
Some of the advantages of silt soil are as follows:
- 1. Well structured and uniform in every way Silt soil has a uniform texture with a minute grain size which is rich in nutrients and minerals making it an ideal garden soil. Silt soils have little variation in grain size and texture. ...
- 2. Rich In Nutrients And Light ...
- 3. Plant Growth
Does silt increase the fertility of the soil?
Water at the bottom of a body of water does not freeze, and the silt provides some insulation, or warmth, for the animal. Silty soil is usually more fertile than other types of soil, meaning it is good for growing crops. Silt promotes water retention and air circulation. Too much clay can make soil too stiff for plants to thrive.
Is silt a living thing of soil?
Silt may occur as a soil, often mixed with sand and clay or as a sediment mixed in suspension with water in rivers and streams and as deposits in the bottom. Silt has a moderate specific area with a typically non-sticky, plastic feel. Silt usually has a floury feel when dry, and a slippery feel when wet. Click to see full answer.
Why is silty soil is better than sandy soil?
Silt, which is known to have much smaller particles compared to sandy soil and is made up of rock and other mineral particles, which are smaller than sand and larger than clay. It is the smooth and fine quality of the soil that holds water better than sand.
What are characteristics of a soil make it a good soil?
Healthy Soil Characteristics Good texture: You often hear gardeners talk about their soil's "crumb." This refers to the texture of the soil. ... Plenty of organic matter: Organic matter is just dead plant and animal tissue, which decomposes and enriches your soil as humus. ... Healthy pH: Soil pH is the measurement of the acidity of your soil. ...
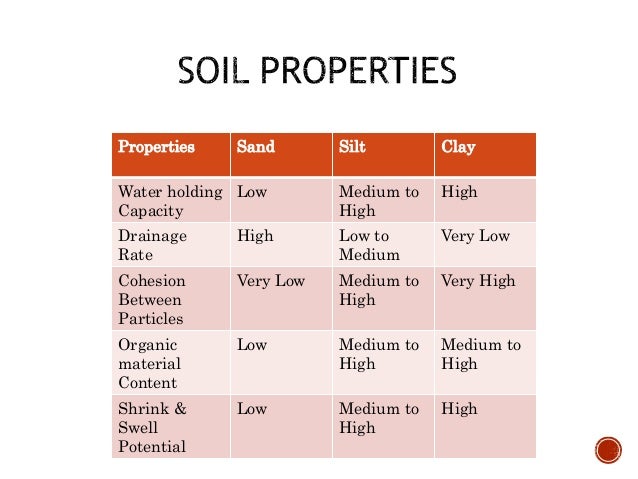
What are the five characteristics of silty soil?
Silt is a solid, dust-like sediment that water, ice, and wind transport and deposit. Silt is made up of rock and mineral particles that are larger than clay but smaller than sand. Individual silt particles are so small that they are difficult to see. ... Silty soil is slippery when wet, not grainy or rocky.
What are 3 characteristics of silt?
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel when dry, and lacks plasticity when wet.
What are the characteristics of silty clay?
Silty clay is generally brownish gray, with soft and creamy texture, flow shape, rich in organic matter, and with clay content more than 50%.
What are the 5 characteristics of soil?
All soils contain mineral particles, organic matter, water and air. The combinations of these determine the soil's properties – its texture, structure, porosity, chemistry and colour.
What is silt soil?
Silt Soil is a light and moisture retentive soil type with a high fertility rating. As silt soils compromise of medium sized particles they are well drained and hold moisture well. As the particles are fine, they can be easily compacted and are prone to washing away with rain.
What is the texture of silt soil?
smoothSilt, being moderate in size, has a smooth or floury texture. Clay, being the smaller size of particles, feels sticky.
Where is silt soil found?
Silt is easily transported by moving currents and it is mainly found near the river, lakes and other water bodies. The silt soil is more fertile compared to the other three types of soil. Therefore, it is also used in agricultural practices to improve soil fertility.
What is the color of silty soil?
GraySome soils are dark and brown. Soils that are dark and brown usually have some materials from plants and animals that have died and broken down. Orange-‐ or red-‐colored soils contain clay. Gray soils contain silt or gravel.
How do you identify silt?
Sand can always be felt as individual grains, but silt and clay generally cannot. Dry silt feels floury, and wet silt is slippery or soapy but not sticky. Dry clay forms hard lumps, is very sticky when wet, and plastic (like plasticene) when moist.
What are the 7 characteristics of soil?
Composition and Characteristics of soil. The scientific study of soil is called pedology. ... Mineral Particles: Mineral particles are the largest ingredient and make up approx 45% of soils . ... Organic Matter: ... Air and Water: ... Texture: ... Colour: ... PH Value:
What is silt used for?
Silty soil is usually more fertile than other types of soil, meaning it is good for growing crops. Silt promotes water retention and air circulation. In many parts of the world, agriculture has thrived in river deltas, where silt deposits are rich, and along the sides of rivers where annual floods replenish silt.
What are 4 soils characteristics?
Soil physical properties include texture, structure, density, porosity, consistence, temperature, and color.
What are the 3 main characteristics for classifying soil?
Soil is mainly classified by its texture, proportions and different forms of organic and mineral compositions.
How do you identify silt?
Sand can always be felt as individual grains, but silt and clay generally cannot. Dry silt feels floury, and wet silt is slippery or soapy but not sticky. Dry clay forms hard lumps, is very sticky when wet, and plastic (like plasticene) when moist.
Which best defines silt?
1. earthy matter, fine sand, or the like carried by moving or running water and deposited as a sediment. intransitive verb.
What elements make up silt?
Silt is actually a granular material, smaller than sand, but larger than clays. It is typically quartz and feldspar in its origins. Silt is typically a result of weathering, where sand sized particles of quartz are broken, into ever smaller particle sizes, along weaknesses in their chemical lattice structure.
What is a silty soil?
Continue Reading. Silty soils are those that have particles in them that are even finer (smaller) than clay particals. Silt can be deposited by water via floods or the natural flow of rivers. It can also be deposited over much larger areas by means of wind erosion.
How small is silt?
Individual silt. particle s are so small that they are difficult to see. To be classified as silt, a particle must be less than .005 centimeters (.002 inches) across. Silt is found in soil , along with other types of sediment such as clay, sand, and gravel. Silty soil is slippery when wet, not grainy or rocky.
Why is silt good for animals?
Silty soil is usually more fertile than other types of soil, meaning it is good for growing crop s. Silt promotes water retention and air circulation.
Why is silty soil dark?
Silty soils and soils with lots of clay in them will hold a lot of water. It is because the water molecules will be trapped among the tiny particles of silt and clay.
What is silt made of?
Silt is made up of rock and mineral particles that are larger than clay but smaller than sand . Individual silt
How does silt affect the environment?
Agricultural and industrial runoff can also clog ecosystems with silt and other sediment. In areas that use chemical fertilizer s, runoff can make silt toxic . Toxic silt can poison rivers, lakes, and streams. Silt can also be made toxic by exposure to industrial chemicals from ships, making the silt at the bottom of
How is silt formed?
Silt is created when rock is erode d , or worn away, by water and ice. As flowing water transports tiny rock fragments, they scrape against the sides and bottoms of stream beds, chipping away more rock. The particles grind against each other, becoming smaller and smaller until they are silt-size.
What is silt soil?
Silt soil is similar to loam soil but contains smaller ratios of both sand and clay particles. Silt soil feels smooth and silky. Silt soil retains water well but may drain slowly depending on the exact clay-silt-sand ratio.
Where is silt found?
Silt is commonly found in floodplains and is the soil component that makes mud. Soils with a lot of silt make excellent farm land, but erode easily. This is the soil blown away in dust storms and carried down stream in floods. Silt soil is similar to loam soil but contains smaller ratios of both sand and clay particles.
Can you add sand to silt soil?
While silt-based soils work fine for most gardeners, small amounts of sand can be added to it to help with water absorption. Till the amendments into the soil. If the procedure is conducted in the fall, the improvements should be apparent by the following spring.
Why is silt used in agriculture?
Silt is easily transported by moving currents and it is mainly found near the river, lake and other water bodies. The silt soil is more fertile compared to the other three types of soil. Therefore, it is also used in agricultural practices to improve soil fertility.
Where is silt found?
Silt is easily transported by moving currents and it is mainly found near the river, lake and other water bodies. The silt soil is more fertile compared to the other three types of soil. Therefore, it is also used in agricultural practices to improve soil fertility.
What is the poorest type of soil?
Sand or sandy soil is formed by the smallest or fine particles of weathering rocks. This soil is known as the poorest type of soil for agriculture and growing plants as they have very low nutritional value and poor water holding capacity.
What is soil made of?
It is mainly composed of mineral, nutrients, water, other inorganic particles and some residues of plants and animals .
Why is sandy soil bad for plants?
Sandy soils are one of the poorest types of soil for growing plants because it has very low nutrients and poor water holding capacity, which makes it hard for the plant’s roots to absorb water . This type of soil is very good for the drainage system.
What is agricultural soil?
This soil is also referred to as agricultural soil as it includes an equilibrium of all three types of soil materials being sandy, clay, and silt and it also happens to have humus. Apart from these, it also has higher calcium and pH levels because of its inorganic origins.
What is the smallest soil?
Clay is the smallest particle amongst the other two types of soil. The particles in this soil are tightly packed together with each other with very little or no airspace. This soil has very good water storage qualities and makes it hard for moisture and air to penetrate into it. It is very sticky to the touch when wet, but smooth when dried. Clay is the densest and heaviest type of soil which does not drain well or provide space for plant roots to flourish.
What are the elements in soil?
The elements that are found in the highest quantities are O, Si, Al, Fe, C, Ca, K, Na, and Mg. These are also the major elements found in the Earth's crust and in sediments ( Table 2.1 ). Oxygen is the most prevalent element in the Earth's crust and in soils. It comprises about 47% of the Earth's crust by weight and greater than 90% by volume ( Berry and Mason, 1959 ).
What is the composition of soil?
Soils are complex assemblies of solids, liquids, and gases. For example, in a typical silt loam soil ideal for plant growth the solid component in the surface horizon represents about 50% of the volume (about 45% mineral and 5% organic matter), gases (air) comprise about 20–30%, and water typically makes up the remaining 20-30%. Of course, the distribution of gases and water in the pore space component can change quickly depending on weather conditions and a host of other factors.
How do crops grow?
Crops grow best when seeds are spaced such that plants obtain maximum sunlight and moisture and are placed at a proper depth within the soil. This is best accomplished by varying the seeding rate according to soil conditions such as texture, organic matter, and available soil moisture. For example, fewer seeds would be planted in sandy soil than in silt loam soils due to the amount of available moisture. To maximize yield per plant, seeds would be sown at a lower density, which would usually produce larger heads (ears) of harvested seeds because of more soil nutrients and sunlight available per plant.
What are the primary minerals in soil?
Other primary minerals found in soils in smaller quantities include pyroxenes, micas, amphiboles, and olivines. Primary minerals occur primarily in the sand (2–0.05 mm particle diameter) and silt (0.05–0.002 mm particle diameter) fractions of soils but may be found in slightly weathered clay-sized fractions.
What are the inorganic components of soil?
The inorganic components of soils include both primary and secondary minerals (defined below), which range in size (particle diameter) from clay-sized colloids (<2 μm or 0.002 mm) to gravel (>2 mm) and rocks. Table 2.2 lists the major primary and secondary minerals that are found in soils.
What is the air-entry value of a soil?
Considering the drying of soil from saturation, θ in Figure 5 (b) stays high until a particular ψ value where it starts to decline. That ψ is called the air-entry value. By the capillary hypothesis, it is assumed to have a nonzero value because the largest fully wet pore of the medium will stay filled until the air–water pressure difference exceeds in magnitude the equivalent ψ value of capillary rise. In natural media, the air-entry value is usually poorly determined, as the decline in θ with ψ starts gradually, beginning at ψ nearly equal to zero. Artificial porous media, however, can be made in such a way that many pores are close to the size of the largest pore, so that air-entry is a sharp and sudden phenomenon.
How does alternating manure and fertilizer affect grass?
They concluded that by alternating manure and mineral fertilizer, 18% more grass containing more crude protein could be grown at the same rate of N compared with using manure alone. Hence, alternating between manure and fertilizer may improve productivity per unit land area without decreasing the rate of N recovery per unit of herbage produced.
What is the texture of soil?
Texture. The texture of soil comes from its contents of sand, silt, and clay. Each of these contents makes up a percentage of the soil, which can vary depending on the type. For example, clay soil has its name because it has at least 40% clay, less than 45% sand, and less than 40% silt. Desert soil is composed mostly of sand (90-95%) ...
How many traits can describe the physical properties of soil?
Twelve traits can describe the physical properties of soil. Each of these physical properties of soil plays a vital role in agriculture and contribute to the overall health of plants. When looking at the soil horizons, and what they contain in a soil profile, knowledge of these physical properties is absolutely essential.
Why is soil porosity important?
Determining the soil porosity can help to ensure that the plants in the soil can absorb enough water and oxygen. When testing for other physical properties of soil, referencing back to the soil porosity can be enlightening, and will also save a lot of time with the entire physical properties analysis.
How does soil density change?
Bulk density in soil can change with excessive agricultural preparation. When soil faces erosion from this tillage, the particles begin to fill pore space, leading to an increase in bulk density.
Why does soil hold more water?
Soils that have large particles and a heavy texture will hold more water because there is more space available within; this promotes drainage. The topsoil part of a soil structure will affect water drainage in agriculture, as well. Topsoil can be granular, blocky, prismatic, or platy.
What is desert soil made of?
Desert soil is composed mostly of sand (90-95%) Each type of soil has a soil triangle, which provides a visual representation of its texture elements. This triangle is called a soil textural triangle. Some soil textural triangles are available online, but you can also create one based on soil testing.
What is soil resistivity?
Soil resistivity refers to the measurement of the conductivity of soil. Resistivity tests determine how well electricity can move through soil.
What is soil texture?
Soil texture describes the makeup of a type of soil. Certain soil textures, such as loam, clay, and sand, are definitive terms for the percentage of sand, silt, and clay within a soil layer. Depending on the texture of a plot of soil, it could determine how well the land will grow crops and other plants.
What is sand soil?
Sand soil has 25% or more of very coarse to medium sand and less than 50% of fine sand. Typically, sand soil does not contain silt or clay.
How many types of soil are there?
Take a sample of the soil in your field or garden and break it down by color and feel to see which of these 28 soil types matches it best. Each layer depth will have different levels of nutrients and minerals, all of which are very important.
Why is brown soil not good for gardening?
Desert soil and brown soil, for example, would not be ideal for gardening because of the lack of nutrients in each type.
Why is ultisol red?
Ultisols. Ultisol soil has a red color to it due to an excess of metal oxides and is rich in clay. Ultisols support the vegetation of forests and are usually in southeastern United States, China, South America, and Africa. The uppermost layer of a ultisol is humus-rich. An example of a Ultisol would be Red Soil.
How to get a soil profile?
Use your garden tools to get a soil profile. Then, use online guides such as the Guide to Texture by Feel, which are provided by the United States Department of Agriculture to help you determine the texture and other elements of the soil.
Which type of soil has the highest carbon content?
Arctic Soil – low in most nutrients; high carbon content. Tundra Soil –has minimal amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus; the soil pH of tundra is very acidic. Permafrost – (similar to arctic soil) high levels of carbon; other nutrients vary depending on what was in the soil at the time of freezing.
