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), and temperature (T) are the four variables required to define the physical condition of a gas. The individual gas laws describe the relationship between two of the four gas law variables, given that the remaining two variables are held constant.
How do you remember the ideal gas assumptions?
Easy mnemonics for ideal gas law derivationsAvogadro's principle (n/V): Our boy Avogadro is all about moles, obviously. ... Boyle's law (PV): just think of the pressure and volume of a huge skin boil about to burst.Charles's law (V/T): Think of Mike Teavee from Charlie and the Chocolate factory.More items...•
Which of the following assumptions is not valid for an ideal gas?
Correct answer: The assumption that the molecules obey Coulomb's law when interacting with each other is not necessary; rather, an ideal gas must disregard Coulomb's law.
What are the assumptions of the kinetic theory quizlet?
Terms in this set (26) Explains how particles in matter behave by making three assumptions: 1) All matter is made of small particles. 2) These particles are in constant, random motion. 3) These particles are colliding with each other and the walls of their container.
What are the main assumptions of kinetic molecular theory quizlet?
Terms in this set (3)Number One. All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in constant motion.Number Two. The speed of the particles' motion depends upon the temperature.Number Three. The total amount of kinetic energy of the colliding particles remains constant.
What is the first assumption of the kinetic theory of matter?
The first assumption in this theory is that matter consists of a large number a very small particles—either individual atoms or molecules. All matter (solid, liquid, and gas) is made up of tiny particles called atoms, or atoms that are joined to form molecules.
What is the 5th matter?
Sometimes referred to as the 'fifth state of matter', a Bose-Einstein Condensate is a state of matter created when particles, called bosons, are cooled to near absolute zero (-273.15 degrees Celsius, or -460 degrees Fahrenheit).