Common Causes
They can be caused by:
- Pneumonia
- Heart disease
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Cystic fibrosis
- COPD
- Lung infections, like bronchitis
- Asbestosis, a lung disease caused by breathing in asbestos
- Pericarditis, an infection of the sac that covers your heart
Related Conditions
listen to anterior thorax breath sounds beginning above clavicles. listen to lateral thorax breath sounds. stand behind the patient. Instruct the client to raise arms. Listen to posterior thorax breath sounds beginning the apex of lungs. compare breath sounds over the right & left sides of the posterior thorax.
What causes decreased lung sounds?
What causes abnormal breathing?
- pneumonia.
- heart failure.
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), such as emphysema.
- asthma.
- bronchitis.
- foreign body in the lungs or airways.
How do you check lung sounds?
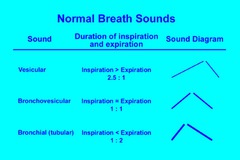
Vesicular - Normal. Vesicular breath sounds are soft and low pitched with a rustling quality during inspiration and are even softer during expiration. These are the most commonly auscultated breath sounds, normally heard over most of the lung surface. They have an inspiration/expiratory ratio of 3 to 1 or I:E of 3:1.
What are the common causes of abnormal breathing sounds?
What is the normal lung sound?

What are the 6 lung sounds?
Normal Lung SoundsBronchovesicular.Bronchial.Tracheal.Crackles.Wheezes.Rhonchi.Pleural Rub.Aortic Stenosis.More items...
What are the 3 normal lung sounds?
Normal breath sounds are classified as tracheal, bronchial, bronchovesicular, and vesicular sounds.
What lung sounds are heard with respiratory failure?
Listening to the chest with a stethoscope (auscultation) reveals abnormal breath sounds, such as crackles, which may be signs of fluid in the lungs. Often, blood pressure is low. Cyanosis (blue skin, lips, and nails caused by lack of oxygen to the tissues) is often seen.
What are the 4 types of breath sounds?
The four most common are:Rales. Small clicking, bubbling, or rattling sounds in the lungs. They are heard when a person breathes in (inhales). ... Rhonchi. Sounds that resemble snoring. ... Stridor. Wheeze-like sound heard when a person breathes. ... Wheezing. High-pitched sounds produced by narrowed airways.
What are the 4 types of normal breath sounds?
Normal breath sounds can be heard throughout the lung fields in a healthy patient and are most often classified as 1 of 4 types: vesicular, tracheal, bron- chosvesicular, and bronchial. In airfilled lungs, vesicular breath sounds are commonly heard over the majority of the lung fields.
What are the five lung sounds?
Breath soundsNormal Breath Sounds (Vesicular Sounds) The intensity and quality of breath sounds depends on the site of Auscultation. ... Bronchial Breathing. ... Soft Breath Sounds. ... Diminished or Absent Breath Sounds. ... Crackles. ... Wheezes. ... Stridor. ... Mediastinal Crunch.More items...
What lung sounds do you hear in pneumonia?
Crackling or bubbling noises (rales) made by movement of fluid in the tiny air sacs of the lung. Dull thuds heard when the chest is tapped (percussion dullness), which indicate that there is fluid in a lung or collapse of part of a lung.
What type of lung sounds are heard with COPD?
According to one 2021 study, crackling sounds are common in COPD. There are two distinct types of crackling sounds detectable in the lungs: coarse and fine. Coarse crackles are more typical of COPD and present as prolonged, low pitched sounds. Fine crackles are more high pitched.
What are normal lungs sounds called?
There are two normal breath sounds. Bronchial and vesicular . Breath sounds heard over the tracheobronchial tree are called bronchial breathing and breath sounds heard over the lung tissue are called vesicular breathing.
What are 3 types of normal breath sounds quizlet?
Terms in this set (5)Normal Breath Sounds. Vesicular, Bronchial or Tracheal, Bronchovesicular.Vesicular Breath Sounds. Soft, low-pitched fine rustling sounds. ... Bronchial or Tracheal Breath Sounds. Loud, high-pitched tubular sounds. ... Bronchovesicular Breath Sounds. Moderately pitched. ... Inaudible Breath Sounds.
What should normal lungs sound like?
Bronchial lung sounds are normal lung sounds heard over the center chest/sternum on inspiration and expiration. They are characterized by the loud, hollow, tubular, high-pitched sound of air passing through the windpipe without obstruction. They should sound roughly the same on inspiration as they do on expiration.
What are normal and abnormal lung sounds?
A normal breath sound is similar to the sound of air. However, abnormal breath sounds may include: rhonchi (a low-pitched breath sound) crackles (a high-pitched breath sound)
What are the three normal lung sounds?
The three normal/healthy lung sounds include bronchial, bronchovesicular, and vesicular lung sounds. These sounds are heard on auscultation of vari...
What are the most common abnormal lung sounds?
The most common abnormal/dysfunctional lung sounds are wheezes, crackles/rales, rhonchi, stridor, and pleural friction rub. These noises are heard...
What are bronchial lung sounds and where are they heard?
Bronchial lung sounds are normal lung sounds heard over the center chest/sternum on inspiration and expiration. They are characterized by the loud,...
What are bronchovesicular lung sounds and where are they heard?
Bronchovesicular lung sounds are heard where the bronchi enter the lungs, best auscultated over the anterior upper lung fields (first and second in...
What are vesicular lung sounds and where are they heard?
Vesicular lung sounds are soft blowing sounds heard over the entire lung field during both inspiration and expiration, though they diminish during...
What are wheezing lung sounds and where are they heard?
Wheezing sounds may occur during inhalation or exhalation. Most commonly, they are a high-pitched, whistle-like sound heard during exhalation while...
What are crackles/rales and where are they heard?
Crackles/rales are sounds that are heard when the lung field has fluid in small airways. Crackles can be heard on inspiration and expiration. Early...
What are rhonchi and where are they heard?
Rhonchi sounds have a continuous snoring, gurgling, or rattle-like quality. Rhonchi occur in the bronchi as air moves through tracheal-bronchial pa...
What is stridor and where is it heard?
Stridor is a high-pitched, musical sound heard on inspiration. The sound is similar to wheezing, but heard over the throat. It is the sound of air...
What is pleural friction rub and where is it heard?
Pleural rubs occur when two inflamed pleural surfaces rub against each other during respiration. This is often heard in pleurisy, or inflammation o...
What are the sounds of a breath?
Types of abnormal breath sounds include wheezing, rhonchi (which sound like low-pitched wheezing), stridor, crackles (also known as rales, and these may be further classified as fine or coarse), and pleural friction rub. Let’s start with wheezing.
What is the sound of a wheezing lung?
Wheezing sounds may occur during inhalation or exhalation and are continuous with a musical quality. The classic wheeze refers to the high-pitched whistle-like sound heard during exhalation as air moves through a narrow or obstructed airway. Listen to the following wheezing lung sounds: Audio Player.
What is a pleural rub?
Pleural Rubs. Pleural rubs occur when two inflamed pleural surfaces rub against each other during respiration. This is often heard in pleurisy, or inflammation of the tissues that lie in the lungs and chest cavity. The sound may be continuous or broken and creaking or grating.
What is the sound of walking on snow?
It can be described as the sound of walking on fresh snow or rubbing leather together. The sound of pleural rubs occurs every time the patient inhales and exhales. Pleural rubs come and go, are not altered with coughing, can usually be localized to a specific location on the chest wall, and will stop when the patient holds their breath.
Why do I hear crackles in my lungs?
Coarse crackles are often heard just in certain spots in the lungs, possibly only on one side or in different spots on both sides. They are usually caused by mucus in the bronchi.
What does a fine crackle sound like?
Fine crackles are high-pitched, brief, discontinuous popping lung sounds. Fine crackles sound like wood burning in a fireplace or cellophane being crumpled. Fine crackles usually start at the base of the lungs where there is fluid in the lungs.
What are the sounds that are heard in the lung field that have fluid in small airways?
Crackles. Previously termed rales, crackles are sounds that are heard in the lung field that has fluid in small airways. Crackles can be heard on inspiration and expiration. Early inspiratory and expiratory crackles are heard in chronic bronchitis. Late inspiratory crackles may indicate pneumonia, CHF, or atelectasis, ...
Abnormal Lung Sounds
Please review our Terms and Conditions of Use and check box below to share full-text version of article.
Summary
Lung sounds are part of the normal respiratory cycle. So-called bronchial sounds result from turbulent airflow that is generated within the normal trachea and larger airways. These sounds are relatively harsh and can be ausculted by placing a stethoscope over the windpipe.
What is the term for the voice over a consolidated lung?
The term used to describe the voice sounds heard over consolidated lung is bronchophony (also called vocal resonance). It can be determined through the stethoscope when the patient says “99”, usually just audible but becoming louder when the lung is consolidated. Pectoriloquy is abnormal transmission of the patient’s voice sounds through the chest wall so that they can be clearly heard through the stethoscope. The term used to describe whispered speech heard over consolidated lung (as in pneumonia), is whispering pectoriloquy. Bronchophony and whispering pectriloquy have the same implications as bronchial breathing i.e. consolidation or cavitation of the lung with improved transmission of sound. Aegophony is a form of bronchophony in which the spoken syllables have a peculiar nasal or bleating quality, and these arise from the transmission of sound through compressed lung just above a pleural effusion.
What is the ration of inspiratory phase?
They are soft, low pitched, and rustling in quality. The inspiratory phase lasts longer than the expiratory phase with a ration (I:E) of 2:1.
Why is auscultation important?
An important feature of auscultation is recording the intensity of the breath sound. Intensity can be reduced due to several factors: Weak sound generation and/or impaired transmission. Various causes are shallow breathing, airway obstruction, bulla, hyperinflation, pneumothorax, pleural effusion or thickening, and obesity.
What is a grating sound?
A discontinuous grating sound or creak in phase with breathing that occurs in the presence of pleural inflammation. Friction rubs are heard better when the stethoscope is applied firmly to the chest wall. Pleural rubs must be distinguished from similar sounds produced by movement of the scapula, ribs and thoracic musculature under the stethoscope. The latter disappear on repositioning of the stethoscope, changing pressure of application to the chest wall or by repositioning of the patient.
What is the difference between coarse crackles and fine crackles?
They are discontinuous, interrupted explosive sounds. Coarse crackles or crepitations are associated with bronchiectasis or resolving pneumonia, whereas fine crackles can be heard with either pulmonary oedema or interstitial fibrosis.
What is a pleural rub?
Pleural rubs must be distinguished from similar sounds produced by movement of the scapula, ribs and thoracic musculature under the stethoscope. The latter disappear on repositioning of the stethoscope, changing pressure of application to the chest wall or by repositioning of the patient.
What is a monophonic wheeze?
Monophonic wheezing consists of a single musical note starting and ending at different times. A local pathology-like bronchial obstruction by tumor, bronchostenosis by inflammation, mucus accumulation, or a foreign body can produce this sound. In case of rigid obstruction, the wheeze is audible throughout the respiratory cycle, and when the obstruction is flexible, wheeze may be inspiratory or expiratory.
