4.2 Models of the atom (ESAAN)
- Dalton's model of the atom (ESAAO)
- Thomson's model of the atom (ESAAP)
- Rutherford's model of the atom (ESAAQ)
- Bohr's model of the atom (ESAAR)
- James Chadwick (ESAAS)
- Other models of the atom (ESAAT)
- John Dalton's atomic model: Dalton's Billiard Ball (Solid Sphere) Model. ...
- J.J. Thomson's model: Plum Pudding model. ...
- Ernest Rutherford's model: Nuclear model. ...
- Niels Bohr's model: Planetary model. ...
- Erwin Schrodinger's model: Electron Cloud Model/Quantum Model. ...
- Wave mechanical model.
What is the best model of an atom?
The models differ in a few ways, but importantly: [8]
- The quantum model represents the true 3D space an atom exists in, the Bohr model only represents a 2D space.
- The Bohr model was a 1D model that used one quantum number to describe the distribution of electrons in the atom. ...
- The Bohr Model treats the electron as a particle in fixed orbits around the nucleus. ...
What is the most recent accepted model of the atom?
The current model of atomic theory is called the Quantum Mechanical Model, otherwise known as the Electron Cloud Model. This current atomic model evolved from the earlier Rutherford-Bohr model, which compared electrons orbiting an atomic nucleus to planets orbiting the sun. The newest understanding of atomic makeup in the Electron Cloud Model better represents observed atomic phoneme since the ...
What best describes Rutherfords model of the atom?
Rutherford's model of the atom is also known as the planetary model because this is when he discovered the nucleus of the atom. He also discovered that the nucleus of the atom, located at the center of an atom, is only 1/3000th the size of the atom's diameter. Also, surrounding the nucleus is an electron cloud.
What are the different kinds of models of atoms?
What is the 4 types of atom?
- The Plum Pudding Model. The so-called plum pudding model was proposed by the scientist J.J. …
- Planetary Model. This theory was proposed by the Nobel Prize winning chemist Ernest Rutherford in 1911 and is sometimes called the Rutherford model. …
- Bohr Model. …
- Electron Cloud Model.

What are the 7 models of the atom?
Atomic modelsJohn Dalton's atomic model.Plum pudding model.Rutherford's model of the atom.Bohr's model of the atom.Electron Cloud Model/Quantum Mechanics Model of Atom.Basic description of the quantum mechanical atomic model:Sources:
What are the 5 models of atoms?
Different Atomic Models and Their ExplanationDalton's Model of the Atom.J.J Thomson's Model of Atom.Rutherford's Atomic Model.Neil Bohr's Theory.Different Atomic Models FAQs.
How many atom models are there?
five atomic modelsTo describe the structure of an atom, some theories were evolved. These theories are known as atomic theories or atomic models. There are five atomic models.
What are the 6 Dalton's atomic theory?
All matter consists of indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are similar in shape and mass, but differ from the atoms of other elements. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of different elements may combine with each other in a fixed, simple, whole number ratios to form compound atoms.
What are the 4 models of atoms?
Although there were many models, four main ones have led to our current concept of the atom.The Plum Pudding Model. The so-called plum pudding model was proposed by the scientist J.J. ... Planetary Model. ... Bohr Model. ... Electron Cloud Model.
What are the 3 types of atom?
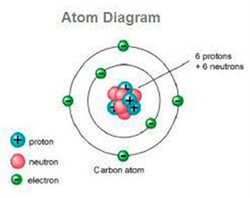
Atoms consist of three fundamental types of particles, protons, electrons and neutrons. Neutrons and protons have approximately the same mass and in contrast to this the mass of an electron is negligible. A proton carries a positive charge, a neutron has no charge and an electron is negatively charged.
What was the first model of atom?
Thomson atomic model, earliest theoretical description of the inner structure of atoms, proposed about 1900 by William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) and strongly supported by Sir Joseph John Thomson, who had discovered (1897) the electron, a negatively charged part of every atom.
What are the models of atoms in order?
A timeline of atomic modelsAtomic model (1808)Plum-pudding model (1904)Nuclear model (1911)Planetary model (1913)Quantum mechanical model (1926-present)
What is the most famous atom model?
the Bohr modelAlthough the most commonly used model of the atom is the Bohr model, scientists are still developing new and improved theories on what the atom looks like. One of the most important contributions to atomic theory (the field of science that looks at atoms) was the development of quantum theory.
What are Daltons 5 Theories?
The general tenets of this theory were as follows: All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.
What is Dalton's Atomic Theory 7?
Dalton based his theory on the law of conservation of mass and the law of constant composition. The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties.
What are the 5 major points of their atomic theory?
1) elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms. 2) these elements will be identical in size, mass and other properties. 3) atoms cannot be destroyed or created. 4) atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compound.
What are Daltons 5 theories?
The general tenets of this theory were as follows: All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.
What are the models of atoms in order?
A timeline of atomic modelsAtomic model (1808)Plum-pudding model (1904)Nuclear model (1911)Planetary model (1913)Quantum mechanical model (1926-present)
What were Daltons 5 big ideas?
Terms in this set (5) Compounds are composed of atoms of more than 1 element. The relative number of atoms of each element in a given compound is always the same. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed during chemical reactions.
What is the basic model of an atom?
The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Protons and neutrons form the atomic nucleus. Electrons are attracted to the protons in the nucleus, but are moving so quickly they fall toward it (orbit) rather than stick to protons.
How many subatomic particles are there in an atom?
Atomic Models: We very well know the fact that everything around us is made of matter. We also know that there are three subatomic particles- electrons, protons and neutrons. But where in an atom are all these subatomic particles located, and what is the structure of an atom? This article will get answers to all these questions and how various discoveries were made of Atomic Models.
What did the discovery of electrons prove?
The discovery of electrons proved for the first time that atoms themselves were made of fundamental particles, which were the constituents of all atoms and therefore, atoms did have a fine structure that was unique to every different atom.
Why is the orbital revolution of electrons around the nucleus not stable?
According to the model, the orbital revolution of electrons around the nucleus is not stable as it will undergo acceleration and emit energy which will result in the loss of energy of electrons, and they will ultimately collide with the nucleus.
What does it mean when most of the space in an atom is empty?
i. As most of the alpha particles passed through undeflected, this means that they did not come across any obstruction in their path. Thus, most of the space in an atom is expected to be empty.
What is constant in a compound?
In a given compound, the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant.
Where do electrons revolve?
The electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths.
Which particles were able to pass through the gold foil undeflected?
i. Most of the alpha particles were able to pass through the gold foil undeflected.
What is the smallest particle in an element?
An atom is the smallest particle of every element. The word atom came from the Greek word Atomos which means indivisible. Atoms are made of electrons, Protons, and Neutrons. Protons and Neutrons reside in the nucleus of the atom and electrons orbit the nucleus. Atoms always have an equal number of protons and electrons and the number of neutrons and protons is usually the same as well. Protons and Neutrons are held together in the nucleus by a strong force called Strong Nuclear force.
What is the center of an atom?
On the basis of this experiment, Rutherford stated that there is a positively charged spherical centre in an atom called the nucleus, and nearly all the mass of an atom (having a radius 10-10m) is packed in the nucleus (having a radius of 10–15 m).
What did Thomson propose?
Thomson proposed a theory according to which he defined atoms to be similar to that of a Christmas pudding.
What does Dalton say about atoms?
Dalton said that the atoms of the same element are similar in all respects and the atoms of different elements are different in all respects.
Why was Bohr's model adopted?
Later, because of a few issues like the stability of the nucleus Bo hr’s model was adopted.
Which model was the first atomic model?
Ans.3 Dalton’s Model of the Atom was the first atomic model.
Where do electrons revolve?
He stated that electrons revolve around the nucleus in a well-defined path called “orbit”.
