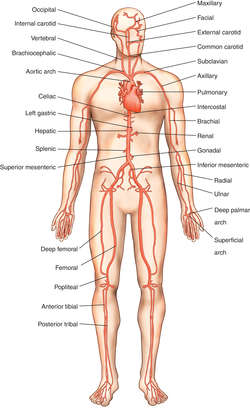
What are the two branches of the common iliac artery?
The branches of the anterior division include:
- Superior vesical artery (supplies vas deferens in males)
- Obliterated umbilical artery (continuation of superior vesical)
- Inferior vesical artery
Are there two brachial arteries in the body?
There are two Brachial arteries but only one Brachiocephalic artery in the body. This is the diagram of branches of arch of aorta : From the picture we can see arch of aorta has three branches : brachiocephalic artery left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery.
What is the purpose of brachial artery?
What is the purpose of the brachial artery? The function of the brachial artery and its branches is to deliver blood to your upper extremities, including your: Biceps brachii muscles, or just biceps. Brachialis muscles (behind your biceps). Elbow joint. Triceps brachii muscles, or just triceps.
What are the branches of the middle cerebral artery?
Parietal lobe
- Anterior parietal: This artery usually originates from a distal MCA branch. ...
- Posterior parietal: Emerges from the posterior end of the Sylvian fissure and extends first posteriorly, and then anteriorly along the posterior of the parietal lobe. ...
- Angular: The angular artery is a significant terminal branch of the anterior or middle trunk of the MCA. ...
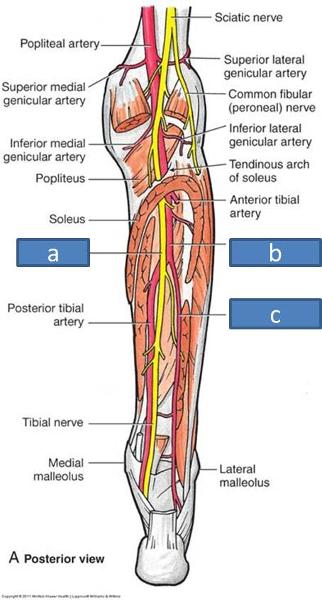
Which is the first branch of the brachial artery?
profunda brachiiBranches. The profunda brachii is the first and main branch of the brachial artery. It arises above the midpoint of the upper arm on the medial aspect of the vessel. However, as it courses posteriorly, it sweeps posterolaterally to the humerus to sit lateral and posterior by the time it reaches the elbow.
What is the largest branch of the brachial artery?
profunda brachii arteryThe profunda brachii artery also referred to as the deep brachial artery, is the first and largest branch of the brachial artery. It originates from the posterior portion of the brachial artery, just inferior to the lower border of the teres major muscle.
How many brachial arteries are there?
Below the cubital fossa, the brachial artery divides into two arteries running down the forearm: the ulnar and radial. In some people, this division occurs higher up, causing these arteries to run through the upper arm. These are the two main branches of the brachial artery.
Are there two brachial arteries?
Yes there are two brachial arteries. One in each arm.
Why is it called brachial artery?
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm....Brachial arteryRight upper limb, anterior view, brachial artery and elbow.DetailsSourceaxillary arteryBranchesProfunda brachii Superior ulnar collateral artery Inferior ulnar collateral artery Radial artery Ulnar artery10 more rows
What is the major artery in the arm?
Here's the main artery, the axillary artery. It emerges from beneath pectoralis minor surrounded by major nerves. As it passes into the arm its name changes. From here on down, it's the brachial artery.
What is the largest artery in the body?
the aortaHow large is the aorta? The aorta is the largest blood vessel in your body. It's more than 1 foot long and an inch in diameter at its widest point.
Where is the brachial artery for blood pressure?
0:060:33Finding the Brachial Artery - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo to locate the brachial artery the easiest way is just to draw a line up the pinky above the bendMoreSo to locate the brachial artery the easiest way is just to draw a line up the pinky above the bend of the elbow. And that's where you'll position your cuff arrow.
How big is the brachial artery?
Ultrasound showed upper-arm brachial artery diameter 8.5 cm above the antecubital fossa as 3.93±0.49 mm. Vascular cross-sectional area measured by oscillometric measurement was 12.3±3.0 mm2. This value was converted to diameter (3.97±0.51 mm) for comparison with ultrasound measurements.
Are there 2 brachiocephalic arteries?
There is no brachiocephalic artery for the left side of the body. The left common carotid, and the left subclavian artery, come directly off the aortic arch. However, there are two brachiocephalic veins....Brachiocephalic artery.Brachiocephalic artery.TA24179FMA3932Anatomical terminology11 more rows
What is the function of the brachial artery?
The brachial artery is the most important source of blood to the arm and hand and is an essential component of the circulatory system. It connects the lower margin of the Teres major tendon in the shoulder to the elbow.
What happens if you cut your brachial artery?
The Brachial artery runs along the inside of your arms. This artery is deep, but severing it will result in unconsciousness in as little as 15 seconds, and death in as little as 90 seconds.
What is the largest artery in the body?
the aortaHow large is the aorta? The aorta is the largest blood vessel in your body. It's more than 1 foot long and an inch in diameter at its widest point.
How big is the brachial artery?
Ultrasound showed upper-arm brachial artery diameter 8.5 cm above the antecubital fossa as 3.93±0.49 mm. Vascular cross-sectional area measured by oscillometric measurement was 12.3±3.0 mm2. This value was converted to diameter (3.97±0.51 mm) for comparison with ultrasound measurements.
Where is the deep brachial artery?
armThe deep brachial artery is a branch of the brachial artery located in the posterior compartment of the arm. Some authors refer to this vessel as the deep artery of arm or the profunda brachii artery. The function of the deep brachial artery is to supply the posterior arm muscles and the shaft of humerus.
Where is common interosseous artery?
cubital fossaThe common interosseous artery is the third main branch of the ulnar artery. It runs in the distal portion of the cubital fossa, posterior to the upper border of the interosseous membrane.
Where is the brachial artery located?
A continuation of the axillary artery in the shoulder, the brachial artery runs along the underside of the upper arm, terminating about a centimeter past the elbow joint. Largely this artery is just below the skin as well as both superficial and deep fascia, which are layers of dense, connective tissue.
What is the function of the brachial artery?
Function. The brachial artery is primarily involved with providing oxygenated blood to the arm and hand. As such, it’s essential for nearly every aspect of upper limb mobility, ensuring that muscle groups and tendons are supplied with the nutrients necessary for proper function.
Why is the brachial artery important?
Because the brachial artery serves such an important role in providing blood to the upper limbs, it can be involved in a number of disorders or conditions. In addition, it can be affected by injury to the area and, in fact, is the most-often injured artery of the upper body due to its vulnerability 3 .
Why is the brachial artery placed on the elbow?
Because the brachial artery is just below skin level —especially around the elbow —doctors use it to measure blood pressure. This explains why the inflatable cuff of the standard blood pressure gauge is placed on the elbow.
Why do surgeons need to clamp the brachial artery?
Surgeons may also need to apply compression of the brachial artery to control blood loss in trauma patients. This is done proximal (above) the site of injury, and, when clamped distal (further down) to the brachial artery, there’s little risk of tissue damage because other arteries can still access the area. 3
Which artery is responsible for wrist bend?
Radial artery: The brachial artery also terminates into the radial artery, which proceeds under the brachioradialis muscle, which is what allows the wrist to bend backward. It also runs laterally to the flexor carpi radialis muscle, which is involved in hand and wrist motion. This artery provides blood to both flexor (back-bending) and extensor (forward-bending) compartments of the forearm.
Where is the Ulnar artery?
Ulnar artery: Starting at the cubital fossa at the end of the brachial artery, the ulnar artery runs through the second and third layers of the flexor muscles in the forearm. It then proceeds above the flexor retinaculum at the wrist, a fibrous band that bends over the carpal bones to form the carpal tunnel, and becomes ...
What is the brachial artery?
22689. Anatomical terminology. The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run ...
Where is the brachial artery palpated?
The brachial artery can be palpated midway along the medial side of the arm.
Which artery gives rise to the following branches?
The brachial artery gives rise to the following branches: It also gives rise to important anastomotic networks of the elbow and (as the axillary artery) the shoulder. The biceps head is lateral to the brachial artery. The median nerve is medial to the brachial artery for most of its course.
Which nerve is lateral to the brachial artery?
The brachial artery is closely related to the median nerve; in proximal regions, the median nerve is immediately lateral to the brachial artery. Distally, the median nerve crosses the medial side of the brachial artery and lies anterior to the elbow joint.
Which artery is the terminal branch of the humerus?
Ulnar artery (a terminal branch) Nutrient branches to the humerus. It also gives rise to important anastomotic networks of the elbow and (as the axillary artery) the shoulder. The biceps head is lateral to the brachial artery. The median nerve is medial to the brachial artery for most of its course.
Where does the deep brachial artery originate?
The deep brachial artery originates from the posteromedial side of the brachial artery at the level of the lower margin of the long head of triceps brachii. It courses posteriorly, passing through the triangular interval of the arm, between the long and medial heads of triceps. The artery then curves around the posterior surface of humerus and emerges into the posterior compartment of the arm.
What is the function of the deep brachial artery?
Some authors refer to this vessel as the deep artery of arm or the profunda brachii artery. The function of the deep brachial artery is to supply the posterior arm muscles and the shaft of humerus.
What is the middle collateral artery?
The middle collateral (posterior descending) artery passes medially and then descends along the lateral intermuscular septum to reach the elbow. It courses over the long head of triceps brachii, being covered with brachialis in its proximal part and with the brachioradialis muscle in its distal part. Along its course, it gives off several perforating branches that supply the surrounding fascia and overlying skin, as well as a small muscular branch for the anconeus muscle. The middle collateral artery terminates posterior to the lateral condyle of humerus by anastomosing with the interosseous recurrent artery, a branch of the ulnar artery. Via this anastomosis, this artery also participates in the arterial network of the elbow.
Which artery gives off small branches to supply the radial nerve?
Along its course through the lateral intermuscular septum, the radial collateral artery gives off small branches to supply the radial nerve, as well as perforating branches to supply the septum itself and the overlying skin.
Which artery supplies the deltoid muscle?
Just prior to its terminal bifurcation, the deep brachial artery gives off three sets of branches; an ascending deltoid branch that anastomoses with the branches of the posterior circumflex humeral artery and supplies the deltoid muscle, muscular collateral branches for the lateral and medial heads of triceps brachii and the nutrient arteries of humerus that feed the humeral shaft.
Which artery follows the radial nerve?
Along its course, the deep brachial artery follows the radial nerve. Together with the nerve, it traverses the radial groove of humerus in the posterior arm, where it is covered by the long head of triceps brachii. Under the long head of triceps, the artery splits into its two terminal branches; radial collateral and middle collateral arteries.
Which artery passes medially and then descends along the lateral intermuscular septum to reach the elbow?
The middle collateral (posterior descending) artery passes medially and then descends along the lateral intermuscular septum to reach the elbow. It courses over the long head of triceps brachii, being covered with brachialis in its proximal part and with the brachioradialis muscle in its distal part.
Which artery supplies blood to the muscles of the upper arm?
The brachial artery supplies blood to the muscles of the upper arm by its branches and to the forearm and hand, by its continuation as the radial and ulnar arteries.
Which artery supplies the blood to the arm, forearm, and hand?
The brachial artery is the main supply of arterial blood to the arm, forearm, and hand .
Where do the superior and inferior collateral arteries arise?
Both of the ulnar collateral arteries arise from the medial surface of the brachial artery and course distally towards the medial aspect of the elbow. They give off smaller branches and anastomose with recurrent vessels that arise distal to the elbow joint.
Where is the profunda brachii?
The profunda brachii is the first and main branch of the brachial artery. It arises above the midpoint of the upper arm on the medial aspect of the vessel. However, as it courses posteriorly, it sweeps posterolaterally to the humerus to sit lateral and posterior by the time it reaches the elbow.
Which artery gives off nutrients to the humerus?
Distal to the profunda, the brachial artery gives off nutrient vessels to the humerus as it slowly courses more medially within the upper arm. As it approaches the elbow, it gives off two further named branches that are part of the peri-articular arterial anastomosis of the elbow.
Where is the ulnar artery located?
The brachial artery bifurcates to form the radial artery and ulnar artery in the cubital fossa at the level of the radial neck, below the bicipital aponeurosis 1.
Can brachial artery be visualized?
It is visualized in radial approaches for angiography and may be used as vascular access for some procedures. It can be well depicted using CT angiography, although indications for such imaging is rare. Modalities used to assess the brachial artery include: US doppler upper limb.
What is the brachial artery?
What is brachial artery. The brachial artery is a branch of a prominent artery – the subclavian artery that changes its name along its course. After leaving the thoracic cavity and passing over the first rib, each subclavian artery becomes an axillary artery. The axillary arteries supply blood to the muscles of the pectoral region and axilla.
Which artery supplies blood to the upper limb?
Beyond this loop, the axillary artery becomes the brachial artery, which supplies blood to the upper limb (see Figure 3). The brachial artery continues down the medial and anterior sides of the humerus and ends just distal to the elbow, supplying the anterior flexor muscles of the brachium along the way.
Where do axillary arteries supply blood?
The axillary arteries supply blood to the muscles of the pectoral region and axilla. The axillary artery crosses the axilla and enters the arm, where it gives rise to the humeral circumflex arteries 1). These vessels supply structures near the head of the humerus.
Which artery pumps blood into the large vessels of the circulatory system?
Brachial artery blood pressure. The heart is responsible for supplying the organs and tissues of the body with blood. To do this it pumps blood into the large vessels of the circulatory system with every beat. The blood that is pumped into these vessels puts pressure on the walls of the vessels.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/truncus-thyrocervicalis-2/nM27JmzxfZTmCEeHKVYbw_Truncus_thyrocervicalis_01.png)