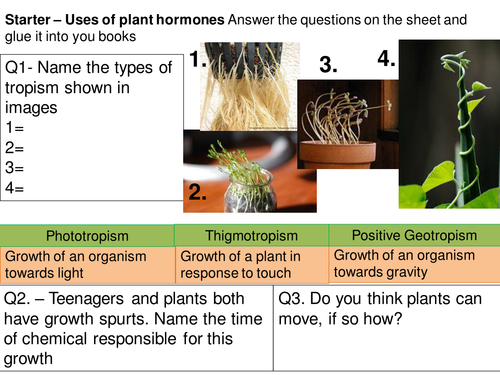
What Are The 5 Tropisms And The Plant's Response To Each?
- Phototropism This plant tropism controls the growth of the plant in response to a light source. This plant tropism controls the growth of the plant in response to a light source. ...
- Thigmotropism Tendrils help the plant to climb a support. ...
- Gravitropism Positive and negative geotropism. ...
- Hydrotropism Plants need to control their geotropic tendencies first before they can perform hydrotropism. ...
- Thermotropism ...
What are the 4 tropisms of a plant?
Thermotropism. What are the 4 tropisms in a plant called? Common tropic responses in plants include phototropism, gravitropism, thigmotropism, hydrotropism, thermotropism, and chemotropism. Phototropism. Plant hormones direct plant body development in response to a stimulus, like light. …
What are the different types of tropic responses?
1 Phototropism, thigmotropism, gravitropism, hydrotropism, and thermotropism are common tropic responses in plants. 2 Plants are different than humans and animals in the way they adapt to their environment; they are sessile. 3 Positive tropism is growth in the direction of the stimuli, while negative tropism is the growth opposite from the stimuli.
What is positive tropism and negative tropism?
If a plant grows in the direction of the stimuli (gravity, for example), that is known as a positive tropism, and negative tropism is the growth opposite from the stimuli. This plant tropism controls the growth of the plant in response to a light source.
How does tropism affect plant growth?
Plant hormones, like auxins, are thought to help regulate the differential growth of a plant organ, causing the plant to curve or bend in response to a stimulus. Growth in the direction of a stimulus is known as positive tropism, while growth away from a stimulus is known as a negative tropism.

1. What is Tropism?
Tropism is the natural ability of an organism to transform or change in response to a stimulus. Natural responses are genetically programmed rather...
2. What are the Types of Tropism?
There are different types of tropism, they are:Phototropism is nothing but the growth and development of plants in response to light.Gravitropism i...
3. What is Gravitropism?
In response to gravity, certain plants show some growth and development, this type of tropism in plants with respect to gravity is called Gravitrop...
4. Explain Hydrotropism and Thermotropism.
Hydrotropism: In relation to the stimulus of water, the movement or the growth of a plant is called hydrotropic movement. This is also called hydro...
5. Explain Chemotropism and Thigmotropism?
Chemotropism: The chemical substances in a plant are responsible for bringing a curvature movement in plant organs. When plants start to grow in re...
6. What is Meant by Tropism? Define Tropism.
Tropism is a biological process in which a biological organism, normally a plant, grows or turns in response to an environmental stimulus. This res...
7. Name any Two Types of Tropism.
Phototropism (response to light), geotropism (response to gravity), chemotropism (response to specific substances), hydrotropism (response to water...
How do tropisms work?
The idea of a tropism was first established in botany, as it was seen that plants would move in response to different stimuli. Scientists notice that no matter how you plant a seed, the roots always establish themselves toward gravity, known as geotropism. The roots are also inherently attracted to water, and will move and turn toward the most water. This hydrotropism is obviously beneficial to plants. In studying this phenomena, scientist found that plants have another tropism. When the water is oxygen deprive, the roots will seek oxygen as well. This is known as aerotropism, and the stimulus is oxygen. As seen by these plant examples, a tropism often has a deep evolutionary base, and is filling an essential need of the organism.
What is a stimulus?
A stimulus can be any signal from the environment, and individual tropisms are often named after the stimulus that causes the movement. In a positive tropism the animal will move toward the stimulus. In a negative tropism, the animal will move away from the tropism. Certain stimuli become genetically engrained because they are always beneficial ...
How do organisms move towards the light?
Therefore, sunlight has evolved as a stimulus for many organisms. Many of these organisms move towards the light. This positive phototropism causes organisms to move toward the light. Many algae, plankton, and small invertebrates exhibit positive phototaxis. This brings them to the same area in the ocean, which contains by far the most light. Even organisms that are not photosynthetic have developed this tropism, which moves them to the same water column as their prey items. Other organisms may exhibit a negative reaction to light, and try to move away from it. Think of a beetle when you uncover it from its hiding place. The beetle will seek darkness, as darkness usually means safety. This tropism has the same stimulus but the opposite direction of the tropism in plants.
What is the term for the tendency to turn or move towards or away from a specific chemical substance?
Chemotropism . A widely spread tropism in the animal kingdom is chemotropism, or the tendency to turn or move towards or away from a specific chemical substance. Some single-celled organisms use different chemotropisms for different purposes.
What is tropism in biology?
Tropism Definition. A tropism is the innate ability of an organism to turn or move in response to a stimulus. As opposed to a learned ability, innate reactions are genetically programmed. Organisms with a tropism will naturally turn toward a stimulus.
What happens if an animal reproduces asexually and cannot move once created?
B is correct. If an animal reproduces asexually and cannot move once created, the animal never displays a taxis towards the stimulus. Although it may exist, it cannot be seen in any of the organism’s behaviors. These animals do not display a tropism toward the center of the colony, they just happen to reproduce in that form. Some larval forms of coral are attracted by tropisms to various spots on the sea floor, which they can settle and form a new colony. However, once the spot is picked, the same tropisms do not drive the actions of the resulting colony of individuals.
Why do fish have negative thigmotaxis?
This helps them both avoid predators and maintain their order in a large school. Another tropism seen in fish is chemotropism. Fish are both drawn to and avoid a variety of different chemicals.
What is tropism in animals?
Chemotropism: Chemotropism, or the inclination to transform or shift towards or away from a particular chemical element, is a common tropism in the animal kingdom. Chemo Tropisms are used by certain single-celled species for a variety of purposes. For example, one chemical may indicate the presence of a partner, while another may indicate the presence of a dangerous or unpleasant environment. These simple organisms would simply shift towards or away from stimuli in the direction that their forefathers found to be most evolutionary rewarding. Certain chemicals also attract animals in higher species, but they may not always travel towards it. To put it another way, although they have tropism, they do not always show taxis. Sharks, for example, have a positive chemotropism for blood, which means they gravitate toward it. A shark, on the other hand, would often examine or test a meal before devouring it, demonstrating that other processes can override a tropism.
What is the term for a virus that preferentially targets a particular host?
Tropism meaning in viruses- Viruses and other pathogens may also cause what is known as "host tropism," "tissue tropism," or "cell tropism," which refers to how various viruses/pathogens have evolved to preferentially target particular host organisms, tissues, or cell types inside those species. Tropisms are named for the stimulus they are reacting to (for example, a phototropism is a reaction to sunlight) and may be positive (towards the stimulus) or negative (against the stimulus) (away from the stimulus).
What is the term for the movement of an animal after a stimulus?
Innate responses, unlike acquired abilities, are genetically programmed. Tropism causes organisms to spontaneously gravitate toward a stimulus. Individual tropisms are also called after the stimulus that triggers the movement, which can be any signal from the setting. The animal would shift toward stimulation in an optimistic tropism.
How do animals use sunlight?
Phototropism: Many photosynthetic animals use sunlight to grow their food. As a result, many species have evolved to use sunlight as a stimulus. Many of these species are attempting to reach the sun. Organisms shift into the light due to positive phototropism. Positive phototaxis is seen in many algae, plankton, and small invertebrates. This takes them to the same spot in the ocean, which has the most light by far. Even non-photosynthetic species have established this tropism, which draws them into the same water column as their prey. Other species can have a negative reaction to light and attempt to avoid it. When you uncover a beetle from its hiding spot, think of it as a beetle. Since darkness is generally associated with defence, the beetle will seek it out. This tropism has the same stimulus as plant tropism, but it works in the opposite direction.
What is tropism in biology?
Define Tropism. Ans. Tropism is a biological process in which a biological organism, normally a plant, grows or turns in response to an environmental stimulus. This response is influenced by the stimulus's direction in tropisms (as opposed to nastic movements which are non-directional responses).
What is the movement or development of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus?
Chemotropism is the movement or development of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus.
What is the movement of an object in response to an electric field?
Exotropism is the continuation of development "outward," i.e. in the same direction as before. Geotropism (also known as gravitropism) is the movement or development of an object in response to gravity.
How do plants exhibit hydrotropism?
Studies conducted on the interaction between gravitropism and hydrotropism in plants indicate that exposure to a water gradient or lack of water can induce roots to exhibit hydrotropism over gravitropism. Under these conditions, amyloplasts in root statocytes decrease in number. Fewer amyloplasts means that the roots are not as influenced by amyloplast sedimentation. Amyloplast reduction in root caps helps to enable roots to overcome the pull of gravity and move in response to moisture. Roots in well-hydrated soil have more amyloplasts in their root caps and have a much greater response to gravity than to water.
How do plants adapt to environmental conditions?
Plants, like animals and other organisms, must adapt to their constantly-changing environments. While animals are able to relocate from one place to another when environmental conditions become unfavorable, plants are unable to do the same. Being sessile (unable to move), plants must find other ways of handling unfavorable environmental conditions. Plant tropisms are mechanisms by which plants adapt to environmental changes. A tropism is a growth toward or away from a stimulus. Common stimuli that influence plant growth include light, gravity, water, and touch. Plant tropisms differ from other stimulus generated movements, such as nastic movements, in that the direction of the response depends on the direction of the stimulus. Nastic movements, such as leaf movement in carnivorous plants, are initiated by a stimulus, but the direction of the stimulus is not a factor in the response.
Why is hydrotropism important for plants?
Hydrotropism is directional growth in response to water concentrations. This tropism is important in plants for protection against drought conditions through positive hydrotropism and against water over-saturation through negative hydrotropism. It is especially important for plants in arid biomes to be able to respond to water concentrations. Moisture gradients are sensed in plant roots. The cells on the side of the root closest to the water source experience slower growth than those on the opposite side. The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays an important role in inducing differential growth in the root elongation zone. This differential growth causes roots to grow toward the direction of water.
What is tendril coiling?
Tendril coiling is a result of differential growth as cells not in contact with the stimulus elongate faster than the cells that make contact with the stimulus. As with phototropism, auxins are involved in the differential growth of tendrils. A greater concentration of the hormone accumulates on the side of the tendril not in contact with the object. The twining of the tendril secures the plant to the object providing support for the plant. The activity of climbing plants provides better light exposure for photosynthesis and also increases the visibility of their flowers to pollinators .
What is a thigmotropism?
Positive thigmostropism is demonstrated by climbing plants or vines, which have specialized structures called tendrils. A tendril is a thread-like appendage used for twinning around solid structures. A modified plant leaf, stem, or petiole may be a tendril. When a tendril grows, it does so in a revolving pattern. The tip bends in various directions forming spirals and irregular circles. The motion of the growing tendril almost appears as if the plant is searching for contact. When the tendril makes contact with an object, sensory epidermal cells on the surface of the tendril are stimulated. These cells signal the tendril to coil around the object.
What is tropism in plants?
A tropism is a growth toward or away from a stimulus. Common stimuli that influence plant growth include light, gravity, water, and touch. Plant tropisms differ from other stimulus generated movements, such as nastic movements, in that the direction of the response depends on the direction of the stimulus.
Why is gravitropism important?
Gravitropism is very important in plants as it directs root growth toward the pull of gravity (positive gravitropism) and stem growth in the opposite direction (nega tive gravitropism). The orientation of a plant's root and shoot system to gravity can be observed in the stages of germination in a seedling.

Tropism Definition
- A tropism is the innate ability of an organism to turn or move in response to a stimulus. As opposed to a learned ability, innate reactions are genetically programmed. Organisms with a tropism will naturally turn toward a stimulus. A stimulus can be any signal from the environment, and individual tropisms are often named after the stimulus that cau...
Types of Tropism
- Phototropism
Many photosynthetic animals produce their food from sunlight. Therefore, sunlight has evolved as a stimulus for many organisms. Many of these organisms move towards the light. This positive phototropism causes organisms to move toward the light. Many algae, plankton, and small inver… - Heliotropism
A similar phenomena occurs in land plants. Terrestrial plants are restricted in their movements, due to their roots. Instead, plants orient their leaves toward the sun, to collect the most sunlight. This tropism is similar to phototropism, but the position of organism cannot change. Instead, the …
Examples of Tropism
- Fish
Fish exhibit many tropisms, and respond to a wide variety of stimuli. Fish usually display negative thigmotaxis, or move away from any stimulus touching them. This helps them both avoid predators and maintain their order in a large school. Another tropism seen in fish is chemotropis… - Plants in a Lab
The idea of a tropism was first established in botany, as it was seen that plants would move in response to different stimuli. Scientists notice that no matter how you plant a seed, the roots always establish themselves toward gravity, known as geotropism. The roots are also inherentl…
Related Biology Term
- Taxis– The movement of an organism caused by a tropism.
- Nastic Movements– Movements of an organisms that respond to the presence of a stimulus, but not its direction.
- Turgor Pressure– The pressure inside the vacuole of plant cells, which can be controlled to move the leaves and stems of plants.
Quiz
- 1. Some animals accumulate in a certain spot because they reproduce asexually and do not move far from each other. This can be seen in coral colonies and bacteria. Is this an example of a tropism towards the spot of the original organism? A. Yes B. No C.Only if the original organism was attracted there by a tropism 2. A certain zooplankton species is a small, multi-celled organis…