
How do I remember the branches of the brachial plexus?
0:001:32Brachial plexus Mnemonics - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAs you know the branches of brachial plexus are divided into three separate cords flirtual calledMoreAs you know the branches of brachial plexus are divided into three separate cords flirtual called medial cord and posterior. Cord.
What are the 6 divisions of the brachial plexus?
Brachial plexusRootsC5, C6, C7, C8, T1CordsLateral Medial PosteriorTerminal branchesMusculocutaneous nerve Axillary nerve Radial nerve Median nerve Ulnar nerveInnervationComplete sensory and motor innervation of the arm2 more rows
What are the types of brachial plexus?
Brachial Plexus Anatomy From the roots, the brachial plexus nerves branch and fuse through the shoulder and down the arm, classified into a few different sections: trunks, divisions, cords and branches.
How many divisions are in the brachial plexus?
6 divisionsTypically, the brachial plexus is composed of 5 roots, 3 trunks, 6 divisions, 3 cords, and terminal branches, as seen in the image below. Brachial plexus with terminal branches labeled.
What are the five roots of the brachial plexus?
The five roots are the five anterior primary rami of the spinal nerves, after they have given off their segmental supply to the muscles of the neck. The brachial plexus emerges at five different levels: C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1.
What are the three major nerve plexus?
The cervical plexus provides nerve connections to the head, neck, and shoulder. The brachial plexus provides connections to the chest, shoulders, upper arms, forearms, and hands. The lumbar plexus provides connections to the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves.
Are there 2 brachial plexus?
The brachial plexus is divided into Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, and Branches. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches that leave the plexus at various points along its length.
What are four 4 types of injuries that may affect the brachial plexus?
These injuries can occur in several ways, including:Contact sports. Many football players experience burners or stingers, which can occur when the nerves in the brachial plexus get stretched beyond their limit during collisions with other players.Difficult births. ... Trauma. ... Tumors and cancer treatments.
What are four 4 types of injuries that may affect the brachial plexus?
These injuries can occur in several ways, including:Contact sports. Many football players experience burners or stingers, which can occur when the nerves in the brachial plexus get stretched beyond their limit during collisions with other players.Difficult births. ... Trauma. ... Tumors and cancer treatments.
What are the 4 major plexuses?
Of the four major nerve plexuses (cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral), only the brachial plexus and sacral plexus can be assessed satisfactorily in the EDX laboratory.
What are the 5 major nerve Innervations of shoulder arm?
The fifth and final level of the brachial plexus are the five nerves that feed the shoulder and arm called "branches." These five branches are named the musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, and ulnar nerves.
What are the five principal plexuses?
Nerve plexuses throughout the body tend to be named after the area in which the plexus occurs and the organs, limbs, and tissues it serves. Examples include the cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral, celiac, and coccygeal plexuses.
What is the structure of the brachial plexus?
Structure. The brachial plexus is made up of nerve cells that make up the different sections of the brachial plexus. Nerves are made up of axon fibers that transmit information to and from the brain. Nerve cells are surrounded by supportive cells called neuroglia.
How many nerves exit the brachial plexus?
1 . Roots (5): The brachial plexus begins when five nerves exit the lower cervical and upper thoracic spinal cord (from the ventral rami). C5-C8: Four nerve roots that exit from the lower section of the cervical spinal cord.
What is the brachial plexus?
Anatomy. The brachial plexus consists of a network of nerve roots, cords, and branches that share common functions. There is one brachial plexus on each side of the body that carries the nerves to each arm. The anatomy can be confusing at first, but is easier to conceptualize by breaking it down into five different regions.
What is the C5-C8 nerve?
C5-C8: Four nerve roots that exit from the lower section of the cervical spinal cord. T1: The first nerve exiting the thoracic spinal cord. The roots of the brachial plexus leave the spinal cord and pass behind the scalenus anterior muscle.
How many nerve trunks are there in the spinal cord?
Trunks (3): Shortly after the five nerves exit the spinal cord, they merge to form three nerve trunks.
Why is it important to understand the anatomy of the brachial plexus?
Understanding the anatomy (roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and terminal branches) of the brachial plexus is important in determining the site of an injury and designing treatment.
Where does the brachial plexus originate?
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that originate in the spinal cord in the neck , travel down the neck (via the cervicoaxillary canal) and into the armpit. It contain the nerves that, with only a few exceptions, are responsible for sensation (sensory function) and movement (motor function) of the arms, hands, and fingers.
What is the term for a brachial plexus injury?
Erb’s palsy refers to an injury to the upper roots of the brachial plexus (typically C5-6). It most commonly occurs as a result of a stretching injury during a difficult vaginal delivery.
What is the plexus of the cervical spine?
The plexus is formed by the anterior rami (divisions) of cervical spinal nerves C5, C6, C7 and C8, and the first thoracic spinal nerve, T1. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the brachial plexus – its formation and anatomical course through the body.
How many trunks does the brachial plexus have?
At the base of the neck, the roots of the brachial plexus converge to form three trunks. These structures are named by their relative anatomical location:
What are the roots of the spinal cord?
The ‘roots’ refer the anterior rami of the spinal nerves that comprise the brachial plexus. These are the anterior rami of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1. At each vertebral level, paired spinal nerves arise. They leave the spinal cord via the intervertebral foramina of the vertebral column.
Which muscle is innervated by the motor?
Motor Functions: Innervates the brachialis, biceps brachii and coracobrachialis muscles.
Where is the brachial plexus?
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibres that supplies the skin and musculature of the upper limb. It begins in the root of the neck, passes through the axilla, and runs through the entire upper extremity. The plexus is formed by the anterior rami (divisions) of cervical spinal nerves C5, C6, C7 and C8, ...
How many major branches are there in the axilla?
Major Branches. In the axilla and the proximal aspect of the upper limb, the three cords give rise to five major branches. These nerves continue into the upper limb to provide innervation to the muscles and skin present. In this section, we shall concentrate on these five nerves.
What is the loss of sensation in the lateral aspect of the upper limb?
A loss of sensation in the lateral aspect of the upper limb is also common with such injuries. An inferior brachial plexus injury is far less common, but can occur when a person grasps something to break a fall or a baby's upper limb is pulled excessively during delivery.
What nerves are damaged when a motorcyclist collides with the floor?
This shows a simulated example of motorcyclist colliding with the floor at an angle, which may damage the brachial plexus nerves. The photo shows how head and shoulder are extremely separated, which may stretch or even tear the nerves in the between area. Protective gear can help prevent nerve damage by providing extra support on the opposite side of the head to prevent over-stretching the neck.
How many branches does the brachial plexus have?
The brachial plexus is divided into five roots, three trunks, six divisions (three anterior and three posterior), three cords, and five branches. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, ...
Why do newborns have upper brachial plexus injuries?
Upper brachial plexus injuries are frequent in newborns when excessive stretching of the neck occurs during delivery. Studies have shown a relationship between a newborn's weight and brachial plexus injuries; however, the number of cesarean deliveries necessary to prevent a single injury is high at most birth weights.
What is the brachial plexus?
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The brachial plexus is a network ( plexus) of nerves (formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve ( C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1 ). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit.
How does protective gear help with nerve damage?
Protective gear can help prevent nerve damage by providing extra support on the opposite side of the head to prevent over-stretching the neck. Main article: Brachial plexus injury. Injury to the brachial plexus may affect sensation or movement of different parts of the arm.
What is the cause of a rupture of the brachial plexus?
A common brachial plexus injury is from a hard landing where the shoulder widely separates from the neck (such as in the case of motorcycle accidents or falling from a tree). These stretches can cause ruptures to the superior portions of the brachial plexus or avulse the roots from the spinal cord.
What is the cord of the axillary artery?
The artery and cords are ensheathed by an extension of the prevertebral fascia known as the axillary sheath – this is a target for brachial plexus nerve blocks. The cords divide around the third part of the axillary artery into their five terminal branches: the musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median and ulnar nerves.
How to stay calm when given a brachial plexus diagram?
The way to stay calm is to look for the “M” shape formed around the axillary artery by the musculocutaneous, median and ulnar nerves. This is a really easy landmark to find and will give you your bearings.
What is the brachial plexus?
The brachial plexus is a complex intercommunicating network of nerves formed by spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1. The brachial plexus, frequently appears in examination questions.
What causes a traction injury?
Traction injury due to excessive lateral neck flexion towards the contralateral side, or excessive shoulder depression, resulting in violent stretching +/- tearing of the upper portion of the brachial plexus
What is the name of the neurological deficits in the neck?
The most common three you’ll need to know about are Erb’s palsy, Klumpke’s palsy and Horner’s syndrome.
Which part of the brachial plexus affects individual nerves?
Any part of brachial plexus – may affect individual nerves/cords or entire plexus
Which is easier to learn, the brachial plexus or the dorsal scapular nerve?
The brachial plexus is easier to learn if you break it down into its component segments and tackle them one at a time: these are roots, trunks, divisions, cords and terminal branches. ROOTS – There are five nerve roots from C5-T1, which give three nerve branches : The dorsal scapular nerve. The long thoracic nerve.
What is a brachial plexus injury?
The brachial plexus can be injured in many different ways — from pressure, stress or being stretched too far. The nerves may also be cut or damaged by cancer or radiation treatment. Sometimes, brachial plexus injuries happen to babies during birth.
How are brachial plexus injuries diagnosed?
A health care provider will examine the hand and arm and test for sensation and function to help diagnose a brachial plexus injury.
What nerves are vulnerable during birth?
In babies, the brachial plexus nerves in the shoulder are vulnerable during birth. Injury to the brachial plexus is fairly common during birth, occurring in one to two births per 1,000. Larger babies in difficult vaginal deliveries are particularly prone to this injury, as are babies of mothers who have diabetes.
How long does it take for a brachial plexus to heal?
Because nerves heal slowly, brachial plexus injury recovery can take several weeks to months, depending on the severity. During this time, regular physical therapy appointments to prevent muscle atrophy and contractures are often necessary.
What is the cause of abrachial plexus avulsion?
A brachial plexus avulsion occurs when the root of the nerve is completely separated from the spinal cord. This injury is usually caused by trauma, such as a car or motorcycle accident. More severe than ruptures, avulsions often cause severe pain. Because it is difficult and usually impossible to reattach the root to the spinal cord, avulsions can lead to permanent weakness, paralysis and loss of feeling.
How much does a brachial plexus injury heal?
Brachial plexus injuries often heal well if they aren’t severe. Many people with minor brachial plexus injuries recover 90%–100% of the normal function of their arms.
What is it called when the nerves are stretched to the point of injury?
When the nerves are stretched to the point of injury, it is referred to as neuropraxia. There are two main ways this injury occurs: compression and traction. In a compression injury, the brachial plexus nerve root is compressed, usually by the rotation of the head.
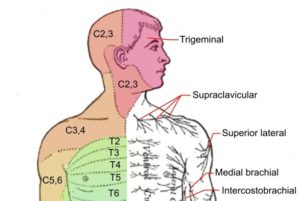
What Is Brachial Plexus?
Anatomy
Roots
Trunks
- The Brachial Plexus could be a network of nerves that offers rise to all or any of the motor and sensory nerves of the upper extremity. It rises from the anterior rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 that sustain various combinations and splits into trunks and divisions until they finally create their terminal branches. These terminal branches are responsible for sensory and motor innervation …
Divisions
- The Brachial plexus originates from the anterior rami of spinal nerves C5-T1, which form the roots of the brachial plexus. The roots quickly merge to make trunks, which subsequently split into divisions. Finally, the divisions combine into cords of the brachial plexus, that give off the terminus branches of the brachial plexus. Apart from the terminal branches of the plexus brachi…
Cords
- The ‘roots’ reference the anterior rami of the spinal nerves that include the brachial plexus. These are the anterior rami of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1. At each vertebral level, paired spinal nerves arise. They move the funiculus via the intervertebral foramina of the back. Each nerve then divides into two parts an anterior and a posterior ramus. The roots of the plexus brachialis are f…
Branches
- Each trunk contains a well-known scheme of origin from the roots of the brachial plexus: 1. The superior trunk is created by the roots of C5 and C6. 2. The middle trunk is created from the basis of C7 only. 3. The inferior trunk is created by the roots of C8 and T1. How to easily remember this: imagine that your fingers are the five anterior branch...
Clinical Significance
- As they reach the posterior aspect of the center third of the clavicle, each of the three trunks divides into an anterior and posterior division. This yields a complete 6 divisions (3 anterior and three posteriors), which still pass inferiorly behind the clavicle to enter the axillary region. The divisions don’t produce to any branches. Instead, they are going on to merge with each other to …
Specific Branches
- The cords of the brachial plexus are formed by the three anterior and three posterior divisions that merge in a very specific way: 1. The lateral cord is created by the merger of the anterior division of the superior trunk and the anterior division of the center trunk. 2. The medial cord may be a direct continuation of the anterior division of the inferior trunk. 3. The posterior cord is made by the me…
Clinical Relations
- Branches of the lateral cord
The lateral cord provides arise to a couple of preterminal branches; the lateral pectoral nerve and the lateral root of the median nerve. It also provides one of the terminal branches of the brachial plexus, the musculocutaneous nerve. - Branches of the medial cord
The medial cord provides the medial pectoral nerve, medial brachial cutaneous nerve, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the medial root of the median nerve, as well as the ulnar nerve (another terminal branch of the brachial plexus).
Overview
- Injury to the plexus brachialis may affect the sensation or movement of various parts of the arm. Injuries are often caused by the shoulder being pushed down and also the head being pulled up, which stretches or tears the nerves. Injuries related to malpositioning commonly affect the nerve plexus nerves, instead of other peripheral nerve groups. because the brachial plexus nerves are …
Structure
- The branches are listed below. They primarily branch from the cords, but some originate from earlier structures.
Function
- Brachial plexus injury Injuries to the plexus brachialis affect both motor and sensory functions within the upper limb. Different injuries, like inflammation, stretching, and wounds within the lateral cervical region of the neck or within the axilla may cause nerve plexus injuries, and also the manifestations rely upon the part of the plexus that’s affected. In any case, injuries to the plexus …
Clinical significance
The brachial plexus is a network (plexus) of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit. It supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand.
Bibliography
The brachial plexus is divided into five roots, three trunks, six divisions (three anterior and three posterior), three cords, and five branches. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at various points along its length. A common structure used to identify part of the brachial plexus in cadaver dissections is the M or W shape …
External links
The brachial plexus provides nerve supply to the skin and muscles of the arms, with two exceptions: the trapezius muscle (supplied by the spinal accessory nerve) and an area of skin near the axilla (supplied by the intercostobrachial nerve). The brachial plexus communicates through the sympathetic trunk via gray rami communicantes that join the plexus roots.
The terminal branches of the brachial plexus (musculocutaneous n., axillary n., radial n., median …