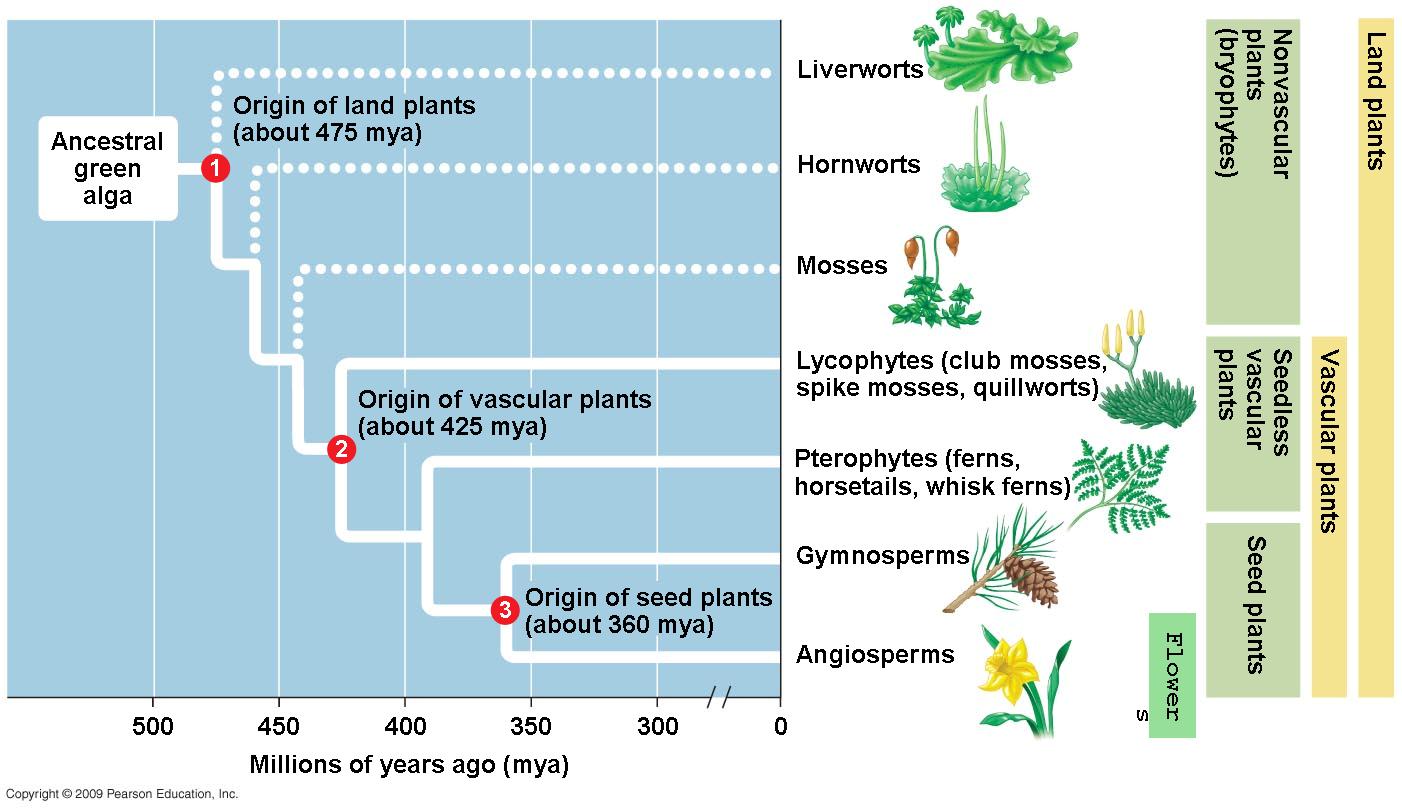
Adaptations of vegetation
- Coniferous trees have thick bark to protect against the cold. They are cone-shaped, with flexible branches which help...
- Pine cones protect the seeds during the harsh winter.
- The thin waxy needles reduce water loss.
- Their evergreen nature means that the needles can photosynthesise whenever there is sufficient sunlight.
- Coniferous trees have thick bark to protect against the cold. ...
- Pine cones protect the seeds during the harsh winter.
- The thin waxy needles reduce water loss.
- Their evergreen nature means that the needles can photosynthesise whenever there is sufficient sunlight.
How do coniferous trees adapt to their environment?
Find out about the location, climate, soil and adaptations of this biome. Coniferous trees have thick bark to protect against the cold. They are cone-shaped, with flexible branches which help them to cope with heavy snow fall. Pine cones protect the seeds during the harsh winter. The thin waxy needles reduce water loss.
What are the characteristics of the coniferous biome?
The coniferous biome, also known as the Taiga, is characterised by evergreen trees. Find out about the location, climate, soil and adaptations of this biome. Coniferous trees have thick bark to protect against the cold. They are cone-shaped, with flexible branches which help them to cope with heavy snow fall.
Why do coniferous trees have thick bark?
Coniferous trees have thick bark to protect against the cold. They are cone-shaped, with flexible branches which help them to cope with heavy snow fall. Pine cones protect the seeds during the harsh winter.
Why do coniferous trees survive snow?
When snow does settle on a coniferous tree’s branches, the shape of the branches and thickness of the needles allow the tree to withstand more weight because the branches have more surface area to support the weight.
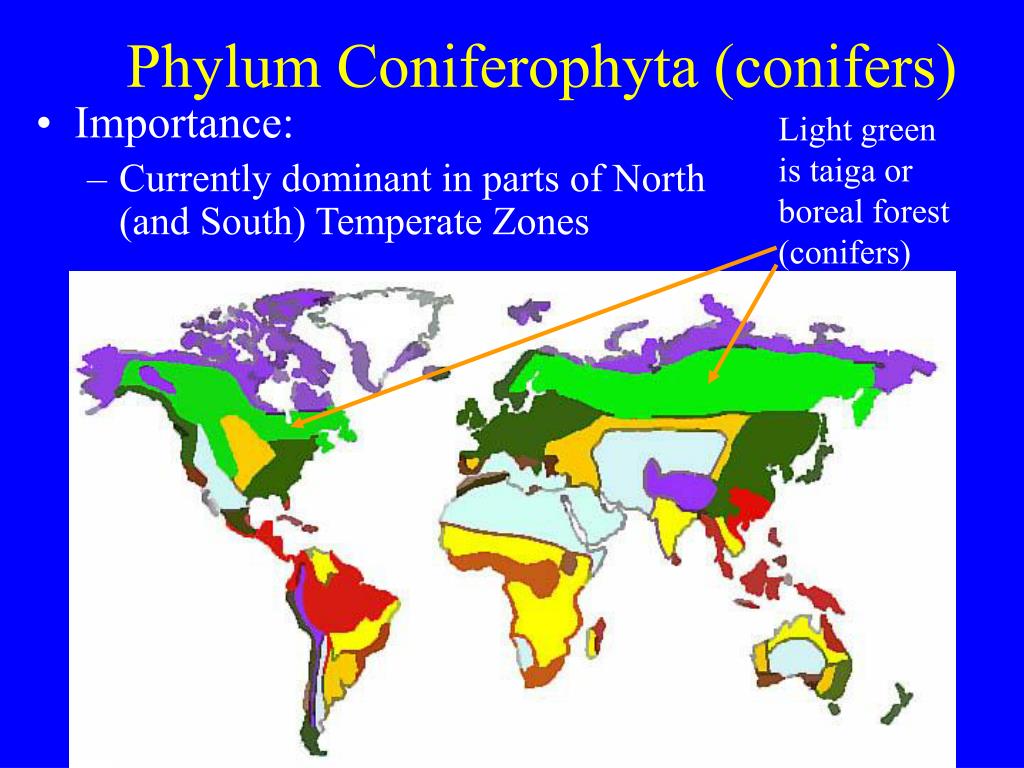
What are 2 adaptations that conifer trees have to help them survive the climate?
They have several adaptations that help them grow in colder, drier conditions. Their needles are heavily cutinized (covered with a protective, waxy coating that slows water vapor loss). Their small surface area helps reduce evaporative water loss.
What adaptations help conifers survive the winter?
The conifer cell walls are stronger than hardwoods, withstanding pressures up to 900 psi, so can better withstand ice expansion. Liquid water in the winter can be found underground and in the snow. Loss of too much water, without replacement, will kill cells.
How are conifers adapted to life on land?
Left: one of the most important adaptations of conifer trees is the thick waxy cuticle that waterproof the leaves. One of the most notable adaptations of conifer trees are the presence of needle-like leaves. These leaves are adapted to survive in harsher and colder conditions compared to broad leaves.
What adaptation allows conifers to grow very tall?
Redwoods and other conifers don't have a lot of the fancy reproductive adaptations that make angiosperms so specious and successful, and they have tracheids, not vessel elements, in their xylem, but they do have cellulose and lignin and that seems to be enough to let them grow as tall as they do.
How do conifers not freeze?
The needles on conifer trees are thick and covered in a waxy layer that helps reduce water loss throughout the year. In winter months, the conifers stop photosynthesizing, and close their stomata, or small openings that allow water to evaporate during photosynthesis.
Why do coniferous trees survive winter?
Coniferous trees have different leaf adaptations. Their needles are long and thin. This means that they have a small surface area. Less surface area means that they have fewer stomata from which to lose water.
What are 5 adaptations that plants need to survive on land?
Plant adaptations to life on land include the development of many structures — a water-repellent cuticle, stomata to regulate water evaporation, specialized cells to provide rigid support against gravity, specialized structures to collect sunlight, alternation of haploid and diploid generations, sexual organs, a ...
Why coniferous trees suit the climate?
Coniferous trees can protect themselves from cold and extreme climate due to the presence of thick bark. They are cone in shape and have very flexible branches that help them to manage and survive even in the time of heavy rainfall and let the snow slip down.
What are the adaptations that coniferous plants have made to survive summers?
Most coniferous trees are evergreen and are specially adapted to survive in this biome. Evergreen trees are cone-shaped to help snow slide off them so the branches won't break. The leaves or needles of evergreen trees lose less water than other kinds of leaves. This also helps them survive.
How do animals adapt to the coniferous forest?
Many animals make their home in coniferous forests, some of which have thick fur to insulate them againsts frigid winters, while others hibernate to endure the cold and some migrate to warmer temperatures.
Why coniferous trees have needles instead of leaves?
Conifers, or cone-bearing trees, evolved to have needles that retain more water and seeds that could hang out until there was enough moisture to take root. It may not seem like it, but needles are leaves.
How do conifer trees survive hot summer and cold winter?
Conifer leaves are shaped like needles (or sometimes are like tiny scales, as for cedars and junipers). How might this help them survive? Having small, needle- or scale-shaped leaves allows conifers to conserve water, which helps them survive summer and winter drought.
How are some trees adapted to live in cold winter?
They have bark Bark provides insulation and protection against freezing and cracking during the winter. Tree bark comes in different textures, densities, and colors - variations that can help a tree tolerate cold temperatures by reflecting light and dispersing heat.
How do pine trees survive winter?
Evergreens have thin needles with a waxy coating: adaptations that also reduce water loss! The outer bark of trees contains many air pockets, rather than living cells filled with liquid that can freeze. The air pockets in bark help provide insulation and protection against freezing and cracking during the winter.
How do trees that lose their leaves in the fall survive all winter?
When the trees lose their leaves, a chemical called abscisic acid (ABA) is produced in terminal buds—the part at the tip of the stem that connects to the leaf. ABA is produced in both deciduous and coniferous trees. It suspends growth and prevents cells from dividing—another key component of dormancy.
Why do coniferous trees have thick bark?
Coniferous trees have thick bark to protect against the cold. They are cone-shaped, with flexible branches which help them to cope with heavy snow fall.
What is the name of the biome that is characterised by evergreen trees?
The coniferous biome, also known as the Taiga, is characterised by evergreen trees. Find out about the location, climate, soil and adaptations of this biome. Part of. Geography. Ecosystems.
