Anatomical Movements
- Flexion and Extension These movements occur in the sagittal plane. ...
- Abduction and Adduction These movements occur in the frontal plane. ...
- Pronation and Supination These movements occur in the transverse or horizontal plane of the body. ...
- Plantarflexion and Dorsiflexion These movements occur in the sagittal plane of the body. ...
- Inversion and Eversion ...
- Protraction and Retraction ...
| Flexion | Bending |
|---|---|
| Extension | Straightening |
| Abduction | Moving away from the reference axis |
| Adduction | Bringing closer to the reference axis |
| Protrusion | Forward |
What are the three types of movement?
- Planes.
- Axes.
- Flexion and extension.
- Abduction and adduction.
- Elevation and depression.
- Internal and external rotation (medial and lateral rotation)
- Circumduction.
- Pronation and supination.
What are the different types of body movement?
types of body movements flexion extension rotation a movement that decreases the angle and brings bone closer tog… movement that increases the distance between bone (straighteni… movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis common movemen… 13 Terms emma_mccoury Types of Body Movement Flexion Extension Rotation
What are the 12 body movements?
The frame movements in people are of the following types:
- Flexion
- Lateral Flexion
- Dorsiflexion
- Plantarflexion
- Extension
- Hyperextension
- Abduction
- Adduction
- Transverse Abduction
- Transverse Adduction
What are the different types of joint movements?
- Pivot Joint: This joint permits rotational movement around a single axis. ...
- Hinge Joint: This joint permits bending and straightening movements along one plane. ...
- Condyloid Joint: Several different types of movements are allowed by this type of joint, including bending and straightening, side-to-side, and circular movements. ...

What are the anatomical movement?
Anatomical movements can be defined as the act or instance of moving the bodily structures or as the change of position in one or more of the joints of the body. Joint actions are described in relation to the anatomical position which is the universal starting position for describing movement.
What are the 5 types movement?
The human body has five basic movement patterns: bending, single-sided, rotational, pushing and pulling.
What are the types of body movements?
Types of body movements include gliding, rotation, angular movements, flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction, and special movements.
What are the 7 types of muscle movements?
The movements and motions that joints and their muscles are capable of include:Abduction.Adduction.Flexion.Hyperflexion.Extension.Hyperextension.Rotation.Internal rotation.More items...
What are the 6 types of body movements?
Abduction and Adduction. Abduction and adduction motions occur within the coronal plane and involve medial-lateral motions of the limbs, fingers, toes, or thumb. ... Circumduction. ... Rotation. ... Supination and Pronation. ... Dorsiflexion and Plantar Flexion. ... Inversion and Eversion. ... Protraction and Retraction. ... Depression and Elevation.
What are the six type of movement?
Movement and physical activity is any body movement that works your muscles and requires more energy than resting. There are 6 types of movement. Walking, running, dancing, swimming, yoga, and gardening are a few examples of physical activity and physical movement.
What are the four types of movements?
The four types of motion are:linear.rotary.reciprocating.oscillating.
What are the types of movement in biology?
Flexion and Extension. ... Abduction, Adduction, and Circumduction. ... Rotation. ... Supination and Pronation. ... Dorsiflexion and Plantar Flexion. ... Inversion and Eversion. ... Protraction and Retraction. ... Depression and Elevation.More items...•
What are the 12 different movement of the joints?
Types of joint movementJointTypeMovementElbowHingeFlexion, extensionKneeHingeFlexion, extensionHipBall and socketFlexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, circumductionShoulderBall and socketFlexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, circumduction
What are the 3 main types of muscles?
There are about 600 muscles in the human body. The three main types of muscle include skeletal, smooth and cardiac. The brain, nerves and skeletal muscles work together to cause movement – this is collectively known as the neuromuscular system.
How many types of muscle movements are there?
In the body, there are three types of muscle: skeletal (striated), smooth, and cardiac.
What are the four types of movements?
The four types of motion are:linear.rotary.reciprocating.oscillating.
What are the 12 different movement of the joints?
Types of joint movementJointTypeMovementElbowHingeFlexion, extensionKneeHingeFlexion, extensionHipBall and socketFlexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, circumductionShoulderBall and socketFlexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, circumduction
What are the types of movement education?
Movement education is about teaching movement through four key concepts: body, space, effort, and relationships.
What are the 6 types of freely movable joints?
Generally speaking, the greater the range of movement, the higher the risk of injury because the strength of the joint is reduced. The six types of freely movable joint include ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot and gliding.
What is the term for the movement of the joints?
The movements produced at joints by muscles are given specific anatomical names, often referred to as “anatomical terms of motion”. We usually make the assumption that the body is in normal resting anatomical position, and that joint movement occurs from this resting position.
What is the second set of movements specific to the foot?
The second set of movements specific to the foot are eversion and inversion. These movements occur about the sagittal axis and along the coronal plane. Eversion refers to bringing the soles of the feet out, so they are facing away from the midline of the body.
What is the difference between adduction and abduction?
Abduction and adduction refer to movements made about a sagittal axis and along the coronal plane. Abduction is moving a body part away from its resting anatomical position in the coronal plane; adduction is returning it to its normal resting position (includes ‘hyperadduction’).
Which plane of motion is the hip flexion?
Flexion and extension of the hip occur in the sagittal plane, and about the coronal axis. Abduction and adduction of the shoulder occur in the coronal plane, and about the sagittal axis. Left and right rotation of the atlantoaxial joint occurs in the transverse plane, and about the vertical axis.
Where does flexion occur?
Flexion and extension of the hip occur in the sagittal plane, and about the coronal axis.
What is the axis of a joint?
There are also several different axes we use to describe the movement of a joint. It is useful to think of an axis as a metal pole, and the joint rotating around this pole.
What are some examples of external rotation?
Examples of external rotation. With the elbows at 90 degrees of flexion, externally rotating the shoulder brings the forearm and hand away from the body – like someone has just scared you! Rotating the lower limb at the hip joint to point the feet away from each other. Active shoulder external rotation.
What is the movement of the hip called?
Adduction is a movement towards the midline. Adduction of the hip squeezes the legs together.
What is the movement of the foot around its long axis called?
Inversion and Eversion . Inversion and eversion are movements which occur at the ankle joint, referring to the rotation of the foot around its long axis. Inversion involves the movement of the sole towards the median plane – so that the sole faces in a medial direction.
What is the movement of the back when lying flat on the back?
This is the supine position, and so this movement is supination. Again, keeping the elbow and shoulder still, flip your hand onto its front, palm down. This is the prone position, and so this movement is named pronation. These terms also apply to the whole body – when lying flat on the back, the body is supine.
How to do supine position?
With your hand resting on a table in front of you, and keeping your shoulder and elbow still, turn your hand onto its back, palm up. This is the supine position, and so this movement is supination. Again, keeping the elbow and shoulder still, flip your hand onto its front, palm down.
What is extension in anatomy?
Extension refers to a movement that increases the angle between two body parts. Extension at the elbow is increasing the angle between the ulna and the humerus. Extension of the knee straightens the lower limb.
What is the term used to describe the actions of muscles upon the skeleton?
Anatomical terms of movement are used to describe the actions of muscles upon the skeleton. Muscles contract to produce movement at joints, and the subsequent movements can be precisely described using this terminology.
What is the term for the movement of the fingers around the long axis?
Therefore, abducting the fingers spreads them out. Medial and Lateral Rotation . Medial and lateral rotation describe movement of the limbs around their long axis: Medial rotation is a rotational movement towards the midline. It is sometimes referred to as internal rotation.
What are the anterior and posterior motions of the upper limb?
For the upper limb, all anterior-going motions are flexion and all posterior-going motions are extension. These include anterior-posterior movements of the arm at the shoulder, the forearm at the elbow, the hand at the wrist, and the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints.
Which part of the body moves the anterior surface of the arm or thigh toward the midline?
Here, the humerus and femur rotate around their long axis, which moves the anterior surface of the arm or thigh either toward or away from the midline of the body. Movement that brings the anterior surface of the limb toward the midline of the body is called medial (internal) rotation.
What is the difference between flexion and extension?
For the vertebral column, flexion (anterior flexion) is an anterior (forward) bending of the neck or body, while extension involves a posterior-directed motion, such as straightening from a flexed position or bending back ward. Lateral flexion is the bending of the neck or body toward the right or left side.
What are the learning objectives of synovial joints?
Identify the joints that allow for these motions. Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles that are attached to the bones on either side of the articulation.
Why is synovial joint important?
Overall, each type of synovial joint is necessary to provide the body with its great flexibility and mobility. There are many types of movement that can occur at synovial joints (Table 1). Movement types are generally paired, with one being the opposite of the other.
What is the term for the abnormal or excessive extension of a joint beyond its normal range of motion?
Hyperextension is the abnormal or excessive extension of a joint beyond its normal range of motion, thus resulting in injury. Similarly, hyperflexion is excessive flexion at a joint. Hyperextension injuries are common at hinge joints such as the knee or elbow.
Where does circumduction take place?
Adduction, abduction, and circumduction take place at the shoulder, hip, wrist, metacarpophalangeal, and metatarsophalangeal joints.
What is the movement of a body region in a circular manner?
Circumduction. Circumduction is the movement of a body region in a circular manner, in which one end of the body region being moved stays relatively stationary while the other end describes a circle. It involves the sequential combination of flexion, adduction, extension, and abduction at a joint.
Which part of the body moves the anterior surface of the arm or thigh toward the midline?
Here, the humerus and femur rotate around their long axis, which moves the anterior surface of the arm or thigh either toward or away from the midline of the body. Movement that brings the anterior surface of the limb toward the midline of the body is called medial (internal) rotation.
What is the difference between flexion and extension?
For the vertebral column, flexion (anterior flexion) is an anterior (forward) bending of the neck or body, while extension involves a posterior-directed motion, such as straightening from a flexed position or bending back ward. Lateral flexion is the bending of the neck or body toward the right or left side.
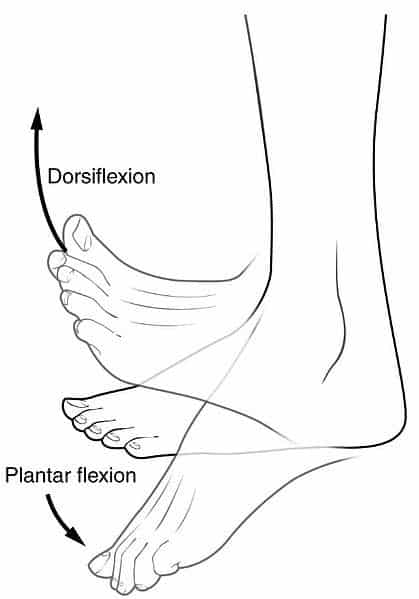
What is dorsiflexion and plantar flexion?
Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion are movements at the ankle joint, which is a hinge joint. Lifting the front of the foot, so that the top of the foot moves toward the anterior leg is dorsiflexion, while lifting the heel of the foot from the ground or pointing the toes downward is plantar flexion. These are the only movements available at the ankle joint (see [link] h ).
What is the position of the forearm?
Supination and pronation are movements of the forearm. In the anatomical position, the upper limb is held next to the body with the palm facing forward. This is the supinated position of the forearm. In this position, the radius and ulna are parallel to each other.
What is synovial joint?
Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles that are attached to the bones on either side of the articulation. The type of movement that can be produced at a synovial joint is determined by its structural type. While the ball-and-socket joint gives the greatest range of movement at an individual joint, in other regions of the body, several joints may work together to produce a particular movement. Overall, each type of synovial joint is necessary to provide the body with its great flexibility and mobility. There are many types of movement that can occur at synovial joints ( [link] ). Movement types are generally paired, with one being the opposite of the other. Body movements are always described in relation to the anatomical position of the body: upright stance, with upper limbs to the side of body and palms facing forward. Refer to [link] as you go through this section.
What is the term for the abnormal or excessive extension of a joint beyond its normal range of motion?
Hyperextension is the abnormal or excessive extension of a joint beyond its normal range of motion, thus resulting in injury. Similarly, hyperflexion is excessive flexion at a joint. Hyperextension injuries are common at hinge joints such as the knee or elbow.
What is the movement of the thumb called?
Thumb opposition is produced by a combination of flexion and abduction of the thumb at this joint. Returning the thumb to its anatomical position next to the index finger is called reposition (see Figure 11.10.2l).
What is the side to side movement of the mandible?
Excursion is the side-to-side movement of the mandible. Lateral excursion moves the mandible away from the midline, toward either the right or left side. Medial excursion returns the mandible to its resting position at the midline.
What is superior rotation?
Superior and inferior rotation are movements of the scapula and are defined by the direction of movement of the glenoid cavity. These motions involve rotation of the scapula around a point inferior to the scapular spine and are produced by combinations of muscles acting on the scapula. During superior rotation, the glenoid cavity moves upward as the medial end of the scapular spine moves downward. This is a particularly important motion that contributes to upper limb abduction. Without superior rotation of the scapula, the greater tubercle of the humerus would hit the acromion of the scapula, thus preventing any abduction of the arm above shoulder height. Superior rotation of the scapula is thus required for full abduction of the upper limb. Superior rotation is also used without arm abduction when carrying a heavy load with your hand or on your shoulder. You can feel this rotation when you pick up a load, such as a heavy book bag and carry it on only one shoulder. To increase its weight-bearing support for the bag, the shoulder lifts as the scapula superiorly rotates. Inferior rotation occurs during limb adduction and involves the downward motion of the glenoid cavity with upward movement of the medial end of the scapular spine.
What is dorsiflexion and plantar flexion?
Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion are movements at the ankle joint, which is a hinge joint. Lifting the front of the foot, so that the top of the foot moves toward the anterior leg is dorsiflexion, while lifting the heel of the foot from the ground or pointing the toes downward is plantar flexion. These are the only movements available at the ankle joint (see Figure 11.10.2h).
What is the position of the forearm?
Supination and pronation are movements of the forearm. In the anatomical position, the upper limb is held next to the body with the palm facing forward. This is the supinated position of the forearm. In this position, the radius and ulna are parallel to each other. When the palm of the hand faces backward, the forearm is in the pronated position, and the radius and ulna form an X-shape.
Which joint allows for flexion and extension?
Each of the different structural types of synovial joints also allow for specific motions. The atlantoaxial pivot joint provides side-to-side rotation of the head, while the proximal radioulnar articulation allows for rotation of the radius during pronation and supination of the forearm. Hinge joints, such as at the knee and elbow, allow only for flexion and extension. Similarly, the hinge joint of the ankle only allows for dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot.
Why is synovial joint important?
Overall, each type of synovial joint is necessary to provide the body with its great flexibility and mobility. There are many types of movement that can occur at synovial joints (Table 11.10.1). Movement types are paired, with one being the opposite of the other.
What is the movement of a body region in a circular manner?
Circumduction is the movement of a body region in a circular manner, in which one end of the body region being moved stays relatively stationary while the other end describes a circle. It involves the sequential combination of flexion, adduction, extension, and abduction at a joint.
What is the term for the movement of the anterior surface of the limb toward the midline of the body?
Movement that brings the anterior surface of the limb toward the midline of the body is called medial (internal) rotation. Conversely, rotation of the limb so that the anterior surface moves away from the midline is lateral (external) rotation (see figure f).
What is the pronation of the forearm?
This is the supinated position of the forearm. In this position, the radius and ulna are parallel to each other. When the palm of the hand faces backward, the forearm is in the pronated position, and the radius and ulna form an X-shape.#N#Supination and pronation are the movements of the forearm that go between these two positions. Pronation is the motion that moves the forearm from the supinated (anatomical) position to the pronated (palm backward) position. This motion is produced by rotation of the radius at the proximal radioulnar joint, accompanied by movement of the radius at the distal radioulnar joint. The proximal radioulnar joint is a pivot joint that allows for rotation of the head of the radius. Because of the slight curvature of the shaft of the radius, this rotation causes the distal end of the radius to cross over the distal ulna at the distal radioulnar joint. This crossing over brings the radius and ulna into an X-shape position. Supination is the opposite motion, in which rotation of the radius returns the bones to their parallel positions and moves the palm to the anterior facing (supinated) position.#N#When it comes to the feet, things get a bit complicated, as the terms supination/pronation are often interchangeably used with inversion/eversion (see definition further below). It would be more correct to say that supination of the foot is a combined movement of inversion, adduction, and plantar flexion, while pronation of the foot is a combined eversion, abduction, and dorsiflexion.
What is pivot joint?
At a pivot joint, one bone rotates in relation to another bone. For example, at the atlantoaxial joint, the first cervical (C1) vertebra (atlas) rotates around the dens, the upward projection from the second cervical (C2) vertebra (axis). This allows the head to rotate from side to side as when shaking the head “no.” The proximal radioulnar joint is a pivot joint formed by the head of the radius and its articulation with the ulna. This joint allows for the radius to rotate along its length during pronation and supination movements of the forearm.
What is the difference between flexion and extension?
In the limbs, flexion decreases the angle between the bones (bending of the joint), while extension increases the angle and straightens the joint. For the upper limb, all anterior motions are flexion and all posterior motions are extension. In the lower limb, bringing the thigh forward and upward is flexion at the hip joint, while any posterior-going motion of the thigh is extension. Knee flexion is the bending of the knee to bring the foot toward the posterior thigh, and extension is the straightening of the knee.
What is the difference between dorsiflexion and plantar flexion?
Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion are movements at the ankle joint, which is a hinge joint. Lifting the front of the foot, so that the top of the foot moves toward the anterior leg is dorsiflexion, while lifting the heel of the foot from the ground or pointing the toes downward is plantar flexion. Accordingly, plantarflexion is what we as dancers call stretching the feet, dorsiflexion is what we call flexing. These are the only movements available at the ankle joint (see figure h).
What is the abduction of the thumb?
For the thumb, abduction is the anterior movement that brings the thumb to a 90° perpendicular position, pointing straight out from the palm. Adduction moves the thumb back to the anatomical position, next to the index finger.
Introduction
Planes
Axes
Flexion and Extension
Abduction and Adduction
- Abduction and adduction refer to movements made about a sagittal axis and along the coronal plane. Abduction is moving a body part away from its resting anatomical position in the coronal plane; adduction is returning it to its normal resting position(includes ‘hyperadduction’).
Elevation and Depression
Internal and External Rotation
Circumduction
Pronation and Supination
Dorsiflexion and Plantarflexion