
What does multifidus attach to? At the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions, one end of the multifidus attaches onto the transverse processes of a spinal vertebra, and the other to the spinous process on the vertebra 2-4 levels higher. Transverse processes are extensions of bone that emanate from the body of the vertebra on either side.
What are the attachments of multifidus?
Attachments of Multifidus: Origin & Insertion Origin: Posterior sacrum (next to foramina); superior iliac spine, mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae, transverse processes of thoracis vertebrae, and articular processes of C4-C7. Insertion: Spinous processes of vertebrae (except C1), 2-4 bones above origin.
What is the lumbar multifidus?
Lumbar Multifidus 1 Description. The multifidus muscle is from the deep muscles of the back that together with the semispinalis and rotatores form the trasversospinales muscles group, it lies deep to the semispinalis ... 2 Anatomy. ... 3 Clinical Relevance. ... 4 Length Tension Relationship. ... 5 Treatment. ... 6 Evidence. ...
Where is the multifidus muscle located?
They travel superiorly to insert on the lateral surface and apices of spinous processes 2 to 5 levels above their origin. As part of the transversospinal muscle group, multifidus is located in the third or deep layer of deep muscles of the back.
How many vertebral levels does the multifidus muscle bridge?
Each multifidus muscle bridges over three to six vertebral levels, spanning between the transverse and spinous processes of certain cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae.
What are the attachments of multifidus?
Multifidus muscleOriginSacrum, Erector spinae Aponeurosis, PSIS, and Iliac crestInsertionspinous processNervePosterior branchesActionsProvides proprioceptive feedback and input due to high muscle spindle density; Bilateral backward extension, unilateral ipsilateral side-bending and contralateral rotation.9 more rows
Where does the multifidus muscles attach to?
Insertion: The multifidus muscle fibers pass upwards and medially to insert onto the spinous process of each vertebrae in the spinal column, except for the very top cervical vertebrae (C1). Nerve Supply: The intrinsic/deep back primarily nerve supply arises from dorsal rami of the spinal nerves..
What is the origin and insertion of the multifidus?
Attachments of Multifidus: Origin & Insertion Origin: Posterior sacrum (next to foramina); superior iliac spine, mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae, transverse processes of thoracis vertebrae, and articular processes of C4-C7. Insertion: Spinous processes of vertebrae (except C1), 2-4 bones above origin.
What bone is the multifidus attached to?
At the sacrum, the multifidus originates at the back of this triangular-shaped bone. It also originates on the medial (facing the center of your back rather than toward the outside) surface of your posterior superior iliac spine.
What is lumbar multifidus?
The lumbar multifidus muscle is a long muscle having several points of origin: The back surface of the sacrum. The posterior superior iliac spine. The mammillary processes of the lumbar vertebrae (bony prominences at the dorsal superior aspect of the lumbar vertebrae).
What is the multifidus innervated by?
medial branch nerveThe most medial of the paraspinal muscles, the multifidus, has an important role in intervertebral stability. It is innervated by the medial branch nerve (MBN) of the posterior ramus of the spinal nerve at each level, which exits the spinal canal supero-lateral to the facet joint [1].
Which is the insertion of the Multifidi and rotatores?
Rotatores Muscles They are shaped like a quadrilateral and attach on the transverse process of the vertebrae. But unlike the multifidus, whose other attachment site is the spinous process, the rotatores originate at the transverse process and insert on the spinous process at one or two vertebral levels higher.
What is the antagonist of multifidus?
Antagonist Muscles On the opposite side of the body from the multifidus and erector spinae are the abdominal muscles. The most well-known ab muscle is the rectus abdominis, which is the muscle that you see when someone has a "six-pack." This muscle runs from the bottom of the ribs down into the front of the pelvis.
Is multifidus part of erector spinae?
The muscle fibers run vertically and attach to the ligamentum nuchae. The intermediate layer, the multifidus, originates from the erector spinae aponeurosis and from the transverse processes up to C4 and extends to the lower border of each spinous process. This muscle spans approximately three levels.
What is the role of the multifidus?
The multifidus muscles produce extension of the vertebral column. They also generate some rotation of the vertebral bodies away from the side of contraction, and they are also active in lateral flexion of the spine.
How do you palpate lumbar multifidus?
1:584:37Multifidi and Rotatores Palpation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI'm going to just locate the spinous processes here and then slide over those large erector spinaeMoreI'm going to just locate the spinous processes here and then slide over those large erector spinae muscles. And then just kind of come in through the side door here laterally.
Is multifidus part of erector spinae?
The muscle fibers run vertically and attach to the ligamentum nuchae. The intermediate layer, the multifidus, originates from the erector spinae aponeurosis and from the transverse processes up to C4 and extends to the lower border of each spinous process. This muscle spans approximately three levels.
What is the main function of the multifidus muscles?
Multifidi muscles insert onto all the vertebrae except the atlas. The multifidus muscles produce extension of the vertebral column. They also generate some rotation of the vertebral bodies away from the side of contraction, and they are also active in lateral flexion of the spine.
Which is the insertion of the Multifidi and rotatores?
Rotatores Muscles They are shaped like a quadrilateral and attach on the transverse process of the vertebrae. But unlike the multifidus, whose other attachment site is the spinous process, the rotatores originate at the transverse process and insert on the spinous process at one or two vertebral levels higher.
What is the antagonist of multifidus?
Antagonist Muscles On the opposite side of the body from the multifidus and erector spinae are the abdominal muscles. The most well-known ab muscle is the rectus abdominis, which is the muscle that you see when someone has a "six-pack." This muscle runs from the bottom of the ribs down into the front of the pelvis.
How to work the lumbar multifidus muscles?
Lateral Flexion Spinal muscles are important for bending your body from side to side, or lateral flexion. Lateral flexion exercises are useful for working your lumbar multifidus muscles. Lie on your side on an incline bench that has been adjusted so that the top of the bench hits you just below your waist. Cross your arms over your chest and bend your torso down to the side so that you're leaning over the top edge of the bench. Keep your back straight, only bending your spine at the waist. Do 10 reps on one side, then repeat with another 10 reps on the other side.
Where is the multifidus muscle located?
The multifidus muscle spans the whole length of the vertebral column but is most developed in the lumbar area. The multifidus muscle is from the local core stabilizers playing an important role in the static and dynamic spinal stability, weakness in the multifidus muscle is associated with low back pain. YouTube. Jonathan Fitzgordon.
What is the function of the multifidus muscle?
The multifidus muscle is an important stabilizer of the lumbar spine. It functions together with transversus abdominis and pelvic floor muscles for spine stability. Multifidus muscle weakness and atrophy is associated with chronic low back pain.
Which muscle group is located deep to the semispinalis and superficial to the rotatores?
The multifidus muscle is from the deep muscles of the back that together with the semispinalis and rotatores form the trasversospinales muscles group, it lies deep to the semispinalis and superficial to the rotatores. The trasversospinales muscles group run laterally from the transverse process and attach medially in the spinous process, filling the groove on either side of the spinous process.
How to strengthen lumbar multifidi?
Exercises. Rotation and twisting movements will help with flexibility and strength in your lumbar multifidi. Perform rotation exercises such as holding a broomstick across your shoulders and, standing with your feet shoulder width apart, twist from one side to the other. If your gym has a rotary machine, use that, too.
How to maintain a TRA connection?
Maintaining your connection to TrA, keep your ankles together, lift your top knee and then lift your ankle. Return your ankle and then your knee.
Does DMF cause movement in the spine?
No movement of your hips, pelvis or spine should occur as you gently activate the dMF. If you compare how heavy your leg is to lift with and without this dMF contraction you should find that it is lighter with the proper contraction.
Attachments of Multifidus: Origin & Insertion
Origin: Posterior sacrum (next to foramina); superior iliac spine, mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae, transverse processes of thoracis vertebrae, and articular processes of C4-C7.
Actions of the Multifidus Muscle
Bilateral action: extends vertebrae (except C1), 2-4 bones above origin.
What Is the Multifidus Muscle?
Deep in the back, there are small muscles that live between the spinous processes at the back of the spinal column that are collective ly known as the multifidus muscle. The multifidus muscle serves the entire spine, from the cervical spine (neck) to the pelvis, running the entire length of both sides of the spine, and focuses specifically on spinal stability. Watch the brief video below on multifidus back pain to see images and MRI comparisons and learn more.
How to prevent multifidus atrophy?
First, exercise can strengthen the multifidus muscle. If you want to minimize your risk of developing multifidus atrophy to begin with, regular exercise before any damage is done is ideal; however, it’s never too late to start, even if your muscles have already weakened.
What happens when the multifidus muscle is off line?
With an abnormally functioning multifidus muscle, as the video below shows, the muscles have gone off-line, the vertebrae are uncontrolled, and the motion of the spine is very sloppy. These uncontrolled motions can cause pain and damage discs, joints, and nerves along the spinal column.
What muscle is used to support the spine?
The multifidus muscle serves the entire spine, from the cervical spine (neck) to the pelvis, running the entire length of both sides of the spine, and focuses specifically on spinal stability. Watch the brief video below on multifidus back pain to see images and MRI comparisons and learn more.
What muscle is in constant control of the movements?
With a normally functioning multifidus muscle, as the video below shows, the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine) are allowed to move, but the multifidus muscle is in constant control of the movements, and the movements are small with only micromotions allowed in precise directions. With an abnormally functioning multifidus muscle, as ...
What is the most important structure for spinal stabilization?
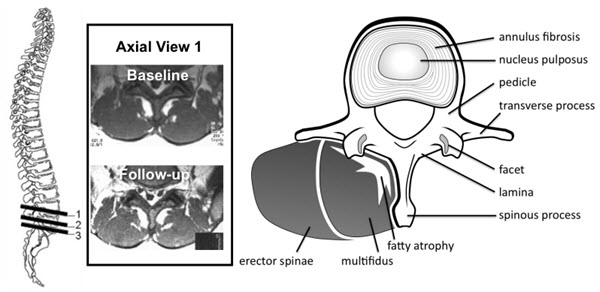
The most important structure for spinal stabilization and support is likely one you’ve never heard about: the multifidus muscle. Study after study has shown that when this muscle’s not happy, the entire neck and back suffer. However, despite the fact that the multifidus is easy to see on an MRI, most physicians or surgeons haven’t studied it ...
Can orthobiologics tighten ligaments?
Stretched and unstable ligaments can also be addressed with orthobiologics to tighten them up. There are also some what not to dos when it comes to keeping your spine healthy and properly functioning. Steer clear of spinal fusions as these can heavily damage the multifidus muscle.

Description
Anatomy
- Origin
The lumbar multifidus muscle is a long muscle having several points of origin: 1. The back surface of the sacrum. 2. The posterior superior iliac spine. 3. The mammillary processes of the lumbar vertebrae (bony prominences at the dorsal superior aspect of the lumbar vertebrae). 4. The tran… - Insertion
Base of spinous process of all vertebrae from L5 to T8, 2-4 levels above origin. The multifidus is connected with the transversus abdominis via the thoracolumbar fascia.
Action
- Multifidus hard a workBilateral contraction extends the vertebral column.
- Unilateral contraction contralaterally rotates the vertebral coloumn to the opposite side.
- Evidence points to the multifidus muscle being continuously active in upright postures. In fact, the multifidus is probably active in all anti-gravity activity.
- The multifidus stabilizes the vertebrae as the spine moves. It is thought that the unique desig…
- Multifidus hard a workBilateral contraction extends the vertebral column.
- Unilateral contraction contralaterally rotates the vertebral coloumn to the opposite side.
- Evidence points to the multifidus muscle being continuously active in upright postures. In fact, the multifidus is probably active in all anti-gravity activity.
- The multifidus stabilizes the vertebrae as the spine moves. It is thought that the unique design of the multifidus endows it with extra strength.
Clinical Relevance
- The multifidus muscle is an important stabilizer of the lumbar spine. It functions together with transversus abdominis and pelvic floor musclesfor spine stability. Multifidus muscle weakness and atrophy is associated with chronic low back pain. Core stabilization programsare suggested to increase multifidus cross section area and decrease low back pain. Trigger points in the multifid…
Physiotherapy
- Treatment: Retraining the stabilising muscles of the core is done in a series of steps.The first step is to learn to isolate the muscle. The second step is to learn to co‐contract it in conjunction with the other muscles of the core. The final step is to co‐contract the entire core (connect simultaneously to the pelvic floor, transversus abdominis & multifidus) in coordination …
Multifidus and Back Pain
- Have a look at this 2 min 30 sec. video for some good information of evidence regarding multifidus and low back problems.