What is the advantage and disadvantage of multiplexed bus? The advantage of time multiplexing is the use of fewer lines, which saves space and, usually, cost. The disadvantage is that more complex circuitry is needed within each module.
Full Answer
Why does bus topology slow down the network?
What happens when a computer fails in bus topology?
What is bus topology?
Why is bus topology important?
Why is bus topology not a secondary connection resource?
Can bus topology be extended?
Is bus topology cheaper than ring topology?
See 4 more
About this website
What is the advantage of multiplexed bus?
Stated succinctly, multiplexing can: Increase dependability by using fewer electrical components. Decrease the cost of maintenance of the electrical system. Reduce the complexity of harness and connection points.
What is the disadvantage of multiplexing technique?
1] Added delays in switching ports. 2] Limitations on which ports can be used simultaneously. 3] Extra IO many require to control multiplexer. 4] Added delays in I/O signals propagating through the multiplexer.
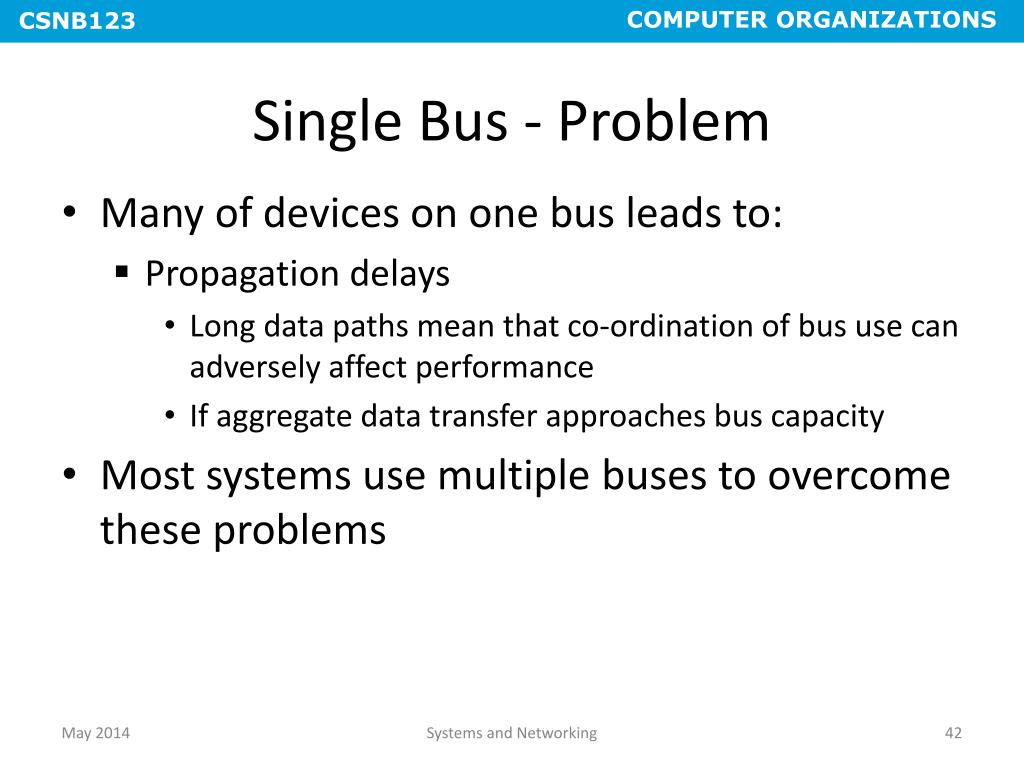
Which is the main disadvantages of an input output bus?
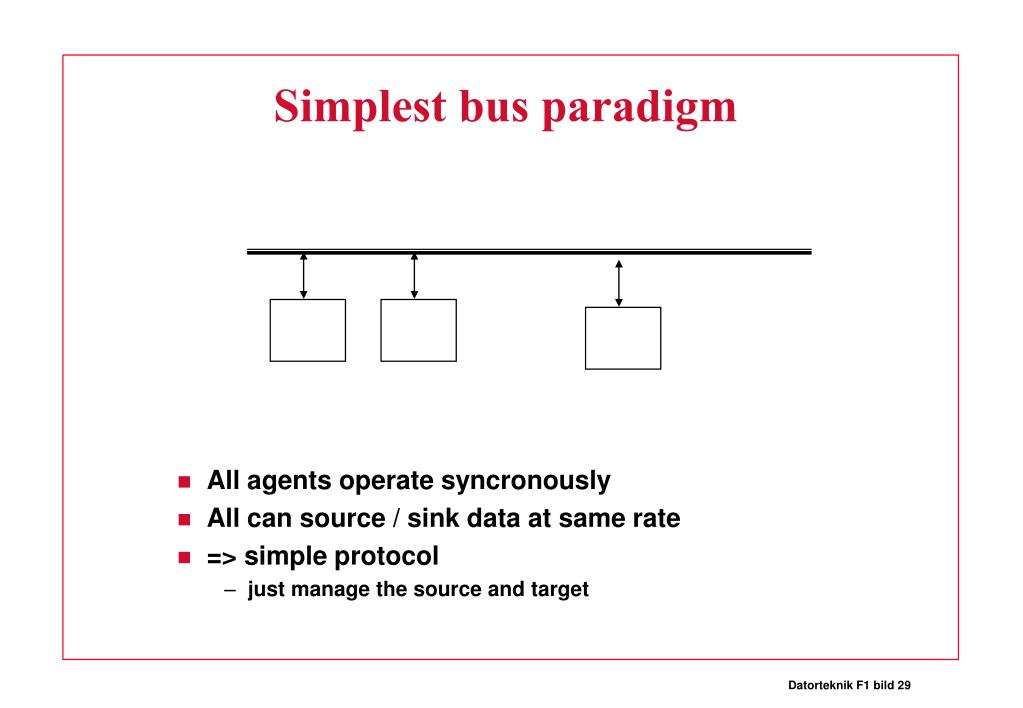
Disadvantages: Every device on the bus must run at the same clock rate. To avoid clock skew, they cannot be long if they are fast.
What is a multiplexed bus?
multiplexed bus A type of bus structure in which the number of signal lines comprising the bus is less than the number of bits of data, address, or control information being transferred between elements of the system.
What is advantage and disadvantage of multiplexing in time?
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Time-division multiplexingAdvantageDisadvantageFrequency division multiplexing is far less flexible and adaptable than time-division multiplexing.In time-division multiplexing, synchronization is pretty much essential.4 more rows•Jan 16, 2022
What are the advantages of using a multiplexer circuit?
A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one analog-to-digital converter or one communications transmission medium, instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement Boolean functions of multiple variables.
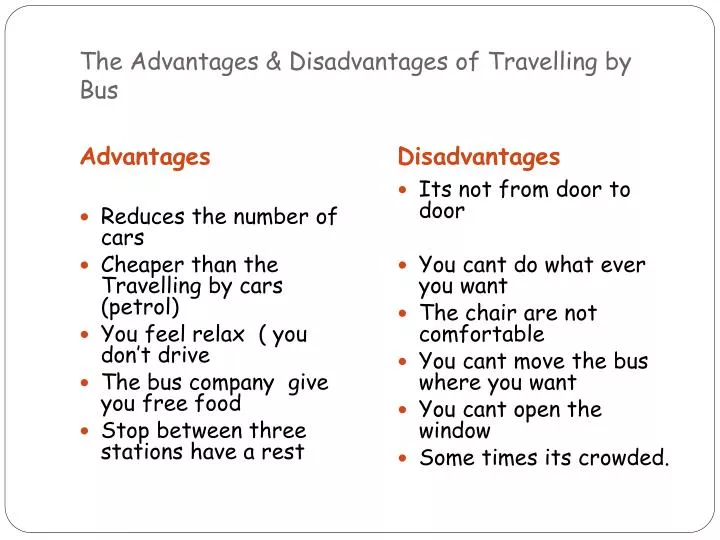
What are the advantages and disadvantages of bus?
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus TopologyAdvantagesDisadvantagesAllows connection or removal of devices easily without affecting other devices.Additional devices make the speed of the network slow.4 more rows•Feb 16, 2022
What are the disadvantages of using buses?
What are the downsides of taking a bus? Busses travel a specific route that only changes during special events or emergency situations. Buses may not travel when youb want to because of their schedule. Buses may not go where you need to go and you may have to walk some distance to where you need to go.
What are the disadvantages of bus topologies?
Disadvantages of Bus Topology :Bus topology is not great for large networks.Identification of problems becomes difficult if the whole network goes down.Troubleshooting individual device issues is very hard.Need terminators are required at both ends of the main cable.Additional devices slow the network down.More items...•
What is multiplexing used for?
Multiplexing is a method used by networks to consolidate multiple signals -- digital or analog -- into a single composite signal that is transported over a common medium, such as a fiber optic cable or radio wave.
What is the advantage of multiplexed address and data bus?
The main reason of multiplexing address and data bus is to reduce the number of pins for address and data and dedicate those pins for other several functions of microprocessor. These multiplexed set of lines used to carry the lower order 8 bit address as well as data bus.
What is multiplexing and 2 types of multiplexing?
Multiplexing is the process of combining multiple signals into one signal, over a shared medium. If analog signals are multiplexed, it is Analog Multiplexing and if digital signals are multiplexed, that process is Digital Multiplexing.
What are the major disadvantages of frequency division multiplexing?
Disadvantages of FDM:It is suffering the problem of cross talk.FDM is only used only when a few low-speed channels are desired.Intermodulation distortion takes place.The circuitry for FDM is complex than TDM.FDM requires more hardware than TDM.FDM system extremely expensive.FDM provides less throughput.More items...
What is a disadvantage of time division multiplexing TDM )?
There are some disadvantages of time division multiplexing which are given below, Synchronization is required in time division multiplexing. Complex to implement. Due to slow narrowband fading, all the TDM channels may get wiped out.
What are the challenges in multiplexing?
Common challenges of conventional multiplex PCR:Limited flexibility of target regions due to PCR thermodynamics.Short reads consumed with long primer sequences.Formation of primer-primer dimers.Bias due to primer induced variability.Complexity of primer design.More items...•
What is the main disadvantage of FDM process?
Disadvantages of fused deposition modeling Not only does FDM's relatively thick layer height mean that it's not ideal for parts with small details, but it also means that finished products will likely have rough surfaces and require post-processing to achieve a smoother finish.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus Topology - GeeksforGeeks
Bus Topology: Alternatively mentioned as line topology, bus topology could even be a specific quiet topology during which each computer and network device is connected to a minimum of one cable or backbone. In general, the term refers to how various devices are acknowledged during a network. counting on sort of network card, coax or an RJ-45 network cable is employed to attach them.
Bus Topology Advantages And Disadvantages | What is Bus Topology ...
Bus Topology Advantages And Disadvantages: Bus topology is the simple form of network setup that involves computers and network devices including servers connected to a single cable. This central cable of the network is known as the bus which is considered the backbone of the system because it has all the control. The devices communicate […]
BUS TOPOLOGY: ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Bus topology diagram Advantages (benefits) of Linear Bus Topology 1) It is easy to set-up and extend bus network. 2) Cable length required for this topology is the least compared to other networks. 3) Bus topology costs very less. 4) Linear Bus network is mostly used in small networks. Good for LAN. Disadvantages (Drawbacks) of Linear Bus Topology 1) There is a limit on central cable length ...
Why does bus topology slow down the network?
Additional devices slow the network down. Because bus topology links every computer and peripheral through a backbone, additional devices will slow down the entire network since only one cable is being used. That also places the entire network at-risk should something happen to that cable.
What happens when a computer fails in bus topology?
If one computer or peripheral should fail when using bus topology, the rest of the network is not affected by this change in performance. The linear nature of the network means that each unit transmits to the backbone and that data is then available to the other units that remain connected.
What is bus topology?
Bus topology isn’t a reference to vehicles. It is a network setup that involves computers and network devices. Each is connected to a single cable, which is called a “backbone” or “spine.”. This creates a localized network that can be used for a variety of purposes.
Why is bus topology important?
Bus topology has an advantage here because it supports multiple nodes instead of just 2 nodes. That is how the original form of an Ethernet network came about. 10Base2, which is popularly known as “thinnet,” utilizes bus topology to create a local area network that can be used to form departments or working groups. 7.
Why is bus topology not a secondary connection resource?
Because each node is independently connected to the backbone, bus topology doesn’t provide a secondary connection resource. If there is a T-connection failure for the connection, then there is no way for data to be shared along the network or to the computer or peripheral that has been separated from the backbone.
Can bus topology be extended?
The size and scope of bus topology is naturally limited. It can, however, be extended quite easily. Joining cable with a repeater or connector allows for additional peripherals or computers to be added to the network.
Is bus topology cheaper than ring topology?
2. It is cheaper than other network options. Compared to ring, star, or hybrid networks, bus topology is the cheapest to implement.
What is multiplexed school bus?
Multiplexed school buses offer factory-installed interface modules that provide a centralized connection point for all added equipment. These factory-installed switches with custom labels are ergonomically positioned for use when integrating equipment such as flashing lights, wheelchair lifts, etc. — improving the overall look and feel of the bus, and increasing driver comfort, productivity and retention.
How many wires does a multiplex module add to a conversation?
Additional people joining the conversation only add one wire per person to the multiplex module.
How many wires are in a school bus?
This allows multiple electrical loads to communicate through one pair of wires compared with having several wires to accomplish the same job. Non-multiplexed electrical systems typically have four to five wires per electrical load.
How did multiplexing start?
Multiplexing began in the telecommunications industry essentially by being able to put more than one call down a single line. And the best method of explaining this complex technology still lies in the communication example.
What is IC school bus wiring?
school buses are outfitted with multiplexed wiring called the International Diamond Logic Electrical System that allows programming to meet specific needs.
Why does bus topology slow down the network?
Additional devices slow the network down. Because bus topology links every computer and peripheral through a backbone, additional devices will slow down the entire network since only one cable is being used. That also places the entire network at-risk should something happen to that cable.
What happens when a computer fails in bus topology?
If one computer or peripheral should fail when using bus topology, the rest of the network is not affected by this change in performance. The linear nature of the network means that each unit transmits to the backbone and that data is then available to the other units that remain connected.
What is bus topology?
Bus topology isn’t a reference to vehicles. It is a network setup that involves computers and network devices. Each is connected to a single cable, which is called a “backbone” or “spine.”. This creates a localized network that can be used for a variety of purposes.
Why is bus topology important?
Bus topology has an advantage here because it supports multiple nodes instead of just 2 nodes. That is how the original form of an Ethernet network came about. 10Base2, which is popularly known as “thinnet,” utilizes bus topology to create a local area network that can be used to form departments or working groups. 7.
Why is bus topology not a secondary connection resource?
Because each node is independently connected to the backbone, bus topology doesn’t provide a secondary connection resource. If there is a T-connection failure for the connection, then there is no way for data to be shared along the network or to the computer or peripheral that has been separated from the backbone.
Can bus topology be extended?
The size and scope of bus topology is naturally limited. It can, however, be extended quite easily. Joining cable with a repeater or connector allows for additional peripherals or computers to be added to the network.
Is bus topology cheaper than ring topology?
2. It is cheaper than other network options. Compared to ring, star, or hybrid networks, bus topology is the cheapest to implement.