Motor behavior is a kind of movement that ranges from involuntary twitches to goal-directed voluntary actions that start from head to toe. People often fail to differentiate motor skills from motor behaviors. Motor skills define the body’s ability to manage the process of moving.
What is an example of motor behavior?
Motor learning, skills, and habits are the classic examples of unconsciously learned and unconsciously recalled memories. Walking is a good example. Walking is a good example. Walking is an extremely complex task involving intricate motor movements, which we generally perform automatically and with great facility.
What is motivated behavior?
What is motivated behavior? behavior that is initiated, sustained, and directed towards the achievement of a goal What is the basic tenet of Maslow's Pyramid of Human Needs? Describe the levels. -you have to achieve the goals at a lower level before moving to the next higher level
What are motor disturbances?
is an umbrella term used to describe any disturbance of motor behaviour such as repetitive movements or automatism. MOTOR DISTURBANCE: "Conditions such as hyperactivity are examples of motor disturbance."
What is motor learning and control?
Welcome to Motor Learning & Control Motor Learning study focuses on the behavioral, biomechanical, and neural bases of development, acquisition, and performance of functional movement skills. Acquisition of skill is examined over the life span in typically developing children and adults and individuals with movement disorders.

What are the characteristics of motor skills?
A motor skill is a function that involves specific movements of the body's muscles to perform a certain task. These tasks could include walking, running, or riding a bike. In order to perform this skill, the body's nervous system, muscles, and brain have to all work together.
What are the four characteristics of motor skills?
There are four characteristics of human actions which any theory of motor control must be able to account for: flexibility, uniqueness, consistency, modifiability.
What are the characteristics of motor development?
Motor development means the physical growth and strengthening of a child's bones, muscles and ability to move and touch his/her surroundings. A child's motor development falls into two categories: fine motor and gross motor.
What does motor behavior focus on?
The Motor Behavior area focuses on research in the disciplines of motor learning and motor control. This collaborative environment prepares practitioners, researchers, and educators reduce injury risk, return to normal function post-injury, and improve health and performance of physically active individual or all ages.
What are the 6 characteristics of motor learning?
Matchperformance improvement. Performance improvement is the most common indicator of learning. ... consistency. Contain higher level of performance overtime. ... attention. ... persistence. ... effort. ... adaptablility. ... negatively accelerating performance curve. ... linear performance curve.More items...
What are the 5 characteristics of skills?
These 5 characteristics should guide the measurement of performance and learning.Improvement. Can the person perform the skill at a higher level?Consistency. Is performance becoming increasingly more consistent?Stability. ... Persistence. ... Adaptability.
What are the 4 characteristics of development?
These are:It is a continuous process.It follows a particular pattern like infancy, childhood, adolescence, maturity.Most traits are correlated in development.It is the result of interaction of individual and environment.It is predictable.It is both quantitative and qualitative.More items...
What are the 7 basic motor skills?
7 Motor Skills needed for better Academic Performance#1 – Hand-eye Coordination. ... #2 – Bilateral Coordination. ... #3 – Core Muscle. ... #4 – Balance and Coordination. ... #5 – Crossing the Midline. ... #6 – Back to Front Activities. ... #7 – Patterning. ... Related Products.
What are the 7 fundamental motor skills?
The critical fundamental motor skills for children to learn are the catch, kick, run, vertical jump, overhand throw, ball bounce, leap, dodge, punt, forehand strike, and two-hand side-arm strike.
What are examples of motor behaviors?
Examples of gross motor skills include sitting, crawling, running, jumping, throwing a ball, and climbing stairs. Even the first time a baby lifts his head is an example of a gross motor skill. There are lots of fun and simple activities you can do with your child to help develop gross motor skills.
What are the main theories and concepts of motor behavior?
The major theories of motor control are described, which include, motor programming theory, systems theory, the theory of dynamic action, and the theory of parallel distributed processing, as well as the factors that influence motor learning and its applications in neurorehabilitation.
What are the 5 motor abilities?
Motor skills are important in early childhood development. Mastery of many motor skills is important for normal daily functions. The five basic motor skills are sitting, standing, walking, running, and jumping.
What are the 4 principles of motor development?
Four principles are drawn from approximately 100 years of research in the area of motor development. The principles are (1) children are not miniature adults, (2) boys and girls (children) are more alike than different, (3) good things are earned, and (4) no body (nobody) is perfect.
What are the 4 skill classifications?
In the following sections we'll explain the following classifications:Open versus closed skills.Continuous, series and discrete skills.Gross versus fine skills.Self-paced versus externally paced.Complex versus simple skills.
What are the 5 fundamental motor skills?
Fundamental movement skills (FMS) are the basic movements traditionally associated with human physical activity. The most common FMS include skills such as running, jumping, throwing, catching, skipping, and hopping.
What are the types of motor skills?
Children develop 2 types of motor (movement) skills: 'fine' motor skills and 'gross' motor skills. Fine motor skills involve using hands and fingers to control smaller objects. Gross motor skills involve the coordination of larger muscles in the body to make larger movements.
What is motor behavior research?
Before the early 1980s, motor behavior research used simple, novel tasks to study early skill learning; this research helps us understand how beginners learn new motor skills. Studying the early stages of learning (novice learners; figure 8.3)
What is motor learning?
Motor learning is an internal state that is relatively permanent; practice is required for it to occur, and it is difficult to observe and measure. Knowledge of performance is given by an instructor who provides feedback about the nature or process of the movement. Knowledge of results is information about the outcome of the movements that a teacher, coach, or trainer may supply. Learning requires both practice and feedback. Extrinsic feedback (for example, KR or KP) must be information that the learner could not obtain on his own, should be corrective, should be provided on about half of the trials, and must be followed by sufficient time to make corrections before the next attempt. Motor programs are proposed memory mechanisms that allow movements to be controlled. As motor programs are developed, they become more automatic, allowing the performer to concentrate on the use of the movement in performance situations. Future research that contrasts predictions and key elements from a dynamical systems view of motor behavior or a motor program view is likely to be both exciting and controversial. If you are planning to study physical activity, you must understand the physiology, biomechanics, and motor behavior underlying the development of movement to address problems such as how children gain control of movement skills, how people achieve expertise, and how these skills deteriorate as people age. One of the most intriguing developmental questions in motor behavior is, “How does the brain and nervous system adjust its control to increases in cognitive function, body size, and strength across childhood and to decreases in these same variables as people age?”
Why was WWII an active time in motor learning history?
WWII period from 1939 to 1945 was an active time in motor learning history because the military was interested in properly selecting and training military pilots based on their motor skills research findings. Motor development had its early beginnings in the area of developmental psychology.
What was the main goal of motor learning in the 1970s?
Motor learning and motor control are distinct but are linked by a common goal: to understand human movement.
What are the characteristics of movement tasks?
Characteristics of movement tasks. Measuring learning and transfer. To study motor skill acquisition, researchers must also study how well skills are retained and how they transfer to other, similar situations. Overview of knowledge in motor behavior. Information Processing Model.
When were motor skills used?
Long history in all three areas of motor behavior, but the reason for the research in each area has changed dramatically. Late 1800s and early 1900s, researchers were primarily interested in using motor skills as a means to understand the mind; motor skills were a tool to examine cognition.
Which system controls the movement of the body?
The brain uses the central nervous system to initiate and control muscles that make the movements.
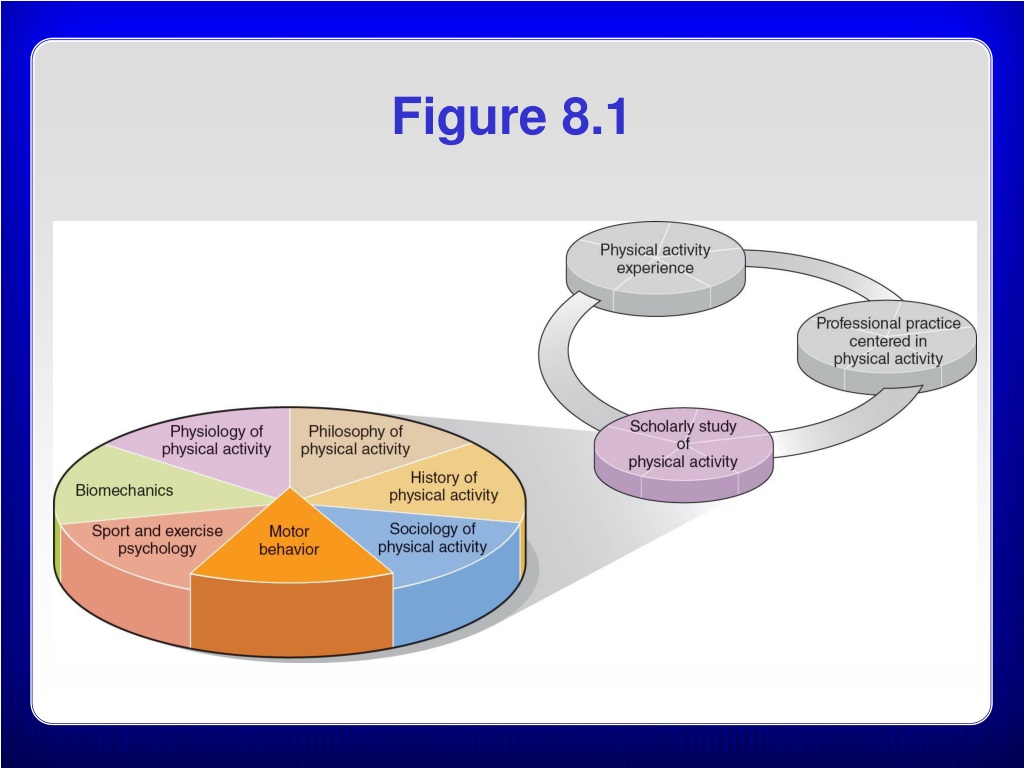
What is motor behavior?
Motor behavior includes every kind of movement from involuntary twitches to goal-directed actions, in every part of the body from head to toe, in every physical and social context from solitary play to group interactions. The development of motor behavior bridges the entire lifespan from the first fetal movement to the last dying breath.
How do motor behaviors emerge?
New motor behaviors can emerge from a mix of interacting factors, some so pervasive that we mistakenly take them for granted, and some so subtle or non-obvious that we fail to recognize the link. Developmental changes in one domain can have cascading effects on development in other domains, sometimes far afield from the original accomplishment8, 9. Moreover, the context in which behavior develops can be very different for individual children, resulting in developmental pathways that sometimes converge at the same outcome and sometimes veer off in unique directions.
What is posture in motor skills?
Posture is the most fundamental of motor actions. It is the foundation upon which other actions are built10. The instant that any part of the body breaks from the support surface—merely raising an arm while supine or lifting the head while prone—torque acting on the body part creates disequilibrium. This is why novice sitting and standing infants lose balance just from turning their heads or lifting their arms. Posture must be sufficiently stable to allow movements of the extremities, and maintaining a stable posture sets up the necessary conditions for looking around, handling objects, holding conversations, or going somewhere. As such, the emergence of most skills—including those not obviously related to posture—must await the development of sufficient postural control. Like every action, posture is perceptually guided and maintained.
How does perception affect motor development?
Posture provides a stable base for locomotion, manual actions, and facial actions. Experience facilitates improvements in motor behavior and infants accumulate immense amounts of experience with all of their basic action systems. At every point in development, perception guides motor behavior by providing feedback about the results of just prior movements and information about what to do next. Reciprocally, the development of motor behavior provides fodder for perception. More generally, motor development brings about new opportunities for acquiring knowledge about the world, and burgeoning motor skills can instigate cascades of developmental changes in perceptual, cognitive, and social domains.
What are the factors that influence the ability to control movement?
At every point in development, adaptive control of movement relies on core psychological functions1, 2. Perception and cognition are required to plan and guide actions3. Social and cultural factors spur and constrain motor behaviors 4. Motor behaviors, in turn, provide the raw material for perception, cognition, and social interaction5, 6. Movements generate perceptual information, provide the means for acquiring knowledge about the world, and make social interactions possible.
Is locomotion reflexive or hardwired?
Precursory locomotor movements are exhibited during fetal and neonatal periods, but locomotion is not reflexive or hardwired. Rather, locomotion is creative and infants must learn to control locomotion adaptively. Locomotion improves with practice, and practice can lead to extraordinary performance4, 7, 40.
Do infants step without a stimulus?
Newborns “air-step” without an eliciting physical stimulus and they step in response to optic flow45, 46. Infants can deliberately modify their leg movements47in various configurations of alternating, simultaneous, and single-leg kicks48, 49. They spontaneously kick their legs while supine50and supine leg kicks are kinematically equivalent to upright steps, and are produced by the same muscle activations50. Moreover, supine kicking continues unabated throughout the period when upright stepping disappears51, and upright steps instantly reappear when infants are held on a motorized treadmill52, 53or when their legs are submerged in a tank of water54. With daily practice in an upright posture, the stepping movements never disappear55, 56. Changes in the body, not the brain, explain the U-shaped trajectory of upright stepping: Between 2–8 months of age, gains in leg fat typically outstrip gains in muscle54. In an upright position, infants cannot lift their chubby legs against gravity, but in a supine position gravity helps to flex the legs; on a treadmill, the moving belt does the work of pulling infants’ legs backward and in a tank of water, the medium alleviates the effects of gravity. Upright practice makes leg muscles stronger.
What is the characteristic curve of a DC motor?
It is the graph plotted between the speed (N) and the armature current (I a) of a DC motor. This characteristic curve is mainly used for selecting a motor for a particular application.
Which motor is used when high starting torque is required?
It is clear from the characteristics that the series motor has high torque at low speed and vice-versa. Thus, the series DC motor is used where high starting torque is required.
What happens to the speed of a compound motor when the load is increased?
When the load is increased, the armature current is also increased which increases the flux per pole. Consequently, the speed of the motor decreases with the increase in the load. Therefore, a cumulative compound motor has poor speed regulation.
What happens to the flux in a DC series motor?
Hence, the flux in a series motor increases with the increase in the armature current and vice-versa.
What is the graph plotted between the speed (N) and the armature torque ( a) for?
The graph plotted between the speed (N) and the armature torque (τ a) for a DC motor is known as the speed-tor que characteristics. It is also known as mechanical characteristics of DC motor.
Why is the magnetic flux constant in shunt motors?
their magnetic flux remains constant because their field winding is directly connected across the supply voltage which is assumed to be constant.
What is cumulative compound motor?
A cumulative compound DC motor is the one in which the series field aids the shunt field i.e. both are in same direction.
What are Motor Skills?
Motor skills are the movements our bodies make to perform daily functions such as lifting, moving, writing, and talking. The motor skills an adult possesses begin to develop at birth and continue through childhood and early adulthood. Motor skills are categorized as gross motor skills or fine motor skills. A person needs to have mastered both to acquire solid movement. Gross motor skills involve the arms, legs, and trunk of the body. Fine motor skills involve small muscle groups such as movements in the hand or wrist.
What are the different types of motor skills?
Motor skills can also be defined as closed motor, open motor, serial motor, and discrete motor. Closed motor skills are skills that can be performed in a stable and predictable environment. Open motor skills are skills that take place in an uncontrolled and unstable environment. Discrete motor skills are movements that are quick and deliberate, and a series of discrete movements together make serial motor skills. These various types of skills are described in more detail below.
What is the difference between open motor and closed motor?
Motor skills can also be categorized as open motor, closed motor, or serial motor movements. Open motor is when the environment around the skill is uncontrolled. Closed motor is the opposite of open motor and requires a stable and controlled environment. Serial motor is a combination of continuous movement with discrete motor, or deliberate, motor skills.
Why are motor skills important?
Motor skills are essential for everyday life. They are the movements our bodies make to perform daily functions such as lifting, moving, writing, and talking.
Why is fine motor development so difficult?
A common cause of difficulty with fine motor in children is developmental coordination disorder or DCD which is also referred to as dyspraxia. Difficulty with fine motor skills can improve with occupational therapy (OT).
When do gross motor skills develop?
Gross motor skills develop as soon as birth and continue to develop into late childhood or early adulthood. Underdeveloped gross motor skills can impact all areas of a person's daily life. Low gross motor skills can make everyday life such as work and school difficult and can cause low self-esteem in the individual. Essential motor skills that develop in early childhood are:
Is basketball an example of motor skill?
Basketball is an example of an open motor skill.
What is motor reacquisition?
the study of the acquisition of motor skills, the performance enhancement of learned or highly experienced motor skills, or reacquisition of skills that are difficult to perform or cannot be performed because of injury or disease.
Which skill is the primary determinant of success?
Skills for which the primary determinant of success is the quality of the performers decisions regarding what to do
Is observable behavior temporary?
Observable behavior, temporary, may not be due to practice, may be influenced by performance variables
Do motor skills go into a classification system?
viewed this way, motor skills go into a classification system
What is the difference between psych and motor behavior?
Psych studies elite athletes in competitive settings whereas motor behavior studies people of all skill levels. Used by pedagogy and adaptive PE areas.
What is motor development?
motor development. goals of motor behavior. -understand how motor skills are learned. -understand how motor skills are controlled. goals of motor learning. understanding the influence of feedback, practice, and individual differences, especially as they relate to the retention and transfer of motor skill.
Why is motor learning important?
Motor learning helps us understand how we learn skills so that the skill becomes automatic. Motor control is essential for every movement from poorly skilled to well skilled. Motor learning is responsible for the shift from poorly skilled to highly skilled movements.
What is the history of motor control?
history of motor control research. research in the late 1800s on the "springlike" qualities of muscle and Sherrington's seminal work on neural control is still useful in explaining how the nervous system controls muscles during movement. The World War 2 era. one of the great interest in motor behavior research.
Why is reaction time slower for complex movements?
first major theoretical paper from the disciple of kinesiology. reaction time was slower for complex movements because those movements took more planning time. Motor development. developmental approach to motor learning and motor control originated in developmental psychology and child development.
Which system controls the movement of the body?
1. the brain uses the central nervous system to initiate and control muscles that make the movements
What is specificity of practice?
specificity of practice. one of the most important and easy to replicate principles in motor behavior. scholars of motor behavior. study how motor skills are learned, controlled, and developed to assist people as they place and experience physical activity. sub disciplines of motor behavior. motor learning.