
Density curves have the following properties:
- The area under the curve always adds up to 100%.
- The curve will never dip below the x-axis.
What are the characteristics of a density curve?
It may seem like I covered a lot of things in this post, but the core ideas are simple:
- On both film and paper, more exposure creates more density. ...
- The range of tones in a subject (or densities on a negative) can be thought of as a scale. ...
- A steeper curve means greater contrast. ...
How to calculate density and relative density?
Density can be measured for all species or separated into the density of individual species or species groups. Similarly, how do you calculate relative density in ecology? Density is determined by the number of plants rooted within each quadrat. Relative density is the density of one species as a percent of total plant density.
What units can measure density?
What are the three equations for density?
- To work out density: p = m / V.
- To work out the mass: m = p x V.
- To work out the volume: V = m / p.
What does density curve mean?
The density curve is symmetrical, centered about its mean, with its spread determined by its standard deviation. The height of a normal density curve at a given point x is given by The Standard Normalcurve, shown here, has mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
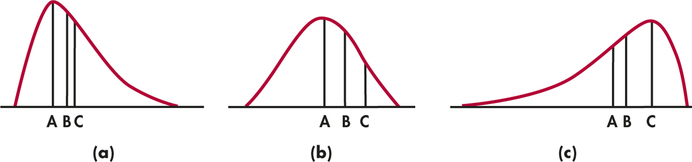
What are the rules of a density curve?
A probability density curve satisfies several rules: It never goes below the horizontal axis, i.e. it's never negative. The total area under the curve is 1. The chance of the quantity falling between a and b is the area under the curve between the point a and b.
What is the density curve?
A density curve is a curve that is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. When considering a specific data point, there is area to the left and area to the right. A NORMAL curve is one that mimics a symmetric histogram and the mean and median are EQUAL.
How do you describe the shape of a density curve?
These density curves are symmetric, single-peaked, and bell-shaped. They are called Normal curves, and they describe Normal distributions. All Normal distributions have the same overall shape. The exact density curve for a particular Normal distribution is described by giving its mean μ and its standard deviation σ .
What are the 2 requirements for a density curve?
1. A fixed number of trials. 2. Each trial is independent of the others.
What is a density curve quizlet?
A density curve is a curve with area exactly 1 underneath it whose shape describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Density curves help us better understand our measures of center and spread.
How do you make a density curve?
4:189:37Density Curves and their Properties (5.1) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn order to be valid. The second rule is that the total area under the curve is always equal to oneMoreIn order to be valid. The second rule is that the total area under the curve is always equal to one now.
Is a density curve a normal distribution?
Density Curves A density curve is an idealized representation of a distribution in which the area under the curve is defined to be 1. Density curves need not be normal, but the normal density curve will be the most useful to us.
Which of the following are properties of the normal distribution curve?
Properties of a normal distribution The mean, mode and median are all equal. The curve is symmetric at the center (i.e. around the mean, μ). Exactly half of the values are to the left of center and exactly half the values are to the right. The total area under the curve is 1.
What height must the density curve have?
Every point on the curve must have a vertical height that is 0 or greater. (That is, the curve cannot fall below the x-axis.) Because the total area under the density curve is equal to 1, there is a correspondence between area and probability.
SOLID THIN FILMS AND LAYERS
J. Caro, ... R. Salvarezza, in Handbook of Surfaces and Interfaces of Materials, 2001
Renewal Phenomena
Mark A. Pinsky, Samuel Karlin, in An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling (Fourth Edition), 2011
Practical Calibration of Cryogenic LWIR Systems
The only practical condition under which a measurement can be made independently of the relative spectral responsivity of the instrument is when the calibration source and the target have the same spectral power density curve. This condition can be achieved when the target is known to radiate as a blackbody at a known temperature.
JAGS
John K. Kruschke, in Doing Bayesian Data Analysis (Second Edition), 2015
SURFACE AND INTERFACE PHENOMENA
Eric W. Forsythe, Yongli Gao, in Handbook of Surfaces and Interfaces of Materials, 2001
Sampling Distributions
Kandethody M. Ramachandran, Chris P. Tsokos, in Mathematical Statistics with Applications in R (Second Edition), 2015
Generalized Linear Mixed Models
S. Rabe-Hesketh, A. Skrondal, in International Encyclopedia of Education (Third Edition), 2010
What is a characteristic curve?
A characteristic curve is a graph of the relationship between the amount of exposure given a film and it’s corresponding density after processing. 1. A typical film characteristic curve is made by plotting density produced, against the log of exposure given ( Log E ).
What does the shape of a film curve mean?
The shape of the curve represents the tonal response of the film to a wide range of exposures and to one particular processing condition. As the slope of the curve decreases, the ability of the film to record the contrast between different exposures also decreases, and stops completely as the curve becomes horizontal.
What is the least amount of blackening in the unexposed area of a film called?
The least possible amount of blackening in the unexposed area of a film is called the minimum density. In the case of black and white film the minimum density is the sum of development fog density and base density.
What is the D-Log E curve?
A graphical representation of a film ‘s response to light. Also called the D-Log E curve or the HD curve. A curve plotted on a graph from two axes, exposure and density, used to describe the characteristics and performance of sensitive emulsions.
What are the two measures of contrast?
Two measures are generally used to express photographic image contrast; gamma and average gradient . The former (writtený) stands for the slope of the straight-line portion of the characteristic curve, and the latter (written bar G) represents the slope of the straight-line portion between two particular points on the characteristic curve.
