Some common factors linked to stunting include:
- Poor nutrition and a lack of access to diverse foods
- Poor sanitation and no access to clean drinking water
- Lack of proper healthcare for children and their mothers
- Inadequate psychosocial stimulation and/or parent-infant bonding
What is stunting in child development?
WHO defines stunting as the impaired growth and development that children experience from poor nutrition, repeated infection, and inadequate psychosocial stimulation. Children are stunted if their height-for-age is less than -2 standard deviations of the WHO Child Growth reference.
What are the factors that lead to stunting?
Factors leading to stunting are established early in life. The findings in these two reports are not unique. There is a consensus that the causes of stunted growth are primarily found early in life or even before conception. Conditions and environment of the girl who later becomes a mother are central.
What are the causes of stunted growth?
Chapter 2. Stunted growth: what actually causes it? The most direct causes are inadequate nutrition (not eating enough or eating foods that lack growth-promoting nutrients) and recurrent infections or chronic or diseases which cause poor nutrient intake, absorption or utilization. Then there is the lack of care and stimulation for development…
What are the long term effects of stunting?
The effects of stunting are lasting and generally irreversible. Children over the age of two who are stunted are unlikely to be able to regain their lost growth potential. In addition, children who experience stunting have an increased risk for cognitive and learning delays.
What are the effects of stunting?
Stunting has long-term effects on individuals and societies, including poor cognition and educational performance, low adult wages, lost productivity and, when accompanied by excessive weight gain later in childhood, an increased risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases in adult life (7).
What are the factors that affect stunting?
Factors significantly associated with stunting were: parasite infestation (OR = 1.8, 95% CI: 1.3–2.5), anaemia (OR = 1.7, 95% CI: 1.3–2.7), low body mass index (OR = 1.2, 95% CI: 1.1–1.3), frequent gastroenteritis (OR = 1.1, 95% CI: 1.06–1.2), first-cousin consanguinity of parents (OR = 1.3, 95% CI: 1.2–1.6) and ...
What is the main cause of stunting in children under the age of five?
Stunting in children under the age of 5 years Stunting is usually associated with low socio-economic conditions, poor maternal health and nutritional status, inappropriate feeding and frequent hospital admissions in early life.
What causes stunting and wasting?
Stunting results from chronic undernutrition, which retards linear growth, whereas wasting results from inadequate nutrition over a shorter period, and underweight encompasses both stunting and wasting.
What are the main causes of malnutrition?
Malnutrition, at its core, is a dietary deficiency that results in poor health conditions....Here, we breakdown four major factors that contribute to malnutrition in children:Poor qualify of diet.Poor maternal health.Socioeconomic status.War and conflict.
What is mean by stunting?
to stop, slow down, or hinder the growth or development of; dwarf: A harsh climate stunted the trees. Brutal treatment in childhood stunted his personality. noun. a stop or hindrance in growth or development.
What foods stunt growth?
Foods that stunt growth of your childJunk food. Experts says that eating junk food can actually stunt the growth of your child. ... Soda. ... Microwave popcorn. ... Soy. ... Sugary cereals. ... Alcohol. ... Sugar. ... Fried foods.More items...
What are the symptoms of stunted growth?
Symptoms associated with delayed growthIf they have certain forms of dwarfism, the size of their arms or legs may be out of normal proportion to their torso.If they have low levels of the hormone thyroxine, they may have a loss of energy, constipation, dry skin, dry hair, and trouble staying warm.More items...
What causes slow growth in babies?
Slow growth occurs when a child is not growing at the average rate for their age. The delay may be due to an underlying health condition, such as growth hormone deficiency. Some growth problems are genetic. Others are caused by a hormonal disorder or the inadequate absorption of food.
What deficiency causes stunted growth?
Growth hormone deficiency can lead to stunted growth. Hypothyroidism -The thyroid gland is responsible for making hormones required for growth and an underactive thyroid gland can lead to stunted growth.
What are 5 effects of malnutrition?
Consequences of malnutritionMuscle function. Weight loss due to depletion of fat and muscle mass, including organ mass, is often the most obvious sign of malnutrition. ... Cardio-respiratory function. ... Gastrointestinal function. ... Immunity and wound healing. ... Psychosocial effects.
How can stunted growth be prevented?
The following are ways to prevent stunting in children:Give Breast Milk For 6 Months In Babies. ... Fulfill Nutritional Needs Since Pregnancy. ... Child Development Monitor. ... Support Breastfeeding With Healthy Complementary Foods. ... Always Maintain Environmental Cleanliness.
What are symptoms of stunted growth?
Symptoms associated with delayed growthIf they have certain forms of dwarfism, the size of their arms or legs may be out of normal proportion to their torso.If they have low levels of the hormone thyroxine, they may have a loss of energy, constipation, dry skin, dry hair, and trouble staying warm.More items...
What causes stunted growth in animals?
The primary causes of stunting are nutrient deficiencies and infection. Recent evidence has shown that cow's milk intake is linked to linear growth, primarily by stimulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1).
What is stunting in malnutrition?
Stunting is defined as low height-for-age. It is the result of chronic or recurrent undernutrition, usually associated with poverty, poor maternal health and nutrition, frequent illness and/or inappropriate feeding and care in early life. Stunting prevents children from reaching their physical and cognitive potential.
How can stunted growth be prevented?
The following are ways to prevent stunting in children:Give Breast Milk For 6 Months In Babies. ... Fulfill Nutritional Needs Since Pregnancy. ... Child Development Monitor. ... Support Breastfeeding With Healthy Complementary Foods. ... Always Maintain Environmental Cleanliness.
What are the consequences of stunting in early life?
Some of those consequences include poor cognition and educational performance, low adult wages, lost productivity and, when accompanied by excessive weight gain later in childhood, an increased risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases in adult life.
What causes poor nutrition?
The most direct causes are inadequate nutrition (not eating enough or eating foods that lack growth-promoting nutrients) and recurrent infections or chronic or diseases which cause poor nutrient intake, absorption or utilization. Then there is the lack of care and stimulation for development…#N#Video [duration 00:07:12]
Is stunting irreversible?
Stunting is largely irreversible: a child cannot recover height in the same way that they can regain weight. Stunted children fall sick more often, miss opportunities to learn, perform less well in school and grow up to be economically disadvantaged, and more likely to suffer from chronic diseases. Chapter 4.
Why is growth stunting in children?
Stunting of linear growth, a highly prevalent problem in children of low- and middle-income countries, is the result of the exposure of the fetus and/or young child to nutritional deficiencies and infectious diseases. Maternal undernutrition results in fetal growth restriction, and infectious diseases in pregnancy can result in preterm delivery. Both of these conditions are important contributors to stunting in early childhood, albeit their relative contribution varies by world region. After birth, growth faltering may begin at 3-5 months of life and becomes more prominent from 6 to 18 months. During this time, the young child is exposed to many infectious diseases, such as diarrhea, that have an adverse effect on growth. There is also increasing evidence that frequent ingestion of microorganisms results in damage to the small intestine. The resulting condition, referred to as environmental enteric dysfunction, even without clinical symptoms, may cause growth faltering. The complementary foods that the child receives in addition to breast milk are often inadequate in nutrients and energy, negatively affecting growth. Harmful exposure during pregnancy and the first 2 years of life, a critical period for growth and development, has led to a programmatic focus on this "1,000 days" in the life cycle. Dietary interventions, including nutrition education and for undernourished women provision of food supplements during pregnancy, result in improvements in fetal growth that position the newborn for healthier growth. Interventions in the first 2 years of life include promotion of exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life and continued breastfeeding for at least the first 2 years, nutritional counseling to assure adequate complementary feeding, and, if necessary in food insecure areas, the provision of supplemental food to be given to the child. Evidence shows that each of the interventions has a beneficial effect on the growth of the young child, yet that the effect is modest in relation to the degree of stunting observed in these underprivileged populations. Nevertheless, in recent years, reductions in the prevalence of stunting in some low-income countries show that substantial improvements are possible as a result of socioeconomic changes along with specific infection control and dietary interventions.
What causes growth to falter?
The resulting condition, referred to as environmental enteric dysfunction, even without clinical symptoms, may cause growth faltering. The complementary foods that the child receives in addition to breast milk are often inadequate in nutrients and energy, negatively affecting growth.
Why is linear growth a problem?
Stunting of linear growth, a highly prevalent problem in children of low- and middle-income countries, is the result of the exposure of the fetus and/or young child to nutritional deficiencies and infectious diseases. Maternal undernutrition results in fetal growth restriction, and infectious diseas …
What causes stunting?
There are many factors that contribute to childhood stunting, and these factors are often linked. Some common factors linked to stunting include:
How does stunting occur in children?
Stunting in children is manifested through a cycle of malnourished mothers, resulting in underweight babies, which experience stunted growth and chronic malnutrition over time. Graphic: Aeri Wittenbourgh
Why do kids get stunted?
Stunting is when a child has a low height for their age, usually due to malnutrition, repeated infections, and/or poor social stimulation. The World Health Organization categorizes children who are stunted as those whose height is lower than average for their age, and at least two standard deviations below the WHO’s Child Growth Standards Median.
What are the effects of stunted children?
A stunted child may also have a poorer immune system, brain function, and organ development. Performing below average in these areas may also limit their future productivity and threaten the health of their future children.
What causes child psychosocial stimulation?
Inadequate psychosocial stimulation and/or parent-infant bonding. None of these causes exist in a vacuum. Gender equality, male engagement in parenting, and conflict can all contribute to a child’s psychosocial stimulation.
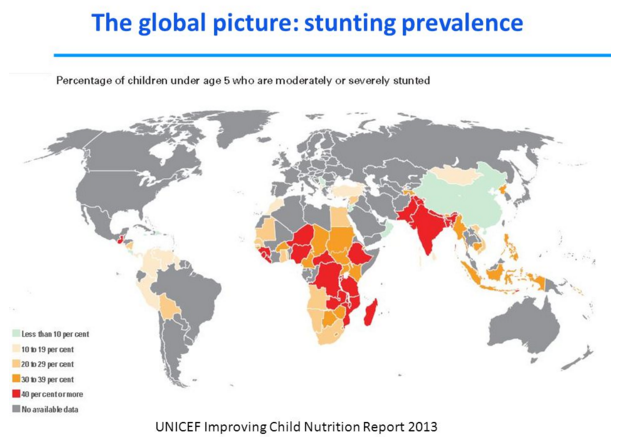
How many children are stunted?
Stunting, or significantly impaired growth and development, threatens almost 25% of children around the world. Here’s a look at the condition and its impact across generations.
Is stunting the same as wasting?
It’s important to note that stunting is different from wasting. If stunting is a low height for a child’s weight, wasting is low weight for a child’s height. The real-world impacts of stunting ripple well beyond linear growth. A stunted child may also have a poorer immune system, brain function, and organ development.
How does stunting affect early childhood?
Stunting in early childhood, especially in the first 1000 days from conception until two years of age impairs growth and adversely affect the functional development of the child. Some of the consequences include poor cognition and academic performance, lost productivity and this when associated with excess weight gain later in childhood, may increase the risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases later in adulthood.
How to prevent stunting in children?
The main goal of UN agencies, government, and other NGOs to prevent stunting is to focus on providing optimal nutrition during the first 1000 days of a child’s life, from conception until the child is two years of age. This stage in a child’s life is very crucial – a “window of opportunity” as the brain develops rapidly and lays a strong foundation for future cognitive and social skill ability. Additionally, it is also the time when the children are at higher risk of infections that lead to diarrhoea and other disorders, which may impede the child’s development and growth.
What is stunted growth?
Stunting is the impaired growth and development in children caused due to poor nutrition, recurrent infections, and lack of psychosocial stimulus. It is a primary indication of malnutrition and infections like diarrhoea, helminthiasis in early childhood and malnutrition during fetal growth caused by an undernourished mother. Stunted growth in children is defined as if the height for age in children is more than two standard deviations of the WHO Child Growth Standards Median.
How to diagnose stunted growth?
Stunted growth is diagnosed by comparing a measurement of children’s height to the WHO 2006 growth reference standards, children who fall below the fifth percentile of the reference population in height for age are defined as stunted. The lower than the fifth percentile corresponds to less than two standard deviations of the WHO Child Growth Standards Median.
Why do babies stunt?
The three key causes of stunting are poor feeding habits, poor maternal nutrition, and inadequate sanitation. Some of the other causes include:
Can growth hormone deficiency cause stunted growth?
Growth hormone deficiency can lead to stunted growth.
Why is stunted growth associated with long term health?
A girl with stunted growth may as an adult pregnant woman have difficulties at the time of childbirth. But some of these associated long-term conditions such as cognitive development, productivity, and adult health may be statistical associations without a causal relationship, as recently pointed out. Stunting does not cause some of these conditions, which share the same root causes with stunting.
What actions are needed to reach the goal of 40% reduction of stunting by 2025?
What actions are needed so that we reach the goal of 40% reduction of stunting by 2025? Still, promotion of breastfeeding, complementary feeding, and measures against child infections dominate. All these are very much needed for child health and survival, but have very small or no effects on stunting. Actions are required to promote the health and nutrition of adolescent girls. The first pregnancy frequently comes too early. Prenatal nutrition in food-insecure situations, and other pre-pregnancy or early pregnancy interventions are needed. In the Danaei paper, the authors conclude: “Reducing the burden of stunting requires a paradigm shift from interventions focusing solely on children and infants to those that reach mothers and families and improve their living environment and nutrition.”
How much will stunting be reduced by 2025?
One of these targets set by the World Health Assembly is to reduce stunting among children less than five years by 40% by 2025. WHO defines stunting as the impaired growth and development that children experience from poor nutrition, repeated infection, and inadequate psychosocial stimulation.
Can a pregnant woman have stunted growth?
A girl with stunted growth may as an adult pregnant woman have difficulties at the time of childbirth. But some of these associated long-term conditions such as cognitive development, productivity, and adult health may be statistical associations without a causal relationship, as recently pointed out.
What is the cause of stuttering?
In more rare cases, stuttering is the result of brain injury or severe psychological trauma. This form of stuttering, known as “acquired” stuttering, differs from developmental stuttering in both its causes and manifestations.
What factors influence stuttering?
While no one factor determines stuttering, the predominate theory suggests that a combination of genetics, language development, and the environment can influence the brain activity of people who stutter.
What causes stuttering in children?
There are many Common Myths that include theories about what causes stuttering. It’s important to remember that no single cause has been found for stuttering: 1 Stuttering is not caused by children’s parents 2 Stuttering is not caused by pointing out a child’s disfluencies 3 Stuttering is not a psychological problem (although it may have psychological effects) 4 Stuttering is not a sign of brain injury or reduced intelligence 5 Stuttering is not caused by learning another language (although it may present differently in bilinguals)
Why do children stutter?
As children produce longer and more complex sentences, their brain experiences higher demand. This increased demand can affect the motor control necessary to produce speech. When motor pathways can’t keep up with language signals, stuttering can occur.
What causes a person to stutter?
Researchers currently believe that stuttering is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, language development, environment, as well as brain structure and function [1]. Working together, these factors can influence the speech of a person who stutters. Stuttering:
When do children start stuttering?
Stuttering most often begins between the ages of two and eight, when children’s language abilities are rapidly expanding. Many children who stutter may know exactly what they want to say, but their motor pathways aren’t quite ready to get the words out.
Which hemisphere is stuttering?
Findings from brain imaging studies indicate that there is more right hemisphere activity in adults who stutter, with less activity in the left hemisphere areas typically responsible for speech production. Some people who stutter have more difficulty processing auditory information and slower reaction times on sensory-motor tasks.
