Types of tonsils
- Palatine tonsils. These are located between the palatoglossal arch anteriorly and the palatopharyngeal arch posteriorly.
- Lingual tonsils. These are small round elevations that sit on the most posterior part of the tongue base. ...
- Tubal tonsils. ...
- Pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids. ...
- Palatine tonsils.
- Lingual tonsils.
- Tubal tonsils.
- Pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids.
Where are the 5 tonsils located?
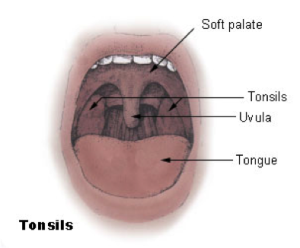
The tonsils (palatine tonsils) are a pair of soft tissue masses located at the rear of the throat (pharynx). Each tonsil is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes, covered by pink mucosa (like on the adjacent mouth lining).
How many types of tonsils are there?
four different typesThere are four different types of tonsils: palatine, pharyngeal (commonly referred to as the adenoid), lingual and tubal. Together these four types of tonsils make up what is called Waldeyer's ring.
What are 4+ tonsils?
Tonsils are graded on a scale from 0 to 4. Zero means you've had them removed, 1 means they're barely visible, 2 means they're normal, 3 means they're large and just about touching that thing that hangs down at the back of your throat called the uvula, and 4 means they're ginormous.
How many tonsils are in the human body?
Technically, there are three sets of tonsils in the body: the pharyngeal tonsils, commonly known as adenoids, the palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils, which are lymphatic tissue on the surface tissue of the base of the tongue, according to Encyclopedia Britannica.
Which tonsils are removed?
The palatine tonsils are removed in a tonsillectomy. Palatine tonsils are collections of lymph tissue on the right and left side of the upper throat (also called the oropharynx). Tonsils are largest in 3-6 year olds and smallest in teen and adult years. Tonsils are part of body's immune system.
What are the 3 types of tonsils?
Anatomy of Tonsils There are three sets of tonsils in the back of the mouth: the adenoids, the palantine, and the lingual tonsils. 1 These tonsils are made up of lymphatic tissue and are typically small in size.
What is the third tonsil called?
the adenoidIt is located in an area called the nasopharynx, and if it is large enough, it can block air from flowing through the nose. The easiest way to understand the adenoid is just to think of it as a third tonsil.
Why have tonsils removed?
Inflamed tonsils A tonsillectomy was once a common procedure to treat infection and inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis). Today, a tonsillectomy is usually performed for sleep-disordered breathing but may still be a treatment when tonsillitis occurs frequently or doesn't respond to other treatments.
How do you treat kissing tonsils?
TreatmentEncourage rest. Encourage your child to get plenty of sleep.Provide adequate fluids. ... Provide comforting foods and beverage. ... Prepare a saltwater gargle. ... Humidify the air. ... Offer lozenges. ... Avoid irritants. ... Treat pain and fever.
Can you live without tonsils?
Yes, You Can Live Without Your Adenoids & Tonsils, But Should You? When the doctor says, “Open up your mouth and say 'ahhhh,'” he may be looking for signs of inflammation of your tonsils - those lumps of tissue at the back of your throat (tonsilitis). And with tonsillitis, sometimes the adenoids are also swollen.
What happens if tonsils are removed?
After tonsillectomy, you can still get colds, sore throats, and throat infections. But you won't get tonsillitis unless the tonsils grow back, which is uncommon. Even though the tonsils are part of the immune system, removing them doesn't affect your body's ability to fight infections.
Can your tonsils grow back?
Is it possible that her tonsils are growing back? It is possible for tonsils to partially grow back. During a tonsillectomy, most of the tonsils are removed. However, some tissue often remains, so tonsils occasionally can regenerate (regrow) — although they probably won't grow back completely or to their original size.
What do normal tonsils look like?
Healthy, normal tonsils are pinkish in color. But your tonsils can appear red and swollen if they're inflamed or infected.
Do you have 4 tonsils?
There are two of them, one on each side. Along with the adenoids, tonsils are part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system clears away infection and keeps body fluids in balance. Tonsils and adenoids work by trapping the germs coming in through the mouth and nose.
Can you live without tonsils?
Yes, You Can Live Without Your Adenoids & Tonsils, But Should You? When the doctor says, “Open up your mouth and say 'ahhhh,'” he may be looking for signs of inflammation of your tonsils - those lumps of tissue at the back of your throat (tonsilitis). And with tonsillitis, sometimes the adenoids are also swollen.
What causes swollen tonsil?
Tonsillitis is most often caused by common viruses, but bacterial infections also can be the cause. The most common bacterium causing tonsillitis is Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus), the bacterium that causes strep throat. Other strains of strep and other bacteria also may cause tonsillitis.
How many tonsils are there in the human body?
There are four types of tonsils in humans; palatine, pharyngeal, lingual and tubal. To quickly remember this, you can use the following mnemonic: " PPL have T onsils", standing for P alatine, P haryngeal, L ingual, T ubal.
Where are tonsils found?
The tonsils are part of MALT ( mucosa associated lymphoid tissue ). MALT can also be found in the bowel, in Peyer’s patches. In general MALT is relatively undeveloped at birth with low cellularity. Tonsils start to develop around 14-15th week of embryonic life, while germinal cenres are absent at this stage. Palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa are believed to be the derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal pouch. The epithelial lining proliferates and forms buds, which form the primordium of the palatine tonsil.
What is the germinal center of a tonsil?
In addition, the center of each of these nodules is densely packed with lymphocytes , and is referred to as the germinal center. The tonsillar crypts (except the pharyngeal tonsil) will penetrate from the surface, almost down to the very center of the tonsil follicle. The luminal surfaces of the tonsils are coated in non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium, which is the same tissue of the surrounding oropharynx.
What is Waldeyer's ring of lymphoid tissue?
Four types of tonsils are arranged into a ring around the pharynx ( oropharynx and nasopharynx ), known as Waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue. This article will look at the anatomy of the tonsils including the blood supply and innervation, as well as some histological anatomy and embryological development.
What is the role of tonsils in the immune system?
They act as the first line of defense against ingested or inhaled pathogens. Four types of tonsils are arranged into a ring around the pharynx ( oropharynx and nasopharynx ), known as Waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue.
How many crypts are in the tonsil?
The tonsil is penetrated by 15-20 crypts. The lumen of the crypts contain lymphocytes, bacteria and desquamated epithelial cells. The palatine tonsils receive their blood supply from the tonsillar branches of five arteries: Ascending palatine branch of the facial artery. Tonsillar branch of the facial artery.
What is the palatine tonsil?
Palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa are believed to be the derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal pouch. The epithelial lining proliferates and forms buds, which form the primordium of the palatine tonsil.
Where are tonsils located in the throat?
The tonsils are in the back of the throat. Strep throat and tonsillitis can lead to inflammation. (Image credit: solar22/Shutterstock)
What are tonsils called?
Technically, there are three sets of tonsils in the body: the pharyngeal tonsils, commonly known as adenoids, the palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils, which are lymphatic tissue on the surface tissue of the base of the tongue, according to Encyclopedia Britannica. When people refer to tonsils, though, they are usually talking about the palatine tonsils. These tonsils are oval, pea-sized clusters of lymph cells in the pharynx at the opening of either side of the throat. Though they may seem large in children, the size of the tonsils tends to get smaller when a person becomes an adult.
What is strep throat?
Strep throat happens when the tonsils are infected by bacteria called Streptococcus, usually class ified by two different strains, A and B. Strep is usually a problem that affects children, though adults can get strep throat, too.
What is the best medicine for tonsil stones?
Typically, doctors will prescribe antibiotics, such as Augmentin, to rid the body of the bacteria. Tonsil stones are a typical affliction of the throat area, as well. This happens when debris gets caught in the groves of the tonsils. Then, white blood cells attack the debris, creating a rock-like stone.
What are the bumps on the back of the throat?
On top of all that, they produce white blood cells and antibodies, according to the Mayo Clinic . According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology, these bumps on the back of the throat are the "first line of defense as part of the immune system.".
How to treat strep?
The treatment for strep is fairly simple. Typically, doctors will prescribe antibiotics, such as Augmentin, to rid the body of the bacteria.
Is the tonsil a useless organ?
Tonsils were once thought to be a useless part made obsolete by evolution . When bothered by an infection, doctors once prescribed the removal of the tonsils through a tonsillectomy. These small organs are actually quite useful, though.
How many tonsils are there in the human body?
Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
What is the function of tonsils?
The tonsils are immunocompetent organs which serve as the immune system's first line of defense against ingested or inhaled foreign pathogens, and as such frequently engorge with blood to assist in immune responses to common illnesses such as the common cold.
What is the Waldeyer's tonsilar ring?
FMA. 9609. Anatomical terminology. The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.
What is the best treatment for tonsillitis?
The most common way to treat tonsillitis is with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, or if bacterial in origin, antibiotics, e.g. amoxicillin and azithromycin. Surgical removal ( tonsillectomy) may be advised if the tonsils obstruct the airway or interfere with swallowing, or in patients with severe or recurrent tonsillitis. However, different mechanisms of pathogenesis for these two subtypes of tonsillar hypertrophy have been described, and may have different responses to identical therapeutic efforts. In older patients, asymmetric tonsils (also known as asymmetric tonsil hypertrophy) may be an indicator of virally infected tonsils, or tumors such as lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma .
How big is a palatine tonsil?
In adults, each palatine tonsil normally measures up to 2.5 cm in length, 2.0 cm in width and 1.2 cm in thickness. The adenoid grows until the age of 5, starts to shrink at the age of 7 and becomes very small in adulthood.
What is the substance that accumulates on the palatine tonsil?
A tonsillolith (also known as a “tonsil stone”) is material that accumulates on the palatine tonsil. This can reach the size of a peppercorn and is white or cream in color. The main substance is mostly calcium, but it has a strong unpleasant odor because of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan and other chemicals.
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
When used unqualified, the term most commonly refers specifically to the palatine tonsils, which are two lymphoid organs situated at either side of the back of the human throat. The palatine tonsils and the adenoid tonsil are organs consisting of lymphoepithelial tissue located near the oropharynx and nasopharynx (parts of the throat).
What is the bacterium that infects the tonsils and throat?
Strep throat: Streptococcus , a bacterium, infects the tonsils and throat. Fever and neck pain often accompany the sore throat.
How are tonsil stones formed?
Tonsilloliths ( tonsil stones ): Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are formed when trapped debris hardens, or calcifies.
What is the pink mucosa on the tonsils?
Running through the mucosa of each tonsil are pits, called crypts. The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system, which helps to fight infections.
What is the procedure for a peritonsillar abscess?
Abscess drainage: A peritonsillar abscess generally must be punctured with a needle, to allow the infection to drain and heal.
What causes a swollen tonsil?
Peritonsillar abscesses must be drained urgently. Acute mononucleosis: Usually caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, “mono” causes severe swelling in the tonsils, fever, sore throat, rash, and fatigue.
What causes a sore throat and a sore throat?
Acute tonsillitis: A bacteria or virus infects the tonsils, causing swelling and a sore throat. The tonsil may develop a gray or white coating (exudate).
What is the role of tonsils in the body?
The tonsils play a role in protecting the body against respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. Each tonsil consists of a network of crypts (pits) that store cells used to fight infection. The tonsils contain B cells, a type of white blood cell that fights infections.
What are the antibodies in the tonsils?
They also produce antibodies against polio, streptococcal pneumonia, influenza, and numerous other infections. Antibodies are proteins that help the body identify and attack harmful invaders. The tonsils also contain several types of T cells, which are white blood cells that destroy cells infected with viruses and help the body build immunity ...
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
Palatine tonsil. The palatine tonsils are located at the back of the throat. One tonsil is located on the left side of the throat and the other is located on the right side. The tonsils play a role in protecting the body against respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. Each tonsil consists of a network of crypts (pits) ...
What is the lingual tonsil covered by?
Like the rest of the tongue, the lingual tonsil is covered by a stratified non-keratinised squamous epithelium.
Which surface of the tonsil is covered by a fibrous capsule?
Each tonsil has free medial surface which projects into the pharynx. The lateral surface is covered by a fibrous capsule, and is separated from the superior constrictor of the tonsillar bed by loose areolar connective tissue.
How to treat tonsillitis?
A complication of bacterial tonsillitis is a peritonsillar abscess (quinsy); a collection pus in the peritonsillar space. All quinsies will require drainage. There are two techniques adopted for this: 1 Needle aspiration following topical local anaesthetic. 2 Incision and drainage, with further opening via use of Magill forceps.
What is the role of palatine tonsils?
They have an important role in fighting infection – the first line of defence against pathogens entering through the nasopharynx or oropharynx.
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
The palatine tonsils are commonly referred to as ‘ the tonsils ‘. They are located within the tonsillar bed of the lateral oropharynx wall – between the palatoglossal arch ( anteriorly) and palatopharyngeal arch (posteriorly). They form the lateral part of the Waldeyer’s ring. Each tonsil has free medial surface which projects into the pharynx.
Which nerves are involved in the pharyngeal tonsil?
The pharyngeal tonsil receives nerve fibres from the vagus and glossopharyngeal cranial nerves.
Which tonsil receives arterial supply from several vessels?
The pharyngeal tonsil receives arterial supply from several vessels:
What are the tonsils in the throat?
In the back of the throat, there is a lymphoid group of tissues known as the tonsils. In the throat, there are four groups of tonsillar tissues, including palatine, lingual, adenoid, and nasopharyngeal. Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa ...
Where are the tonsils located?
Adenoid and nasopharyngeal tonsils - they are located at the back of the nose. They are partially surrounded by the Eustachian tubes. They can cause conditions such as difficulty in nasal breathing, ear infections, and sinusitis.
What is the pink mucosa of the tonsils?
Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa of each tonsil are called crypts. Tonsils help to fight infections and are a part of the lymphatic system. Removal of tonsils does not seem to increase the chances of infections.
Why is it important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading?
In clinical settings, it is important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading, as well as perform reliable monitoring. The grading scale of tonsils helps the clinicians to record the change in the tonsil size and communicate accordingly.
Why is tonsil grading important?
In clinical settings, it is important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading, as well as perform reliable monitoring. The grading scale of tonsils helps the clinicians to record the change in the tonsil size and communicate accordingly. Various grading systems may provide results that may be interpreted differently by the users. This makes the assessment of tonsil size by using tonsil grading system unreliable. Due to the variability in tonsil grading systems, there can be confusion in communicating the tonsil size. Hence, it is necessary to compare the existing tonsillar grading scales and to check the reliability and reproducibility. However, the reliability of this needs to be studied. Due to recurrent infection or as a part of generalized lymphoid hypertrophy, tonsils undergo hypertrophy. There is a good correlation between clinical tonsil grade and tonsil volume in snorers and obstructive sleep apnea.
What is the BMI of a person with a palate position of 3 and 4?
If the palate position is 3 and 4, then the tonsil size is 3 or 4. The BMI of the person is less than 40 kg/ m 2. Stage III: defined by palate position of 3 or 4 and the tonsil score is 0, 1, or 2. BMI of the person is more than 40 kg/ m 2. Brodsky developed a grading system.
How to check airway muscle tone in children?
To check the airway muscle tone in children, clinicians look for the symptoms, such as snoring, daytime fatigue, and trouble in concentrating. This is to rule out obstructive sleep apnea. Enlarged tonsils can limit the airflow. In the etiology of obstructive sleep apnea, this can be a significant risk factor.
How much of the oropharynx is the tonsil?
This is the normal size of the tonsils. In this size, the tonsils extend to the pillars. Tonsils occupy less than 25 percent of the oropharynx. The tonsils are not visible properly.
What is Tonsil Grading?
The tonsil grading is a scale that ENT doctors rely upon to check the change in the tonsil size. It is used to determine the size of the tonsils as well as grade the tonsils and monitor the sizes regularly to document any changes.
Why do tonsils increase in size?
Why the Tonsils Increase in Size? According to Dr. Siddhartha Vashishta, ENT doctor from Pristyn Care, “The tonsils inflame when there is an infection in the throat. The common causes of a throat infection are influenza viruses and bacteria.”.
Why do doctors take tonsils out?
When the doctors recommend taking out the tonsils due to the several complications it causes , the doctors use this grading to decide upon the best technique for curing the obstructive sleep apnea. According to the Friedman grading system, there are four grades of the palates decided on the basis of the appearance.
Why is my tonsil size 3 and 4 so enlarged?
The main reason being that there is an infection that requires immediate medical attention.
What scale is used to grade tonsillitis?
There is another grading scale that ENT specialists use when tonsillitis causes complications such as obstructive sleep apnea. The Friedman grading is a palate grading that is used to inspect the size of the upper airway.
Why do doctors monitor tonsils?
Hence, doctors continuously monitor the tonsils of the children to check if their sizes have changed due to any cause. Also, they use a grading system to rule out the possibility of any other problem in the throat that is stagnating their growth.

Overview
Structure
Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
The palatine tonsils tend to reach their largest size in puberty, and they gradually undergo atrophy thereafter. However, they are largest relative to the diameter of the throat in young children. In adults, each palatine tonsil normally measures up to 2.5 cm in length, 2.0 cm in width and 1.2 c…
Function
The tonsils are immunocompetent organs which serve as the immune system's first line of defense against ingested or inhaled foreign pathogens, and as such frequently engorge with blood to assist in immune responses to common illnesses such as the common cold. The tonsils have on their surface specialized antigen capture cells called Microfold cell (M cells) that allow for the uptake of antigens produced by pathogens. These M cells then alert the B cells and T cells in th…
Clinical significance
The palatine tonsils can become enlarged (adenotonsillar hyperplasia) or inflamed (tonsillitis). The most common way to treat tonsillitis is with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, or if bacterial in origin, antibiotics, e.g. amoxicillin and azithromycin. Surgical removal (tonsillectomy) may be advised if the tonsils obstruct the airway or interfere with swallowing, or in patients with severe or recurrent tonsillitis. However, different mechanisms of pathogenesis for these two sub…
Additional images
• Illustration of frontal view of tonsils
External links
• Media related to Tonsils at Wikimedia Commons