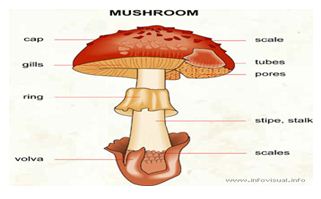
What are the characteristics of Agaricus? Members of Agaricus are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores.
What are the characteristics of Agaricus campestris?
Commonly called the "meadow mushroom," Agaricus campestris is a European species characterized by a white cap, stocky stature, non-staining surfaces and flesh, pink-then-brown gills, habitat in grass, and microscopic features (including a lack of true cheilocystidia, and spores 6.5–8.5 µm long).
What are the salient features of Agaricus?
The following points highlight the twenty salient features of agaricus. 1. The primary mycelium produced by the germination of basidiospores is of short duration. It consists of cells each with a haploid (n) nucleus (A). 2.
What is the difference between Agaricus and other mushrooms?
They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of Agaricus also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus on the stalk.
What is the mycelium of Agaricus?
The mycelium of the Agaricus is subterranean. It has a tendency to grow in all directions from a central point to form a large invisible circular colony. The mycelium also increases in diameter year after year and the being at all times on the outer edge, because the central mycelium dies away with age.
What is the importance of Agaricus?
The mushroom is traditionally believed to fight physical and emotional stress, stimulate immune system, improve the quality of life in diabetics, reduce cholesterol, prevent osteoporosis and peptic ulcer, treat circulatory and digestive problems and fight cancer (2).
What type of fungi is Agaricus?
Agaricus campestris is a widely eaten gilled mushroom closely related to the cultivated button mushroom Agaricus bisporus....Agaricus campestrisKingdom:FungiDivision:BasidiomycotaClass:AgaricomycetesOrder:Agaricales9 more rows
What is the common name for Agaricus?
button mushroomAgaricus bisporus (button mushroom)
Is Agaricus a flowering plant?
It is a non-flowering plant.
How do you identify Agaricus?
2:217:50Identifying the Field Mushroom, Agaricus campestris - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey all have a stout white stem. Most or all actually have a skirt unless it's brushed off will gotMoreThey all have a stout white stem. Most or all actually have a skirt unless it's brushed off will got damaged. Like. This one here they do not grow from an egg sack or a bulbous base and importantly.
What is Agaricus example?
Agaricus campestrisAgaricus bisporusAgaricus arvensisAgaricus xanthoder...Agaricus silvaticusAgaricus bitorquisAgaricus/Lower classifications
What is the Colour of Agaricus?
Agaricus bisporus is an edible basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Europe and North America. It has two color states while immature – white and brown – both of which have various names, with additional names for the mature state.
Which part of Agaricus is edible?
fruiting body basidiocarpSolution : (a) The edible part of mushroom is the fruiting body basidiocarp. The common mushrooms are Agaricus bisporus , lentinus , Volvariella , Plaurotus , etc .
Which disease is caused by Agaricus?
bisporus and the causal agents responsible for the most severe diseases, namely the bacteria Pseudomonas tolaasii and Pseudomonas reactans and the fungi Trichoderma aggressivum and Lecanicillium fungicola.
What is the structure of Agaricus?
Members of Agaricus are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores.
Is Agaricus edible fungi?
Agaricus bisporus is an edible mushroom. It also belongs to the division Basidiomycetes of kingdom Fungi.
How do Agaricus reproduce?
However, for a mushroom farmer, reproduction of Agaricus is totally asexual. They do not sow spores, instead they use pieces of mycelium (the name given to cluster of hyphae), induce it to grow and then stimulate it to produce fruiting bodies. Some of the mycelium remains and can be used to continue the process.
What is the fruiting body of Agaricus?
The fruiting body of the species of Agaricus it is generally fleshy and large in size. The hat changes shape over time, being initially hemispherical, and then becoming slightly flattened after a certain period of life of the organism has elapsed. They are usually whitish or brownish species.
Where do Agaricus minieri live?
Organisms of the species Agaricus minieri they are very specific in terms of their habitat, thriving only in dunes. Some species grow better directly on plant debris and others are common on the roadsides.
What is the name of the mushroom that has a ring on its stipe?
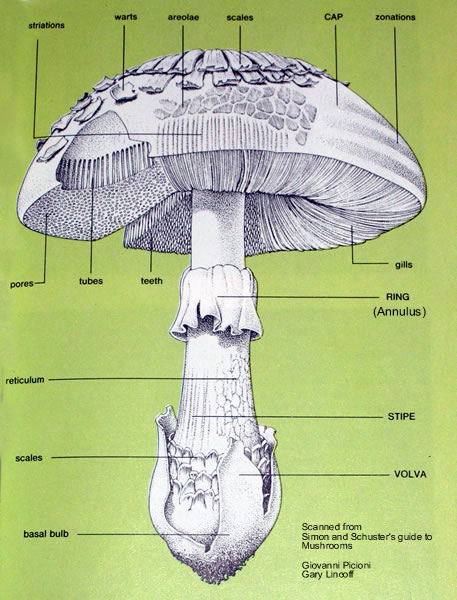
Agaricus is the generic name of a group of Basidiomycota fungi belonging to the Agaricaceae family that are characterized by developing fruiting bodies in the form of fleshy and generally large mushrooms. They have a hat that changes from hemispherical to slightly flattened, with a ring on the stipe and separate blades from the stipe.
What is the name of the fungus that produces fruiting bodies?
Agaricu i the generic name of a group of Baidiomycota fungi belonging to the Agaricaceae family that are characterized by developing fruiting bodie in the form of flehy and generally large muhroom. Th
How big is a fungus on a hat?
This fungus can reach up to 18 cm in diameter of the hat, but generally does not exceed 13 cm. Its surface is covered by a powdery cuticle in which scales and spots can appear with age.
What is the color of the hymenium?
The hymenium has numerous free blades, that is, not attached to the stipe. These blades are fleshy and light-colored in recent fruiting, which later acquire pink tones and finally in senescent organisms turn into colors derived from the blackish- brown tone.
Is Agaricus xanthodermus poisonous?
Agaricus xanthodermus it is toxic, although it does not cause death . Among the effects of its intake are gastrointestinal disorders such as abdominal cramps, nausea and diarrhea. Other symptoms of poisoning that appear less frequently are drowsiness, headaches and dizziness.
characteristics
The fruiting body of Agaricus species is generally fleshy and large in size. The hat changes shape over time, being initially hemispherical, and then becomes slightly flattened after a certain period of life of the organism has elapsed. They are normally whitish or brownish species.
Taxonomy
The genus Agaricus is located taxonomically within the family Agaricaceae, class Agaricomycetes, division Basidiomycota. The taxonomy of this genus is complicated because, although it was coined by Carlos Linnaeus in 1735, it was used to cover a great diversity of terrestrial fungi provided with plates and feet.
Habitat and distribution
Fungi of the genus Agaricus can grow in different habitats depending on the species. Many of them prefer open meadows and fields with abundant grasses, others prefer more wooded areas. Some grow under cypress trees and other tree species in the Cupressaceae family.
Agaricus bisporus
The common mushroom is the best-known representative of the genus and the species of mushroom that has the highest production worldwide, because it is highly appreciated in the kitchen and has very important nutritional and medicinal properties. Its cultivation is carried out both traditionally and commercially.
Agaricus campestris
Fungus whose fruiting body has a cap up to 12 cm in diameter and a foot 7 cm high, with a simple ring. It is an edible species with a very good taste as well as being rich in vitamins and minerals, but it provides very few calories, which is why it is very suitable to help you lose weight.
Agaricus silvicola
Also edible species that is distributed in northern Europe and North America. Its fruiting body appears in autumn and features a hat up to 10 cm in diameter and a 4 cm tall stem.
Agaricus xanthodermus
It is characterized because its fruiting body has a convex cap that in some mature specimens takes on the appearance of a cube with a flattened, dry and scaly surface that can reach up to 15 cm in diameter. Another important characteristic is that the foot has a yellow coloration.
Where does Agaricus grow?
It is cosmopolitan in distribution. About 17 species of Agaricus have been reported from India. It is commonly known as kukurmutta in U.P. and dhingri in Punjab.
What is the habitat of Agaricus?
It is a saprophytic fungus found growing on soil humus, decaying litter on forest floors, in the fields and lawns, wood logs and manure piles. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the fruiting body of mycelium?
The secondary mycelium grows extensively under the soil and becomes organised into special tissue to form the fruiting body or basidiocarp. The fruiting body appears like umbrella above ground. It is made up of dikaryotic hyphae. These hyphae are called tertiary mycelium. The mycelium is subterranean. The hyphae are septate and branched. The cells communicate with one another by means of a central pore in the septum. It is a typical dolipore septum.
What is the first step in sexual reproduction of Agaricus?
The vegetative hyphae with uninucleate haploid cells from mycelia of opposite strains (heterothallic) or from the same mycelium (homothallic) come into contact and fuse. Each of such fusion results into a bi-nucleate (dikaryotic) cell. The dikaryotic cell, by successive divisions, gives rise to the bi-nucleate or dikaryotic mycelium. This dikaryotic mycelium is perennial and produces the characteristic fruiting body of the mushroom year after year.
Why does mycelium increase in diameter year after year?
The mycelium also increases in diameter year after year and the being at all times on the outer edge, because the central mycelium dies away with age. ADVERTISEMENTS: When the mycelium becomes mature at tips, sporophores are produced. These sporophores appear in a circle (Fig. 2).
How big is a pileus?
The mature pileus is 5 to 12.5 cm in diameter. From the underside of the pileus hang approximately 300 to 600 strips or plates of tissues known as gills or lamellae. The gills are white or pinkish in young condition and turns brown or purplish black at maturity.
Which region of the gill is a compact layer of diametric cells?
The hyphae of the trama region curve outwards towards each surface of the gill. They end in small diametric cells forming a compact layer known as sub-hymenium.
Where did the agaricus mushroom come from?
Modern commercial varieties of the common agaricus mushroom originally were light brown in color. The white mushroom was discovered in 1925 growing among a bed of brown mushrooms at the Keystone Mushroom Farm in Coatesville, Pennsylvania. Louis Ferdinand Lambert, the farm's owner and a mycologist by training, brought the white mushroom back to his laboratory. As with the reception of white bread, it was seen as a more attractive food item and became grown and distributed. Similar to the commercial development history of the navel orange and Red Delicious apple, cultures were grown from the mutant individuals, and most of the cream-colored store mushrooms marketed today are products of this 1925 chance natural mutation.
How big are spores?
The spores are oval to round and measure approximately 4.5–5.5 μm × 5–7.5 μm, and the basidia usually two-spored, although two- tetrasporic varieties have been described from the Mojave Desert and the Mediterranean, with predominantly heterothallic and homothallic lifestyles, respectively.
What is a common mushroom?
The common mushroom has a complicated taxonomic history. It was first described by English botanist Mordecai Cubitt Cooke in his 1871 Handbook of British Fungi, as a variety (var. hortensis) of Agaricus campestris. Danish mycologist Jakob Emanuel Lange later reviewed a cultivar specimen, and dubbed it Psalliota hortensis var. bispora in 1926. In 1938, it was promoted to species status and renamed Psalliota bispora. Emil Imbach (1897–1970) imparted the current scientific name of the species, Agaricus bisporus, after the genus Psalliota was renamed to Agaricus in 1946. The specific epithet bispora distinguishes the two-spored basidia from four-spored varieties .
How many colors does bisporus have?
It has two color states while immature – white and brown – both of which have various names, with additional names for the mature state. A. bisporus is cultivated in more than seventy countries and is one of the most commonly and widely consumed mushrooms in the world.
What is the name of the mushroom that is white?
When immature and white, this mushroom may be known as common mushroom, white mushroom, button mushroom, cultivated mushroom, table mushroom, and champignon mushroom (or simply champignon ). When immature and brown, it may be known variously as Swiss brown mushroom, Roman brown mushroom, Italian brown mushroom, cremini/crimini mushroom, chestnut mushroom (not to be confused with Pholiota adiposa ), and baby bella.
Where is Champignon mushroom from?
For the Brazilian musician, see Champignon (musician). Agaricus bisporus is an edible basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Europe and North America.
What is the poisonous destroying angel?
The common mushroom could be confused with young specimens of the deadly poisonous destroying angel ( Amanita sp.), but the latter may be distinguished by their volva or cup at the base of the mushroom and pure white gills (as opposed to pinkish or brown of A. bisporus ). Thus it is always important to clear away debris and examine the base of such similar mushrooms, as well as cutting open young specimens to check the gills. Furthermore, the destroying angel grows in mossy woods and lives symbiotically with spruce .
How many salient features does Agaricus have?
The following points highlight the twenty salient features of agaricus.
What is the structure of a mushroom?
11. The mature mushroom is a massive structure consisting of a stalk-like stipe supporting at its top a broad umbrella-shaped cap, the pileus. More than half way up, the stipe bears a membranous ring, the annulus.
What is the name of the tiny white apical swellings on the branches of the underground mycelial?
9. The basidiocarps arise as tiny, white apical swellings on the branches of the underground mycelial strands called rhizomorphs (C).
What is the name of the young basidium?
16. The probasidium containing the diploid nucleus or synkaryon is called the young basidium. It represents the short-lived diplophase in the life cycle.
Which basidiospores germinate to give rise to haploid mycelia?
20. The liberated basidiospores which are true meiospores (H), germinate to give rise to the haploid (primary) mycelia (A).
Which nuclei migrate into basidiospores?
18. In the mature basidium the haploid nucle i migrate into the basidiospores through their respective sterigmata (G).
Which mycelium produces mushrooms?
4. The secondary mycelium is abundant, and long-lived (perennial). It produces mushrooms (basidiocarps) year after year (C).
Where is Agaricus campestris found?
As a "field guide species," Agaricus campestris is well-known, widely distributed, and fairly common in North America. However, from a technical, scientific standpoint it is unclear whether (and where) Agaricus campestris actually occurs on our continent. East of the Rocky Mountains, according to Richard Kerrigan in his monumental treatment of Agaricus in North America (2016), "all similar collections . . . that have been sequenced distinctly belong to species other than A. campestris ." In western North America, according to Kerrigan, " [c]ontinued use of the name A. campestris . . . seems appropriate, but must be understood to apply in the far west on a provisional or approximate basis until western material is better known."
How long are spores in the campestris?
Unfortunately for those who do not have access to a microscope, examination of spores is the only way to approach accurate identifications within the North American campestris group, short of sequencing DNA. In the west, Agaricus porphyrocephalus var. pallidus has spores in the 6–6.5 µm range, length-wise, while Agaricus cf. campestris has longer spores (7–9 µm long). In eastern North America, campestris -like possibilities include Agaricus porphyrocephalus var. pallidus (most spores 6–6.5 µm long), Agaricus andrewii (6.5–8 µm), and Agaricus argenteus (8–8.5 µm).
What is the name of the mushroom that grows in grass?
by Michael Kuo. Commonly called the "meadow mushroom," Agaricus campestris is a European species characterized by a white cap, stocky stature, non-staining surfaces and flesh, pink-then-brown gills, habitat in grass, and microscopic features (including a lack of true cheilocystidia, and spores 6.5–8.5 µm long).
Where does the saprobic plant grow?
Ecology: Saprobic; growing alone, gregariously, or in arcs and fairy rings, in meadows, fields, lawns, and grassy areas; North American distribution uncertain, but at present not known from east of the Rocky Mountains.
What color are Agaricus bisporus?from wayofleaf.com
They appear in varying shades of white and brown, with dark gills and an annulus (ring) on their stems. They produce a chocolate brown spore print.
Where does Agaricus bisporus grow?from en.wikipedia.org
Agaricus bisporus is an edible basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Europe and North America. It has two color states while immature – white and brown – both of which have various names, with additional names for the mature state.
How many spores does Agaricus bisporus have?from mushroomexpert.com
As its species epithet indicates, the distinguishing feature of Agaricus bisporus is microscopic: unlike most other species of Agaricus, its basidia bear two spores each, instead of four. Agaricus brunnescens is a synonym. Description:
What is a common mushroom?from en.wikipedia.org
The common mushroom has a complicated taxonomic history. It was first described by English botanist Mordecai Cubitt Cooke in his 1871 Handbook of British Fungi, as a variety (var. hortensis) of Agaricus campestris. Danish mycologist Jakob Emanuel Lange later reviewed a cultivar specimen, and dubbed it Psalliota hortensis var. bispora in 1926. In 1938, it was promoted to species status and renamed Psalliota bispora. Emil Imbach (1897–1970) imparted the current scientific name of the species, Agaricus bisporus, after the genus Psalliota was renamed to Agaricus in 1946. The specific epithet bispora distinguishes the two-spored basidia from four-spored varieties .
What is the white button mushroom?from en.wikipedia.org
In the U.S., the white button form of A. bisporus alone accounts for about 90% of mushrooms sold .
What is the name of the mushroom that is white?from en.wikipedia.org
When immature and white, this mushroom may be known as common mushroom, white mushroom, button mushroom, cultivated mushroom, table mushroom, and champignon mushroom (or simply champignon ). When immature and brown, it may be known variously as Swiss brown mushroom, Roman brown mushroom, Italian brown mushroom, cremini/crimini mushroom, chestnut mushroom (not to be confused with Pholiota adiposa ), and baby bella.
Where did the agaricus mushroom come from?from en.wikipedia.org
Modern commercial varieties of the common agaricus mushroom originally were light brown in color. The white mushroom was discovered in 1925 growing among a bed of brown mushrooms at the Keystone Mushroom Farm in Coatesville, Pennsylvania. Louis Ferdinand Lambert, the farm's owner and a mycologist by training, brought the white mushroom back to his laboratory. As with the reception of white bread, it was seen as a more attractive food item and became grown and distributed. Similar to the commercial development history of the navel orange and Red Delicious apple, cultures were grown from the mutant individuals, and most of the cream-colored store mushrooms marketed today are products of this 1925 chance natural mutation.

Overview
Phylogenetics
The use of phylogenetic analysis to determine evolutionary relationships amongst Agaricus species has increased the understanding of this taxonomically difficult genus, although much work remains to be done to fully delineate infrageneric relationships. Prior to these analyses, the genus Agaricus, as circumscribed by Rolf Singer, was divided into 42 species grouped into five sections based on reactions of mushroom tissue to air or various chemical reagents, as well as …
Etymology
Several origins of genus name Agaricus have been proposed. It possibly originates from ancient Sarmatia Europaea, where people Agari, promontory Agarum and a river Agarus were known (all located on the northern shore of Sea of Azov, probably, near modern Berdiansk in Ukraine).
Note also Greek ἀγαρικόν, agarikón, "a sort of tree fungus" (There has been an Agaricon Adans. genus, treated by Donk in Persoonia 1:180.)
Taxonomy
For many years, members of the genus Agaricus were given the generic name Psalliota, and this can still be seen in older books on mushrooms. All proposals to conserve Agaricus against Psalliota or vice versa have so far been considered superfluous.
Dok reports Linnaeus' name is devalidated (so the proper author citation appar…
List of species
The fungal genus Agaricus contains about 200 species worldwide.
• Agaricus abruptibulbus Peck (1905) – abruptly bulbous agaricus
• Agaricus albolutescens Zeller (1938)
• Agaricus aestivalis Pilat (1951)
Edibility and toxicity
The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, A. bisporus, with A. campestris also being well known. A. porphyrocephalus is a choice edible, and some others are edible as well.
A notable inedible species is the yellow-staining mushroom, A. xanthodermus. One species reported from Africa, A. aurantioviolaceus, is reportedly deadly poisonous.
External links
• MycoKey - The Genus Agaricus
• Mushroom Expert - The Genus Agaricus
• Varieties of California, USA on MYKOWEB .com
• Agaricus page at Index Fungorum
Characteristics
- The fruiting body of Agaricus species is generally fleshy and large in size. The hat changes shape over time, being initially hemispherical, and then becomes slightly flattened after a certain period of life of the organism has elapsed. They are normally whitish or brownish species. The hymenium has numerous free blades, that is, not attached to th...
Taxonomy
- The genus Agaricus is located taxonomically within the family Agaricaceae, class Agaricomycetes, division Basidiomycota. The taxonomy of this genus is complicated because, although it was coined by Carlos Linnaeus in 1735, it was used to cover a great diversity of terrestrial fungi provided with plates and feet. This name was later used with the interpretation t…
Habitat and Distribution
- Fungi of the genus Agaricus can grow in different habitats depending on the species. Many of them prefer open meadows and fields with abundant grasses, others prefer more wooded areas. Some grow under cypress trees and other tree species in the Cupressaceae family. The organisms of the Agaricus minieri species are very specific in terms of their habitat, thriving onl…
Agaricus bisporus
- The common mushroom is the best-known representative of the genus and the species of mushroom that has the highest production worldwide, because it is highly appreciated in the kitchen and has very important nutritional and medicinal properties. Its cultivation is carried out both traditionally and commercially. There are several varieties of the species, of which the mos…
Agaricus campestris
- Fungus whose fruiting body has a cap up to 12 cm in diameter and a foot 7 cm high, with a simple ring. It is an edible species with a very good taste as well as being rich in vitamins and minerals, but it provides very few calories, which is why it is very suitable to help you lose weight. This species, despite having better organoleptic qualities than the common mushroom, is not cultivat…
Agaricus silvicola
- Also edible species that is distributed in northern Europe and North America. Its fruiting body appears in autumn and features a hat up to 10 cm in diameter and a 4 cm tall stem. Silvicula agaricus. Taken and edited from: Jerzy Opioła.
Agaricus xanthodermus
- It is characterized because its fruiting body has a convex cap that in some mature specimens takes on the appearance of a cube with a flattened, dry and scaly surface that can reach up to 15 cm in diameter. Another important characteristic is that the foot has a yellow coloration. This species has a wide distribution in the northern hemisphere, it grows associated with grasses, de…
References
- Agaricus. On Wikipedia. Recovered from: en.wikipedia.org.
- Agaricus xanthodermus. On Wikipedia. Recovered from: en.wikipedia.org.
- P. Callac (2007). II. The genus Agaricus. In JE Sánchez, DJ Royse & HL Lara (Eds). Cultivation, Marketing and Food Safety of Agaricus bisporus. Ecosur.
- C. Lyre. Common mushroom (Agaricus bisporus): characteristics, taxonomy, nutritional prop…
- Agaricus. On Wikipedia. Recovered from: en.wikipedia.org.
- Agaricus xanthodermus. On Wikipedia. Recovered from: en.wikipedia.org.
- P. Callac (2007). II. The genus Agaricus. In JE Sánchez, DJ Royse & HL Lara (Eds). Cultivation, Marketing and Food Safety of Agaricus bisporus. Ecosur.
- C. Lyre. Common mushroom (Agaricus bisporus): characteristics, taxonomy, nutritional properties, reproduction, nutrition. Recovered from: lifeder.com.