
Among the main characteristics of the Protistas kingdom are:
- They are eukaryotic organisms (with a nucleus delimited by a membrane), lacking differentiated vegetative tissues,...
- The size of the protists is highly variable, from microscopic unicellular forms to multicellular organisms several...
- They are found in a wide variety of places: soil, fresh water, ocean floor,...
What are the characteristics of protists?
Protists are broadly classified into 5 subdivisions based on their general characteristic features. They are classified as: Outline the characteristics of Kingdom Protista. All protists are eukaryotic organisms. This means that they have a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other cell organelles.
What is kingdom Protista?
One of the five kingdoms of life, Kingdom Protista consists of organisms known as protists which do not fit the criteria for other kingdoms. Learn about examples, characteristics, and the method of classification which make up this kingdom. Updated: 09/22/2021 What Is Kingdom Protista? Imagine you are cleaning or organizing around your house.
Is Protista unicellular or eukaryotic?
Protista are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. The members of the kingdom Monera are mostly aquatic in habitat. The cell wall is present in some protists and absent in some other forms. The eukaryotic cell of protists possesses a well-defined nucleus, and membrane-bound organelles also present.
What are the boundaries of the Protista?
However, the boundaries of this kingdom are not well defined. Members of Protista are primarily aquatic. This kingdom forms a link with the others dealing with plants, animals and fungi. Being eukaryotes, the protistan cell body contains a well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Some have flagella or cilia.
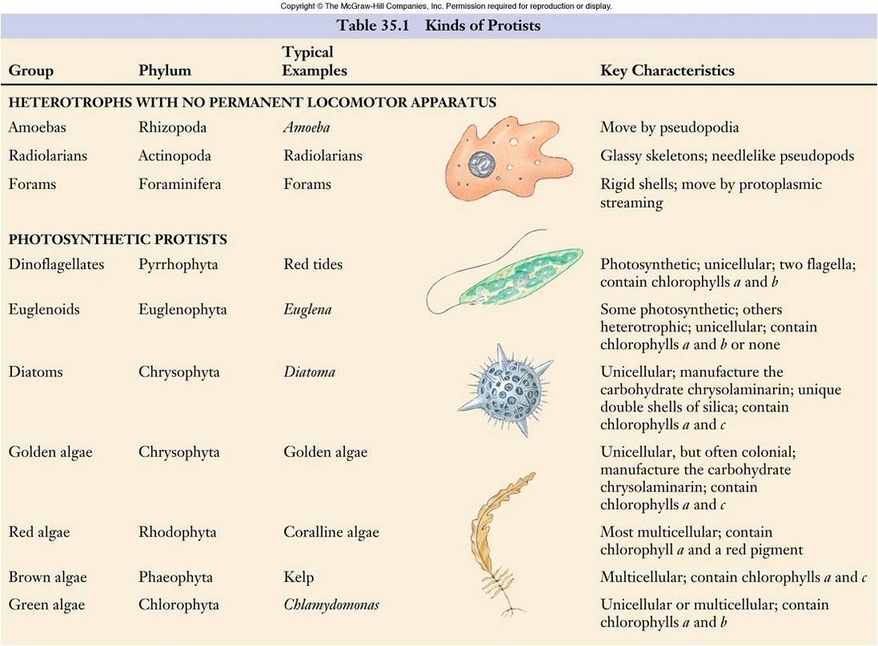
What are 5 characteristics of protista?
Characteristics of ProtistsThey are eukaryotic, which means they have a nucleus.Most have mitochondria.They can be parasites.They all prefer aquatic or moist environments.
What are the main characteristics of Kingdom Protista give examples Class 9?
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista: (i) They are unicellular eukaryotic organism i.e., they have membrane bound nucleus and organelles. (ii) Some of these organism use appendages such as hair like cilia or whip-like flagella for moving around. (iii) Their mode of nutrition can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
What are the characters of Protista kingdom give examples?
Photosynthetic Protists Examples of protists include algae, amoebas, euglena, plasmodium, and slime molds. Protists that are capable of photosynthesis include various types of algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, and euglena. These organisms are often unicellular but can form colonies.
What are the characteristic features of kingdom?
The living organisms are divided into five different kingdoms – Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, and Monera on the basis of their characteristics such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, mode of reproduction and body organization.
What are protists examples?
Giant kelpMarimoForamsSea lettuceParamecium caudatumRhizariaProtist/Representative species
What are the 5 kingdoms and examples of each?
The Five Kingdoms of LifeKingdom Monera (Prokaryotic bacteria and blue green algae).Kingdom Protista (Unicellular Eukaryotic organisms- protozoans, fungi and algae).Kingdom Fungi (Multinucleate higher fungi).Kingdom Plantae (Multicellular green plants and advanced algae).Kingdom Animalia (Multicellular animals).
What are the examples of kingdom Plantae?
PlantGlaucophyteGreen algaeRed algaeRoseAvocadoArchaeplastida/Lower classificationsWhat are examples of members of the kingdom Plantae? Some examples of members in the plant kingdom include mosses, liverworts, ferns, trees, shrubs, herbs, and corn-bearing plants such as pine and spruce.
What are the 4 main types of protist?
Protists include: (1) protozoa, the animal-like protists, (2) algae, the plant-like protists, and (3) slime molds and water molds, the fungus-like protists.
What is the term for a protist that moves through pseudopodia?
Amoebas are examples of protists that move using pseudopodia. These temporary extensions of the cytoplasm allow the organism to move as well as to capture and engulf organic material through a type of endocytosis known as phagocytosis, or cell eating. Amoebas are amorphous and move by changing their shape. They reside in aquatic and moist environments, and some species are parasitic.
What are some examples of heterotrophic protists?
Examples of heterotrophic protists include amoebas, paramecia, sporozoans, water molds, and slime molds. Amoebas are examples of protists that move using pseudopodia.
What are some examples of protists?
Examples of protists include algae, amoebas, euglena, plasmodium, and slime molds. Protists that are capable of photosynthesis include various types of algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, and euglena. These organisms are often unicellular but can form colonies.
How do other protists acquire nutrition?
Still, other protists acquire nutrition predominately by absorbing nutrients from their environment.
Why are protists grouped together?
Protists do not share many similarities, but are grouped together because they do not fit into any of the other kingdoms.
How do protists move?
These organelles are protrusions formed from specialized groupings of microtubules that move to propel protists through their moist environment. Other protists move by using temporary extensions of their cytoplasm known as pseudopodia. These extensions are also valuable in allowing the protist to capture other organisms that they feed on.
What are protists classified as?
Protists reside under the Eukarya Domain and are thus classified as eukaryotes. Eukaryotic organisms are distinguished from prokaryotes in that they have a nucleus that is surrounded by a membrane. In addition to a nucleus, protists have additional organelles in their cytoplasm. The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complexes are important for the synthesis of proteins and exocytosis of cellular molecules. Many protists also have lysosomes, which aid in the digestion of ingested organic material. Certain organelles may be found in some protist cells and not in others. Protists that have characteristics in common with animal cells also have mitochondria, which provide energy for the cell. Protists that are similar to plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts. Chloroplasts make photosynthesis possible in these cells.
What Is Kingdom Protista?
Imagine you are cleaning or organizing around your house. To assist in this process, you separate your items into categories to help you locate them later. Maybe you have a box for books, a drawer for school supplies, and a cubby for electronics. You start to realize, however, that you have a bunch of extra bits and pieces that do not fit into any of your other groups. So, you create a special container for them: your 'other' container. This is pretty much what happened with Kingdom Protista.
What are protozoans called?
The animal-like protists are also known as protozoans, which is Latin for 'first animals.' All protozoans are single-celled heterotrophs and are categorized based on their movement. Paramecia are examples of protozoans that use cilia, or tiny hairs, to propel themselves through the water. Amoebas are able to change their shape and move through extensions of cytoplasm called pseudopodia, Greek for 'false feet.' The plasmodium is the parasite that causes malaria. It cannot move on its own, but rather depends on its host for locomotion.
Why is my fish tank green?
An algal bloom of Volvox, a single-celled protist that lives in colonies, is the cause of green water in your fish tank. The fungus-like protists are the slime molds and water molds. They are mostly single-celled organisms that live in the moist soil of forest floors and compost piles.
What is the Greek word for the first eukaryotic organism?
It contains the protists, or the organisms that do not fit into any of the other categories. Protista is Greek for the very first. These organisms were traditionally considered the first eukaryotic forms of life, predecessors to the organisms in the plant, animal, and fungus kingdoms.
How do protists get energy?
Or, they can be autotrophic, which means they obtain energy from the environment through photosynthesis, the process of capturing light energy and storing it in carbohydrates.
What caused the Great Potato Famine in Ireland?
A parasitic water mold was responsible for the Great Potato Famine in Ireland that killed almost one million people in the 1800s. Lesson Summary. Kingdom Protista contains the protists, or all the organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms of life.
How many kingdoms are there on Earth?
All the life on planet Earth is organized into five kingdoms based on whether or not the organism is single-celled, how it obtains energy, and how (or if) it moves. Kingdom Protista is the hodge-podge category. It contains the protists, or the organisms that do not fit into any of the other categories.
What is the name of the body that connects the flagella to the body?
The two flagella join with each other at a swelling called paraflagellar body. Euglena is a connecting link between animals and plants. Nutrition in Euglena is mixotrophic, when the light is available it is photosynthetic, in darkness, it is saprophytic absorbing food from surrounding water.
How do protists reproduce?
Protists reproduce asexually and sexually by, the process involving cell fusion and zygote formation. It may be photosynthetic or holotrophic. These could also be saprotrophic, parasitic and symbionts. On the other hand, some could have mixotrophic nutrition (holotrophic + saprobic).
What are the characteristics of the kingdom Protista?
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista. We place all single-celled eukaryotes under Protista. However, the boundaries of this kingdom are not well defined. Members of Protista are primarily aquatic. This kingdom forms a link with the others dealing with plants, animals and fungi. Being eukaryotes, the protistan cell body contains a well-defined ...
What is a zygote in a slime mould?
It occurs in some dinoflagellates (Example: ceratium, gymnodinium; von stosch, 1973) and cellular slime moulds. The zygote is in the form of 2n. It usually divides by meiosis (also called zygotic meiosis). These produce vegetative cells with the chromosome number of 1n. These cells divide repeatedly by mitosis.
What is the name of the organism that develops pseudopodia?
Amoebid Protozoans: They develop pseudopodia which are temporary protoplasmic outgrowths. These are used for locomotion and engulfing food articles. Sarcodines are mostly free-living, found in fresh water, sea water and on damp soil.
What is Trypanosome Gambiense?
Trypanosome gambiense : The parasite of sleeping sickness. It is transmitted by tsetse fly. It causes Gambian sleeping sickness.
What are cilia in protozoa?
Ciliated Protozoans: Ciliates are protozoan protists. These develop a number of cilia during a part or whole of the life cycle. They use cilia for locomotion and driving food. There is a high degree of morphological and physiological specialisation. There are definite regions for ingestion and egestion. The region of ingestion consists of an oral groove, cytostome (mouth) and gullet.
What is the Protista kingdom – simple definition
We begin by explaining what the Protista kingdom is , before going into details about its characteristics, classification and other aspects.
What are the characteristics of the Protista kingdom
They are eukaryotic organisms (with a nucleus delimited by a membrane), lacking differentiated vegetative tissues, except in those structures destined for the reproduction process.
Classification of the Protista kingdom
The complex and diverse characteristics of protists or protoctists make their classification one of the most difficult and convoluted in the evolution of living beings. Many have been the scientists who throughout history have tried to determine a classification for the Protista kingdom as accurate as possible.
Examples of the Protista kingdom
After knowing all this, we still wonder what are the organisms that belong to the protist kingdom , so here we summarize that some of the main genera and most representative species to give examples of the Protista kingdom or examples of the protoctists are:
Importance of the Protista kingdom
The diverse kingdom of the protists had, from its origin, a great importance within the world of scientific taxonomy and biology, among other branches of science.
What is the history of Protista?
History of Kingdom Protista. Coming to the history of this kingdom, according to the evolution, this kingdom Protista acts as a connecting link between the prokaryotic kingdom Monera and other multicellular kingdoms like Fungi, Animalia and Plantae. The term ‘Protista’ was given by German biologist Ernst Haeckel in the year 1866.
What are the three sub-types of photosynthetic protists?
It is of three sub-types namely, Dinoflagellates, Chrysophytes and Euglenoids. 1. Dinoflagellates. The group of around 1000 species of photosynthetic protists belongs to the division – Pyrrophyta and class – Dinophyceae.
What are the characteristics of Euglena?
The members show the following characteristics: These are green, autotrophic in nutrition (plant character). These are Euglena like unicellular flagellates (animal character) found mostly in stagnant freshwater. They have two types of flagella – Long Whiplash and Short Tinsel.
What are the three groups of Protista?
The kingdom Protista is divided into three groups, namely, Plant-like Protists, Fungi-like Protists and Animal-like Protists.
How do diatoms reproduce?
In Diatoms, the cell wall form two thin overlapping shells, that fit together as in a soapbox.
What is the combination of fungi and animals called?
They possess the characters of both animals and fungi, therefore, combinedly called fungus-animals.
What are the two types of flagella?
They have two types of flagella – Long Whiplash and Short Tinsel. Instead of a cell wall, they have a protein-rich layer called pellicle, which makes their body flexible. The food is stored in proteinaceous granules known as pyrenoids. Reproduction is only by the asexual method.
What kingdom are myxomycetes in?
Myxomycetes . Some scientists classify them in the Fungi kingdom . Most of these organisms are saprophytes but others are parasites. These protists reproduce by means of spores, are fed by phagocytosis and move with the help of pseudopods.
What are protists fed?
Maintain varied nutrition methods that include filtration and phagocytosis . The best-known protists are amoebas, unicellular living beings that lack definite shape. They are fed by phagocytosis but their popularity is due to their condition as parasites in the intestines of the members of the Animalia kingdom .
Which kingdom contains mainly unicellular organisms but the totality of its members is eukaryotic?
The groups of plants, animals and fungi are often easily differentiated from each other, but in the case of protists differentiation is not so simple. This kingdom contains mainly unicellular organisms but the totality of its members is eukaryotic. It is also known as the Protoctist realm .
What are the characteristics of a protist kingdom?
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PROTIST KINGDOM. It is a very diverse kingdom. The only thing that protists usually have in common is that they are not animals, they are not plants, they are not fungi and many are unicellular. 1.
Why are oomycetes called aquatic molds?
Oomycota (Oomycetes). They are known as aquatic molds because of their resemblance to members of the Fungi kingdom. They are nourished by absorption and reproduce sexually and asexually. Many oomycetes are parasites and others are saprophytes.
What are the different types of algae?
They are usually classified according to their photosynthetic pigments. Thus, there are brown algae, red algae, yellow algae and green algae. Oomycota (Oomycetes).
What are the organisms that resemble hair called?
Organisms with numerous cilia , structures that resemble hairs. Rizópodos . They are a kind of false feet that are called pseudopods. Sporozoans . They are microscopic organisms that parasitize animals. Myxomycetes . Some scientists classify them in the Fungi kingdom .
What is the protist kingdom?
Protista kingdom, also called protoctista, is understood to be one of the groups in which biology classifies living beings, more specifically eukaryotes, together with the animal, plant and fungi kingdom: all are called protists those eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants or fungi.
Classification of protists
The kingdom of the protists is traditionally divided into very different supergroups, as follows:
Reproduction of protists
The reproduction of protists can be both sexual and asexual, and sometimes the same species can alternate between one model and another, according to environmental conditions. Sexual reproduction occurs through the generation of gametes and cell fusion, while asexual occurs by cellular fission and mitosis. In no case are embryos produced.
Importance of protists
Thanks to the protists the different kingdoms of eukaryotes would be produced.

Characteristics of Kingdom Protista
- We place all single-celled eukaryotes under Protista. However, the boundaries of this kingdom are not well defined. Members of Protista are primarily aquatic. This kingdom forms a link with the others dealing with plants, animals and fungi. Being eukaryotes, the protistan cell body contains a well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles...
Grouping of Unicellular Protists
- We can classify unicellular protists into three major groups: 1. Photosynthetic Protists. Example:Dinoflagellates, Diatoms, Euglenoids 2. Consumer Protists. Example:Slime moulds or Myxomycetes 3. Protozoan Protists.Example:Zooflagellate, Sarcodina, Sporozoa, Ciliata
Life Cycles in Protists Showing Zygotic Meiosis
- By life cycle, what we mean is nothing but a sequence of events between any given phase in one generation and that similar phase in the succeeding generation. It occurs in some dinoflagellates (Example: ceratium, gymnodinium;von stosch, 1973) and cellular slime moulds. The zygote is in the form of 2n. It usually divides by meiosis (also called zygotic meiosis). These produce vegeta…
Major Groups of Protists
- Chrysophytes
This group comprises of the diatoms and golden algae (desmids). We find them in fresh water as well as in marine environments. They are microscopic. These organisms float passively in water currents (plankton). - Dianoflagellates
These organisms are usually marine and photosynthetic. They have an appearance of various colours like yellow, green, brown, blue or red. Their colour is influenced and decided by the main pigments present in their cells. The cell wall has stiff cellulose plates on its outer surface. Thes…
Solved Examples For You
- Question: Give some examples of disease-causing protozoans. Answer: The various types of disease-causing protozoa include: 1. Trypanosome gambiense: The parasite of sleeping sickness. It is transmitted by tsetse fly. It causes Gambian sleeping sickness. 2. Trypansoma rhodesiense:It causes Rhodesian sickness. The parasite is transmitted by the bites of tsetse fly (Glossina palp…