
Dry rot is caused when dampness combined with lack of ventilation provides the ideal conditions for fungal attack. It can affect all types of property, historic or modern and can grow within the cracks and cavities in the walls, feeding off debris and wood behind the plaster.
What is the best treatment for dry rot?
The fungicides and biocides used to treat and repair dry rot are:
- Modern, water-based microemulsions.
- Low odour, low hazard and Health and Safety Executive (HSE) approved.
- Enable treated rooms to be re-occupied after just one hour.
Can dry rot affect your health?
Dry rot spores in themselves are not harmful to your health. However, the damp conditions the fungus needs to germinate can represent a health hazard for older people, infants and those with respiratory conditions.
How to detect dry rot?
- infrared thermography;
- short-wave radar;
- automatic weather stations; and
- total building monitoring using specialist data loggers.
What do you need to know about dry rot?
What are the causes of tire dry rotting?
- Sunlight and hot climate conditions. If you are not using a summer tire during the summer season, you likely experience dry rotting. ...
- Low tire pressure. It is not appropriate that you drive your car with a flat tire or one with low pressure. ...
- Improper car storage and tire storage. ...

How do I get rid of dry rot?
Any affected timbers should be removed and replaced with pre-treated timber. Any remaining timbers at risk of being affected by the dry rot should be treated with an effective fungicide. Where the dry rot has passed through the masonry, it should be isolated using physical containment and / or masonry sterilisation.
How do you stop dry rot in wood?
Boric acid (borate) is one of the most effective fungicides for use in treating wood rot. It can be applied to wood during construction to prevent future rot, or as a treatment to stop an active decay fungus from growing.
Is dry rot caused by water?
Like all wood rotting fungi, dry rot requires water, although what makes it particularly common and destructive is that it can survive in moisture levels as low as 22%. It's common to have a level of dampness in your home (8%-16% is considered normal), but excess moisture will result in damp.
Can dry rot be prevented?
Applying a fungicide with borate to kill fungus is one of the best ways to prevent dry rot.
How quickly does dry rot spread?
Dry rot can spread up to 80 mm per day, if it has optimal conditions for growth. In order to achieve this intense growth, dry rot needs temperatures between 66- and 70-degrees Fahrenheit. Further, unlike many other fungi, dry rot does not need a lot of moisture to grow quickly.
What happens if dry rot is left untreated?
Dry rot is a type of dampness primarily found in aged homes and buildings. If left untreated, it can cause wooden structures to weaken and the building's foundation will get disturbed.
How much does it cost to fix dry rot?
The national average materials cost to repair dry rot is $69.53 per repair, with a range between $65.05 to $74.00. The total price for labor and materials per repair is $528.53, coming in between $338.51 to $718.55. Your actual price will depend on your location, job size, conditions and finish options you choose.
Is dry rot covered by insurance?
Is dry rot covered by insurance? Dry rot is a general exclusion for most insurers. If the dry rot can be proven to be the fault of bad building work – like, for example, botched plumbing – you might be able to claim back some of the costs.
Can dry rot spread from house to house?
After that, the dry rot spores will start to appear and develop into the fungus; from there, the fungus can spread throughout your house to other wooden structures.
Does vinegar stop dry rot?
White vinegar will stop wood rot because it is a fungicide, which has antimicrobial properties. As wood rot is caused by fungi that require an acidic environment ranging from 0-5.5 (pH), white vinegar solves the problem by changing the pH level in the wood.
How can you tell if you have dry rot?
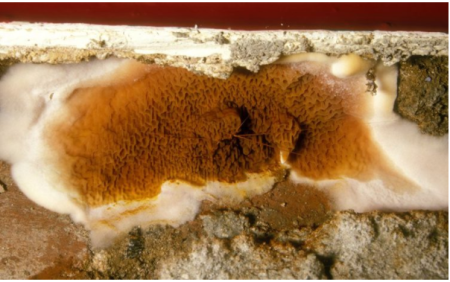
Identifying Dry Rot grey-whitish 'skin' tinged with yellow and lilac patches. mushroom-like fruiting body – soft, fleshy and looks like a pancake or a bracket – often orangey in colour, rust coloured in the centre, with wide pores. red dust from spreading spores, often found around fruiting bodies.
Do termites cause dry rot?
The common type of wood rot you may encounter and what is often confused with termite damage is dry rot. Dry rot is caused by fungi that attack wood and destroys its interior structure, hollowing it out from the inside.
Does vinegar stop dry rot?
White vinegar will stop wood rot because it is a fungicide, which has antimicrobial properties. As wood rot is caused by fungi that require an acidic environment ranging from 0-5.5 (pH), white vinegar solves the problem by changing the pH level in the wood.
Will baking soda stop wood rot?
Fungicides to defeat brown rot include: baking soda, hydrogen peroxide, tea tree oil, boron solutions, ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, vinegar, etc. Since the dry rot fungus requires an acidic environment from pH 0 to 5.5, certain of these fungicides work because they change the pH.
Can rotting wood be saved?
If you catch rotted wood in time, you can successfully repair it with epoxy resin. Repairing rotted wood means you'll be able to stain or paint it again to blend in with the surrounding wood.
Does bleach stop wood rot?
Bleach can be used to effectively kill wood rot and stop its spread. It attacks the fungi that causes rot and stops it from growing. Bleach can be applied as a spray or directly on the rotten areas with a cotton swab.
What is dry rot?
Dry rot is a common synonym for wood decay, but the term actually refers to a wide variety of fungi, all of which share a common characteristic–their love of wood. They feed off of the cellulose and humidity found in wood until it decays.
What causes dry rot in homes?
Three environmental conditions need to be met in order for dry rot to start growing:
Where to look for dry rot in the house?
In a home, the three conditions necessary for the development of dry rot are easily met. Furthermore, poor ventilation and stale air can increase humidity and keep fungal spores inside. Moisture intrusion resulting from condensation, leaks or flooding can provide the large quantities of water necessary for fungal growth.
How to prevent dry rot?
As the saying goes, prevention is better than the cure. And it just so happens that dry rot can be prevented by following these simple steps.
Why is it important to know when to call a dry rot remediation company?
Since the fungus can grow quickly (often hidden from plain sight), it is important for homeowners to be aware of the proper steps to take in order to detect, eliminate and prevent dry rot in their homes. It is also important for homeowners to understand when they should call remediation professionals.
How to tell if a wood is dry rot?
It is not uncommon for dry rot to grow out of sight; for example, behind walls or in your attic. In these cases, look for these signs that may hint at its presence: 1 Wood that’s crumbling or falling apart, 2 The presence of mycelium (white or grey thread-like structures that resemble plant roots), even on inorganic materials 3 Stains or discoloration that may represent water damage or moisture intrusion 4 Bubbling paint or wallpaper
How to get rid of dry rot on wood?
There are many other ways to get rid of dry rot, depending on the size of your problem. Specially engineered anti-fungal cleaners can eliminate small contaminations. Similarly, a heat treatment can be applied to contaminated areas that are limited in size, as long as the dry rot has not penetrated deep inside the wood.
What is dry rot?
Dry rot occurs when there is moisture ingress or dampness present in a property, this moisture can be present as a result of the following forms of dampness:
How does dry rot get its name?
Dry rot gets its name due to the dry and brittle state it leaves timber after exhausting away the woods nutrients. So for spores to germinate, moisture must be present within the wood above the fibre saturation point.
How does dry rot affect properties?
Dry rot can affect all types of properties regardless of their age as long as there are certain environmental elements allowing it to survive and spread. These elements are a source of food (wood), oxygen, moisture and temperature. In optimal environmental conditions, dry rot can grow up to one meter per month!
What is dry rot?
Dry rot is a fungal growth that feeds off of the cellulose that exists in timber. It can spread through most building materials, including brick walls, and when left untreated causes serious structural problems.
Where is dry rot found?
Dry rot is often found in lofts of older buildings where ventilation has not been installed. Another place that it often forms is to floor joists below floors, particularly where the air bricks or vents are either blocked or not working effectively.
Why is condensation a problem in a house?
Poorly insulated homes will have colder internal surface which will lead to condensation forming during the winter. Even in modern homes, if the building was not constructed properly, a gap in the insulation or a cold bridge in the structure can allow condensation to form. This will increase the risks of dry rot developing.
How to prevent dry rot in bathroom?
To minimise the risk of dry rot starting due to condensation you should ensure that all bathrooms and rooms with sinks are fitted with effective mechanical extract fans, ideally that meet the flow rates set out in the Building Regulations Approved Document F.
What is the main source of moisture in the UK?
The main source of moisture in the UK that forms dry rot is not from leaks, but instead from condensation. High levels of condensation form in our homes when we shower, wash dishes, wash clothes, and when we lie in bed all night breathing into a room with the doors and windows closed.
What is damp proofing?
A damp proof course is a waterproof layer of material in the external walls of a building that is designed to prevent moisture from moving any further up the wall than where the damp proof course is fitted.
What is the most common fungus that is associated with dry rot?
The most common fungus that is associated with dry rot is called Serpula Lacrymans. As it feeds off timber it grows and spreads leaving the timber dry and brittle with square-edged, cuboidal cracking that is easily recognisable. This ultimately leaves the timber significantly weakened and incapable of performing its structural role.
Why is dry rot called brown rot?
The term was used because the damage was present in cured or dried timber of ships and buildings and was thought to be caused by internal ‘fermentations’ rather than water. This contributes to the Etymological fallacy that dry rot requires less or no water than other species that use the brown rot decay mechanism.
How to treat dry rot in wood?
In some cases after this is done, decayed areas can be treated with special epoxy formulations that fill-in the channels of the damaged wood, killing the rot and improving structural integrity. However, this type of treatment can actually promote decay in wood in exterior service unless the epoxy application is designed to shed water. Epoxy or other polymers will trap moisture behind the patch, causing more decay in the surrounding previously uninfected zones unless the repaired zone is protected from recurring water events. Commercial ethylene glycol (commonly sold as antifreeze) and many other toxic diffusible compounds can diffuse into the wood to kill the fungus, but they also can diffuse out of wood that is repeated wetted. Diffusion of these toxic compounds out of the wood, and into surrounding soils and plants is not appropriate from a toxicity or environmental standpoint, and these types of treatment are not recommended for wood in-service. Certain copper compounds, such as copper naphthenate, are available as a brushable solution and are frequently used when dry-rot damage is repaired by splicing in new wood; after removal of bulk rotten wood the remaining original surface is saturated with such a compound (typically green in color) before application of the new wood.
What causes wood to decay?
Wood decay caused by the brown rot fungus Serpula lacrymans ( true dry rot) Damaged wall with fungal growth. Dry rot is wood decay caused by certain species of fungi that digest parts of the wood which give the wood strength and stiffness. It was previously used to describe any decay of cured wood in ships and buildings by a fungus which resulted ...
What causes brown rot in wood?
Dry rot is the term given to brown rot decay caused by certain fungi that deteriorate timber in buildings and other wooden construction without an apparent source of moisture. The term is a misnomer because all wood decaying fungi need a minimum amount of moisture before decay begins. The decayed wood takes on a dark or browner crumbly appearance, with cubical like cracking or checking, that becomes brittle and can eventually crush the wood into powder. Chemically, wood attacked by dry rot fungi is decayed by the same process as other brown rot fungi. An outbreak of dry rot within a building can be an extremely serious infestation that is hard to eradicate, requiring drastic remedies to correct. Significant decay can cause instability and cause the structure to collapse.
What is dry rot in a boat?
An explanation of the term "dry rot" circles around boatyards periodically. In the age of wooden ships, boats were sometimes hauled for the winter and placed in sheds or dry dock for repair. The boats already had some amount of rot occurring in the wood members, but the wood cellular structure was full of water making it still function structurally. As the wood dried out, the cell walls would crumble. In other words, the wood was already rotten and as the boat dried, the wood collapsed and crumbled, causing the workers in the yard to determine it was "dry rot", when in fact, the wood had been rotten all along.
What causes a structure to collapse?
Significant decay can cause instability and cause the structure to collapse. The term dry rot, or true dry rot, refers to the decay of timbers from only certain species of fungi that are thought to provide their own source of moisture and nutrients to cause decay in otherwise relatively dry timber.
How many stages of dry rot are there?
The life-cycle of dry rot can be broken down into four main stages. Dry rot begins as a microscopic spore which, in high enough concentrations, can resemble a fine orange dust. If the spores are subjected to sufficient moisture they will begin to grow fine white strands known as hyphae.
What is dry rot in tires?
What Is Tire Dry Rot? Most people only think about checking the tread on their tires to make sure it hasn’t worn down too far. That’s an important part of tire maintenance, but just because the tread is good doesn’t mean your tires don’t need to be replaced. Even a tire with a good tread can suffer from tire dry rot.
Why do tires dry out?
Tire dry rot happens when a tire’s rubber compounds slowly break down over time due to weather exposure, temperature fluctuations or physical wear.
How to tell if a tire is rotting?
Spotting Signs of Tire Rot. Just as you would check your tires’ tread, you should check for signs of dry rot, which is easy to spot on the sidewall. Look for cracks or flaking in the rubber, which may even come off in small pieces if you touch it with your fingers.
Why is dry rot called dry rot?
The name is actually a misnomer because at one time it was thought that dry rot did not require moisture in order to flourish.
WHAT IS DRY ROT?
is a type of wood decay caused by a fungus. It’s also known as brown rot in some parts of the country. Dry rot feeds on organic matter – particularly wood – and once it gets into the wood, it continues to spread until it has colonized an extremely large area.
How does dry rot spread?
Like most other forms of fungus, dry rot spreads through spores traveling through the air. In this respect, you can think of dry rot as being like a type of mold (with all the implications that has for prevention and treatment). The fungus produces spores, which spread through the air, carried on the wind until they land on a surface. If the surface is wood and has the requisite level of moisture, then the spores will germinate.
Why is dry rot bad?
The name is actually a misnomer because at one time it was thought that dry rot did not require moisture in order to flourish.
What temperature does dry rot spread?
In addition to moisture, dry rot spores also have an optimal temperature, preferring wood that is between 71 and 77 degrees. This means that dry rot tends to flourish in warm parts of the country, or more readily during the spring and summer months. Dry rot does not spread easily when the temperatures are either side of this window. Dry rot also needs oxygen to flourish.
What happens when dry rot is in wood?
Once dry rot gets into the wood, the wood is left weakened and brittle and often has a ‘crumbly’ or ‘blocky’ appearance.
How does dry rot affect wood?
What makes dry rot so damaging is that the fungus effectively ‘eats’ the wood, breaking down the cellulose and the hemicellulose, both of which are critical to the strength of the wood. Once the dry rot has broken down these compounds, wood no longer has the same resilience as it initially had, and is therefore of no use in construction. If the wood is already part of a structure, it can fundamentally damage the weight-bearing ability, thereby leading to collapse.
How does dry rot occur?
In order for dry rot to occur, the wood must first be exposed to excess moisture and air. As this moisture permeates the wood, it becomes a breeding ground for bacteria and micro-fungi which in turn begin to break down the wood’s cell structure. This creates room for more moisture. Once the moisture level exceeds 30 percent, the wood is susceptible to the dry rot fungus.
What is dry rot?
Dry rot is actually a species of wood fungus known as Serpula lacrymans. This fungus normally feeds off of woodland timber, but is known to also affect wood in both ships and buildings. Its common name comes from the way in which it consumes the cell walls which give timber its strength, leaving it dry and brittle.
Why is my house exposed to dry rot?
Due to the fact that dry rot spores exist throughout the atmosphere, your home is already exposed to them, even if the wood itself is not infected.
How does dry rot spread?
As with many fungi, dry rot spreads through airborne spores. Upon landing in a hospitable location, the spores germinate and begin to spread rapidly. Colonies of dry rot are known to spread through masonry in search of additional wood, creating even more damage to your home.
What is the best way to treat dry rot in wood?
Borate-based preservatives are often used to treat new wood, and may also be used as a means to destroy dry rot in existing wood. This method involves either drilling holes in the affected wood and injecting a borate solution or spraying the solution over the infected wood. The most common borate solution used for treating an existing problem is Bora-Care.
How to get rid of dry rot on wood?
An expensive but highly effective method is to remove all wood which has been affected by dry rot. The surrounding areas should be treated with fungicides to kill any additional traces of the fungus. This method has been traditionally used to combat dry rot, which was considered very difficult to eliminate.
How much does it cost to repair dry rot in a house?
But what about repairing more extensive damage? Homewyse gives a basic estimated range of $319 to $728 for simple repairs using local materials and a contractor.
How to prevent dry rot in a house?
Any area of the home with a plumbing fixture. The only way to prevent dry rot is to keep wood dry. Period. Regular inspections of thehome, and taking immediate action when dampness or dry rot is located will keep the damage to a minimum.
Why is my wood rotting?
Causes of Dry Rot in Wood. Fungus and damp conditions cause dry rot. The important thing to keep in mind, there are millions of fungus spores living around us all the time. When given the right conditions, spores will thrive on the wood in our homes.
How to test for rot in wood?
If spotted, test the wood for rot by touching the wood with a screwdriver or other hard object. If the wood is easily penetrated, flakes away, or spongy feeling – you have rot. If the wood still spears in good condition, take steps to dry the damp wood with a fan or even a humidifier (in basements).
What causes brown rot in wood?
There are different types of rot in wood. But all types are caused by fungus – nature’s garbage disposal. Dry Rot, (also referred to as “Brown-Rot”), is the most common type and fastest spreading. Wise Property Care (1) has a complete list of all types of rot causing fungus.
What happens if you have dry rot on your roof?
If dry rot has started, the blade will insert deep into the siding. Inspect your roof for any missing shingles or tiles. Open spaces allow water to penetrate the lower layers and could cause the wood framing to get damp and leave you open for dry rot.
How to tell if a window has dry rot?
Check door frames and window sills/trim for gaps, crumbling edges, spongy feeling wood. Remember dry rot spreads, so if signs are noticed just in corners or small sections, there’s a chance it could spread to the framing hidden in the walls.
When is it necessary to replace dry rot?
Replacing dry rot is necessary for larger sections when patching just won’t do. This is necessary when siding is rotted, more than 50% of a window or door frame is rotted, or the rot expands over areas larger than 1 cubic foot.
How do you know if you have a dry socket?
Signs and symptoms of dry socket may include: Severe pain within a few days after a tooth extraction. Partial or total loss of the blood clot at the tooth extraction site, which you may notice as an empty-looking (dry) socket. Visible bone in the socket.
What does it mean when you have a dry socket after a tooth extraction?
Partial or total loss of the blood clot at the tooth extraction site, which you may notice as an empty-looking (dry) socket. Pain that radiates from the socket to your ear, eye, temple or neck on the same side of your face as the extraction.
How long does it take for a tooth to dry out after extraction?
If you develop dry socket, the pain usually begins one to three days after your tooth is removed. Dry socket is the most common complication following tooth extractions, such as the removal of third molars (wisdom teeth). Over-the-counter medications alone won't be enough to treat dry socket pain.
How to get rid of a blood clot in your socket?
Drink lots of water after the surgery. Avoid alcoholic, caffeinated, carbonated or hot beverages for as long as your dentist or oral surgeon recommends. Don't drink with a straw for at least a week because the sucking action may dislodge the blood clot in the socket.
What to do for dry socket after surgery?
These steps may include recommending one or more of these medications, which may help prevent dry socket: Antibacterial mouthwashes or gels immediately before and after surgery. Oral antibiotics, particularly if you have a compromised immune system. Antiseptic solutions applied to the wound.
Can oral contraceptives cause dry socket?
Oral contraceptives. High estrogen levels from oral contraceptives may disrupt normal healing processes and increase the risk of dry socket. Improper at-home care. Failure to follow home-care guidelines and poor oral hygiene may increase the risk of dry socket. Having dry socket in the past.
Overview
Dry rot is wood decay caused by one of several species of fungi that digest parts of the wood which give the wood strength and stiffness. It was previously used to describe any decay of cured wood in ships and buildings by a fungus which resulted in a darkly colored deteriorated and cracked condition.
The life-cycle of dry rot can be broken down into four main stages. Dry rot begi…
Discussion
Dry rot is the term given to brown rot decay caused by certain fungi that deteriorate timber in buildings and other wooden construction without an apparent source of moisture. The term is a misnomer because all wood decaying fungi need a minimum amount of moisture before decay begins. The decayed wood takes on a dark or browner crumbly appearance, with cubical like cracking or checking, that becomes brittle and can eventually crush the wood into powder. Che…
Historical use of the term "dry rot"
'Dry rot' is an 18th-century term that generally described what is now called brown rot. The term was used because the damage was present in cured or dried timber of ships and buildings and was thought to be caused by internal ‘fermentations’ rather than water. This contributes to the Etymological fallacy that dry rot requires less or no water than other species that use the brown rot decay mechanism.
Treatment of dry rot timber
Dry rot can be very difficult to remediate unless all of the decayed wood and spores are removed. In some cases after this is done, decayed areas can be treated with special epoxy formulations that fill-in the channels of the damaged wood, killing the rot and improving structural integrity. However, this type of treatment can actually promote decay in wood in exterior service unless the epoxy application is designed to shed water. Epoxy or other polymers will trap moisture behind t…
See also
• Mold health issues
• Wet rot
• Wood-decay fungus