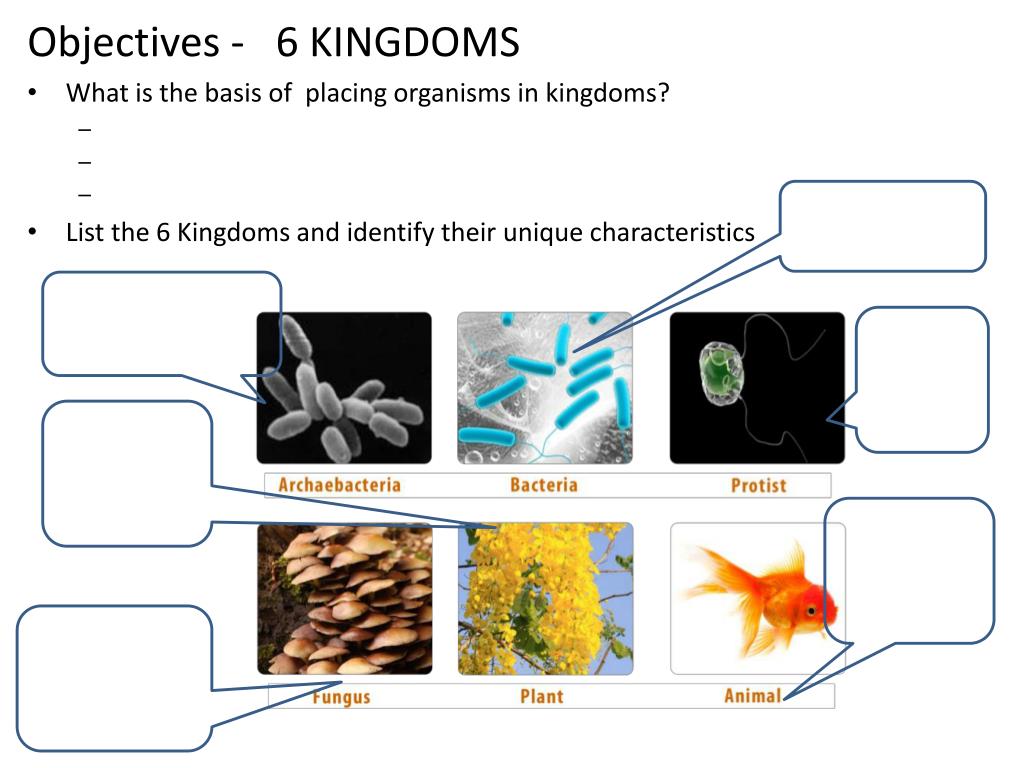
What are the 6 kingdoms of life
Kingdom
In biology, kingdom regna) is the second highest taxonomic rank below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla. Traditionally, textbooks from the United States used a system of six kingdoms while textbooks in Great Britain, India, Australia, Latin America and other countries used five kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera).
Archaea
Archaea constitute a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms are prokaryotes, and have no cell nucleus. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria, but this classification is outmoded.
Bacteria
Bacteria are a type of biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, an…
...
-Budget Travel.
| 5 KINGDOMS | MONERA |
|---|---|
| 6 KINGDOMS | EUBACTERIA |
| ORGANIZATION | Prokaryotic, unicellular organisms |
| TYPES OF ORGANISMS | unicellular and colonial--including the true bacteria (eubacteria) |
| REPRODUCTION | asexual reproduction -- binary fission |
What are the differences among the five kingdoms of life?
- Domain: Bacteria
- Organisms: Bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), and actinobacteria
- Cell Type: Prokaryotic
- Metabolism: Depending on species, oxygen may be toxic, tolerated, or needed for metabolism
- Nutrition Acquisition: Depending on species, nutrition intake may occur through absorption, photosynthesis, or chemosynthesis
- Reproduction: Asexual
What are the 5 kingdoms of nature?
What are the organisms of each kingdom like?
- Animal kingdom. What is the shape of the animal kingdom? ...
- Plant kingdom. The second of nature’s kingdoms, the plant kingdom (also called the plant kingdom), is made up of organisms that exhibit the following characteristics: multicellular, autotrophic, eukaryotic, immobile, ...
- Mushroom kingdom. ...
- Protist Kingdoms. ...
- Kingdom of Monera. ...
What are the four eukaryotic kingdoms?
What are 5 types of cells?
- Stem cells. Stem cells are cells that are yet to choose what they are going to become. …
- Bone cells. There are at least three primary types of bone cell:
- Blood cells. There are three major types of blood cell:
- Muscle cells. …
- Sperm cells. …
- Female egg cell. …
- Fat cells. …
- Nerve cells.
What are the 6 kingdoms of living things?
Guide to the Six Kingdoms of Life
- Archaebacteria. Archaebacteria are single-celled prokaryotes originally thought to be bacteria. ...
- Eubacteria. These organisms are considered to be true bacteria and are classified under the Bacteria domain. ...
- Protista. The protista kingdom includes a very diverse group of organisms. ...
- Fungi. ...
- Plantae. ...
- Animalia. ...

What are the 6 kingdoms of life in order?
Every living thing comes under one of these 6 kingdoms. The six kingdoms are Eubacteria, Archae, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
What are the six kingdoms of life and some of their characteristics?
The six kingdoms are:Animal, Plant, Protist, Fungi, Bacteria, Archaea . Bacteria is both a domain and a kingdom. Archaea is also both a domain and a kingdom. Within the Eukarya domain, there are four more kingdoms: Animal, Plant, Fungi, and Protist.
What are the 6 kingdoms of life most to least complex?
The Kingdoms of Life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows:Archaebacteria.Eubacteria.Protista.Fungi.Plants.Animals.
What are the characteristics of each kingdom?
What are the major characteristics of each kingdom of living organisms?KingdomCell TypeCharacteristicsPlantaeEukaryoticSingle-celled or multicellular, capable of photosynthesisAnimaliaEukaryoticMulticellular organisms, many with complex organ systems3 more rows
What are the six kingdoms of life quizlet?
The six categories are: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
What are the 6 kingdoms and their domains?
In this system, living organisms are divided into three domains, each of which has six kingdoms. Three Domains consist of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya and six Kingdoms consist of Eubacteria (true bacteria), Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria), Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
What defines each kingdom of life?
It is based mainly upon differences in nutrition; his Plantae were mostly multicellular autotrophs, his Animalia multicellular heterotrophs, and his Fungi multicellular saprotrophs. The remaining two kingdoms, Protista and Monera, included unicellular and simple cellular colonies.
How do you remember the six kingdoms?
To easily remember the levels of taxonomic classification, remember this: Dead King Philip Cried Out For Goodness Sake. Since you already know the three big groups of organisms—Domain Archaea, Domain Bacteria and Domain Eukarya, let's now proceed to the kingdoms under these domains.
What are the kingdoms of life?
6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: 1. Archaebacteria. 2. Eubacteria. 3. Protista. 4. Fungi.
Which kingdom is a fungus?
4. Fungi Kingdom. ➤ Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that are classified in their kingdom. ➤ They may be unicellular (yeast and molds) and multicellular (mushrooms) organisms. ➤ Fungi do not contain chlorophyll like plants. Hence, they are not capable of photosynthesis.
What kingdom is strep throat in?
Eubacteria Kingdom. ➤ This kingdom makes up most of the bacteria in the world. ➤ They are found everywhere, such as in soil, water, and other living things. ➤ They are very common to humans as parasites like Streptococci, which causes strep throat.
What is the smallest unit of life?
What is a cell: The cell is the smallest unit of life. It is also known as the “building blocks of life”. The study of cells is called cell biology, cellular biology, or cytology.#N#Also Read – Plant Cell
Do organisms have multiple cells?
➤ Organisms exist as either single cells or multiple cells#N#➤ Unicellular organisms are made up of only ONE cell.#N#➤ On the other hand, Multicellular organisms consist of more than one cell.
Is moss a nonvascular plant?
Moss is an example of a nonvascular plant. ➤ The Plant kingdom is the second largest kingdom with over 25,000 known species. 6. Animals (Animalia) Kingdom. ➤ The animal kingdom is the largest kingdom with over 1 million known species. ➤ All animals are multicellular and made of Eukaryotic cells.
What kingdom are mushrooms in?
Fungi. The Fungi kingdom is recognizable to us as mushrooms, molds, mildews and yeasts. Unlike the organisms in the Archaebacteria and Eubacteria kingdoms, Fungi are multi-celled organisms. Early scientists classified mushrooms and other fungi in the Plant kingdom but they do not produce their own food as plants do.
What is a plant in the Protista kingdom?
Any microscopic organism that does not fall into the bacterial, fungi, plant or animal kingdoms is considered a part of the Protista kingdom. Plants. The Plant or Plantae kingdom encompasses all flowering plants, mosses and ferns. Plants are multi-celled, complex organisms and are considered Autotrophic.
What are living organisms classified by?
Updated March 13, 2018. By Mark Gillespie. From the tiniest bacterium to the largest blue whale, all living organisms are classified by their characteristics. The biologist Carolus Linnaeus first grouped organisms into two kingdoms, plants and animals, in the 1700s. However, advances in science such as the invention of powerful microscopes have ...
Which kingdom is the second largest?
The Plant kingdom is thought to be the second largest with over 25,000 known species. Animals. The largest kingdom of organisms is the Animal or Animalia kingdom. This kingdom is made up of complex, multi-celled organisms ranging from sea sponge colonies to elephants.
What is the oldest living organism?
Their existence was not discovered until the 1980s. However, Archaebacteria are the oldest known living organisms. They are single-celled and thrive in extremely hot boiling water found in environments like volcanic thermal vents in the ocean and hot springs like the geysers at Yellowstone Park.
How many kingdoms are there in biology?
Kingdoms in Biology. The term kingdom, when used in biological taxonomy, is a separation and categorization of different types of life. There are six kingdoms of life organized into three domains of life in U.S. textbooks. Domain. Kingdoms. Eukaryota. Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista. Archaea. Archaea.
Which kingdom includes all plants?
The kingdom Plantae includes all plants. Like all members of the kingdom Animalia, these organisms are eukaryotic and may reproduce sexually or by mitosis. If it’s alive, has more than one cell, and uses the sun for energy through photosynthesis, it belongs in the kingdom Plantae .
What kingdom is Protista?
The kingdom Protista consists of any eukaryotic organism that isn’t an animal, plant or fungus. They only reproduce asexually or via meiosis. These organisms are also autotrophs, which don’t need to feed on other forms of life for sustenance.
How many phyla are there in fungi?
Fungi in the kingdom Fungi are also eukaryotic organisms. They reproduce sexually and asexually by producing spores. There are five phyla in the kingdom Fungi, which include: Ascomycota (truffles, morels, yeasts) Basidiomycota (mushrooms, puffballs, jelly fungi) Chytridiomycota (water molds, chytrids)
What are the domains of Eukaryota?
Domain. Kingdoms. Eukaryota. Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista. Archaea. Archaea. Bacteria. Bacteria. The four kingdoms that make up the domain Eukaryota include eukaryotic organisms, or organisms that have cells with nuclei.
What is the domain of Archaea?
The domain Archaea includes the prokaryotic (or one-celled) organisms, and the entire bacterial world is found in the kingdom Bacteria, which makes up the domain Bacteria. Each kingdom is then divided into subcategories, or phyla. These kingdom examples make up a classification system for all living things on Earth.
What is the last kingdom of bacteria?
The final kingdom is the kingdom Bacteria, sometimes known as the kingdom Eubacteria. It includes all types of bacteria, which are biologically different from archaea. Bacteria are one-celled prokaryotic organisms that reproduce asexually. The kingdom includes a range of 40-100 phyla, with many more proposed phyla.
How many kingdoms are there in the Eukarya?
Bacteria is both a domain and a kingdom. Archaea is also both a domain and a kingdom. Within the Eukarya domain, there are four more kingdoms: Animal, Plant, Fungi, and Protist. Animals are multicellular organisms with eukaryotic cells.
Which kingdom has the largest number of species?
The animal kingdom is the largest, with over 1 million known species. Animals are heterotrophs, which means they must find and ingest their own food. All animals can move on their own at some point in their life cycle. Most animals reproduce by combining the DNA of two living organisms to create a new one.
What is the scientific study of how living things are grouped together, the ever-changing process of classifying life forms
For as long as humans have lived, people have tried to classify organisms, or sort them into groups, based on their similarities and differences. Taxonomy is the scientific study of how living things are grouped together, the ever-changing process of classifying life forms.
What are the living things on Earth?
The world is filled with living things of all kinds: insects, fish, humans, trees, mushrooms, and much more. The diversity of life is one reason Earth is such an interesting place!
What are the characteristics of living things?
Living Things all have these characteristics: 1 They are made of cells. 2 They respond to stimuli 3 They adapt to their environment. 4 They require, take in, and use energy. 5 They can reproduce, or have offspring 6 They grow, develop, and die. 7 They contain DNA, molecules that contain instructions for life.
Who first classified organisms?
Organisms were first classified by Aristotle, who lived in ancient Greece over 2,000 years ago. He divided all living things into two main groups: Plants and Animals. He sorted plants into smaller groups such as Small, Medium, and Large, and sorted animals into Land, Water, and Air. You can probably see that this system wasn't very useful. In such a system, birds, bats and bumblebees were grouped together, simply because they all fly.
What does "living" mean in science?
They contain DNA, molecules that contain instructions for life. In science, "living" is used to describe anything that is or has ever been alive (dog, flower, seed, log).
