
Each nucleotide consists of three components:
- a nitrogenous base: cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A) or thymine (T)
- a five-carbon sugar molecule (deoxyribose in the case of DNA)
- a phosphate molecule.
What parts of DNA nucleotide are most important?
The molecular structure of DNA
- The four nucleotide monomers are distinguished by their bases. ...
- Phosphodiester bonds in DNA polymers connect the 5’ carbon of one nucleotide to the 3’ carbon of another nucleotide. ...
- Chromosomes are made of two DNA polymers that stick together via non-covalent hydrogen bonds. ...
What are the three parts of a nucleotide of DNA?
- nucleotide. consists of three parts: a five carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- deoxyribose. the five carbon sugar in a DNA nucleotide.
- what does the phosphate group consist of?
- nitrogenous base.
- purines.
- pyrimidines.
- base-pairing rules.
- complementary base pairs.
What are nucleotides within DNA are composed of?
DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These building blocks are made of three parts: a phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases. To form a strand of DNA, nucleotides are linked into chains, with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating.
What are correctly describes the components of DNA?
DNA is made up of nucleotides consisting of the sugar ribose, a carbon ring, and one of four phosphorus bases. DNA is made up of nucleotides consisting of the sugar deoxyribose, a phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases. DNA is made up of proteins consisting of the sugar ribose, a carbon ring, and one of four phosphorus bases.

What are the 3 chemical components of A nucleotide?
Nucleotides contain three characteristic components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose, and one or more phosphate groups. The nitrogenous bases are derivatives of two parent heterocyclic compounds, purine and pyrimidine. The major pyrimidine bases are cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
What are the 4 chemicals used in DNA?
The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
What are the chemical components of a DNA molecule quizlet?
What are the chemical components of a DNA molecule? DNA is composed of a sequence of subunits, each containing a phosphate, a deoxyribose sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), or cytosine (C).
Is DNA made of nucleotides?
At the most basic level, all DNA is composed of a series of smaller molecules called nucleotides.
What chemicals are used in DNA testing?
Chemicals Used in DNA AnalysisEthylenediaminetetraacetate for DNA Purification. ... Magneisum Chloride for DNA Amplification. ... Ethidium Bromide for DNA Staining.
What are the 5 components of DNA?
(The Double Helix) DNA is made up of six smaller molecules -- a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate molecule and four different nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine).
What chemicals are used in DNA fingerprinting?
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) is a large, flat basic molecule that resembles a DNA base pair. Because of its chemical structure, it can intercalate (or insert) into a DNA strand. Ethidium bromide is commonly used in molecular biology laboratories to stain electrophoresis gels.
What is the chemical formula for DNA?
C15H31N3O13P2Deoxyribonucleic acid | C15H31N3O13P2 - PubChem.
What are the three parts of DNA?
Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: 1 Nitrogenous Base#N#Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. 2 Pentose Sugar#N#In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. In RNA, the sugar is ribose. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars. The carbons are numbered sequentially, to help keep track of where groups are attached. The only difference between them is that 2'-deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom attached to the second carbon. 3 Phosphate Group#N#A single phosphate group is PO 43-. The phosphorus atom is the central atom. One atom of oxygen is connected to the 5-carbon in the sugar and to the phosphorus atom. When phosphate groups link together to form chains, as in ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the link looks like O-P-O-P-O-P-O, with two additional oxygen atoms attached to each phosphorus, one on either side of the atom.
What are the building blocks of DNA and RNA?
Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA and RNA used as genetic material. Nucleotides also are used for cell signaling and to transport energy throughout cells. You may be asked to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded to each other. Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA .
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
Although DNA and RNA share some similarities, they are built from slightly different sugars, plus there is a base substitution between them. DNA uses thymine (T), while RNA uses uracil (U). Both thymine and uracil bind to adenine (A).
What are the two categories of nitrogenous bases?
Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines.
How many phosphate groups are in a free nucleotide?
The number 5 carbon of the sugar is bonded to the phosphate group. A free nucleotide may have one, two, or three phosphate groups attached as a chain to the 5-carbon of the sugar. When nucleotides connect to form DNA or RNA, the phosphate of one nucleotide attaches via a phosphodiester bond ...
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
The carbons are numbered sequentially, to help keep track of where groups are attached. The only difference between them is that 2'-deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom attached to the second carbon.
What is the name of the nucleotide molecule?
In nucleic acids, nucleotides contain either a purine or a pyrimidine base—i.e., the nucleobase molecule, also known as a nitrogenous base—and are termed ribo nucleotides if the sugar is ribose, or deoxyribo nucleotides if the sugar is deoxyribose. Individual phosphate molecules repetitively connect the sugar-ring molecules in two adjacent ...
What are the two types of organic molecules that make up nucleotides?
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth.
How do nucleotides function in cellular signaling?
In addition to being building blocks for the construction of nucleic acid polymers, singular nucleotides play roles in cellular energy storage and provision, cellular signaling, as a source of phosphate groups used to modulate the activity of proteins and other signaling molecules , and as enzymatic cofactors, often carrying out redox reactions. Signaling cyclic nucleotides are formed by binding the phosphate group twice to the same sugar molecule, bridging the 5'- and 3'- hydroxyl groups of the sugar. Some signaling nucleotides differ from the standard single-phosphate group configuration, in having multiple phosphate groups attached to different positions on the sugar. Nucleotide cofactors include a wider range of chemical groups attached to the sugar via the glycosidic bond, including nicotinamide and flavin, and in the latter case, the ribose sugar is linear rather than forming the ring seen in other nucleotides.
What are the three subunits of a nucleo tide?
A nucleo tide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase —the two of which together are called a nucleo side —and one phosphate group. With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleo side mono phosphate", "nucleoside di phosphate" or "nucleoside tri phosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group.
What are the structural elements of three nucleo tides?
Structural elements of three nucleo tides —where one-, two- or three-phosphates are attached to the nucleo side (in yellow, blue, green) at center: 1st, the nucleotide termed as a nucleoside mono phosphate is formed by adding a phosphate (in red); 2nd, adding a second phosphate forms a nucleoside di phosphate; 3rd, adding a third phosphate results in a nucleoside tri phosphate. + The nitrogenous base ( nucleobase) is indicated by "Base" and " glycosidic bond " (sugar bond). All five primary, or canonical, bases —the purines and pyrimidines —are sketched at right (in blue).
How are nucleotides synthesized?
In vivo, nucleotides can be synthesized de novo or recycled through salvage pathways. The components used in de novo nucleotide synthesis are derived from biosynthetic precursors of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, and from ammonia and carbon dioxide.
What is the name of the nucleotide that contains the five carbon sugar deoxyribose?
This nucleotide contains the five-carbon sugar deoxyribose (at center), a nucleobase called adenine (upper right), and one phosphate group (left). The deoxyribose sugar joined only to the nitrogenous base forms a Deoxyribonucleoside called deoxyadenosine, whereas the whole structure along with the phosphate group is a nucleotide, a constituent of DNA with the name deoxyadenosine monophosphate.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
There's an A, C, G, and T in DNA, and in RNA there's the same three nucleotides as DNA, and then the T is replaced with a uracil. The nucleotide is the basic building block of these molecules, and is essentially are assembled by the cell one at a time and then strung together by the process of either replication, in the form of DNA, ...
What is the building block of nucleic acids?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids. RNA and DNA are polymers made of long chains of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
There are just 3 components of nucleotide: nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (sugar) and phosphate group. In DNA, complementary nitrogen bases on opposite strands are connected with hydrogen bond. This is how two DNA strands are held together. Single strand in DNA is kept because of phosphate groups and deoxyribose molecules that are mutually connected and build DNA. There are 5 carbon atoms in deoxyribose molecule. Phosphates are connected to third and fifth carbon atom (it is always counted from carbon that is connected to the nitrogenous base towards carbon that is outside the ring- carbon with 2 hydrogen atoms). Carbon atoms in deoxyribose are labeled with number and apostrophe (') so it looks like 1'- first, 2'- second, 3'- third, 4'- fourth and 5'- fifth. Those are often called prime carbons. Phosphates are connected to 3' and 5' so in genetics, 3' may also be called 3 prime end and 5' may be called 5 prime end. An enzyme called RNA polymerase (there are three types of this enzyme- I, II and III of which RNA polymerase I synthesizes rRNA (ribosomal), RNA polymerase II synthesizes mRNA (messenger) and miRNA (micro) and RNA polymerase III synthesizes tRNA (transfer)) can synthesize RNA in any direction (from 5' to 3' or from 3' to 5') but in DNA replication, an enzyme called DNA polymerase can add nucleotides only to 3 prime end. Since there are two strands are separated in this process, for one strand (leading strand) it is simple- just adding nucleotides but for other strand (lagging strand) it's more complicated because it starts with 5' and nucleotides can not be added on this strand. This problem is solved by an enzyme- RNA primase that adds some RNA primers so it starts with 3' but with RNA nucleotides. These RNA nucleotides are replaced with DNA nucleotides by enzyme DNA ligase, and then, nucleotides can be added to lagging strand.
What are the components of DNA?
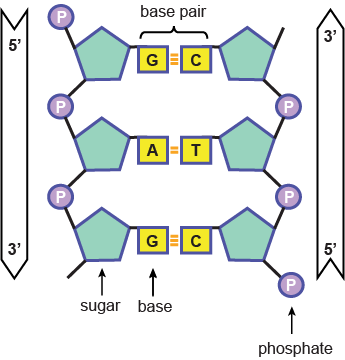
The three components are 1) a five carbon deoxyribose sugar, 2) a phosphate group, and 3) a nitrogenous base (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, or Cytosine). The sugar and phosphate compose the backbone of the DNA’s structure.
What is the nitrogenous base?
Nitrogenous base- The nitrogenous base is bound to the 1′ carbon and is what determines if a nucleotide is a G uanine (G), C ytosine (C), A denine (A), or a T hymine (T). These are the 4 types of DNA nucleotides. They can fall into one of two categories: pyrimidines and purines. The pyrimidines (single ring nitrogenous bases) are cytosine and thymine, while the purines (double ring nitrogenous bases) are adenine and guanine. Adenine and thymine pair, while cytosine and guanine pair. These pairings are what give DNA its double helix structure.
Why is DNA negatively charged?
Phosphate group- If you are familiar with chemistry, the phosphate group (PO4) has 3- charge, which ultimately is the reason that DNA is negatively charged. This charge is very important in the process of packaging DNA into chromosomes. The phosphate group is bound to the 5′ carbon of the nucleotide we are investigating. This phosphate group binds an oxygen molecule to the free hydrogen of another nucleotide’s 3′ carbon (which is found on the deoxyribose of another nucleotide), and this forms what is known as the phosphodiester backbone.
What are the basic units of DNA?
Nucleotide are the basic units of DNA molecule. Our Genetic Material Deoxyribonuclei acid (DNA) are made up of sub-units called monomers. In DNA, the monomers are called nucleotides, and these are linked together to form a polynucleotide chain that can be hundreds, thousands, or even millions of nucleotides in length.
What is the name of the molecule that contains sugar?
A molecule comprising the sugar joined to a base is called a nucleoside. This is converted into a nucleotide by attachment of a phosphate group to the 5′ carbon of sugar. Up to three individual phosphates can be attached in series. The individual phosphate groups are designated α,β and γ with the α phosphate being the one attached directly to the sugar. Nucleoside=Sugar+Nitrogenous base
Which molecule has one OH group?
Sugar molecule (blue) that connects nitrogenous base and phosphate group is called 2-deoxyribose (it has just one OH group). In RNA, there is sugar ribose (it has two OH groups).
Overview
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver.
Structure
A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group. With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate gr…
Synthesis
Nucleotides can be synthesized by a variety of means both in vitro and in vivo.
In vitro, protecting groups may be used during laboratory production of nucleotides. A purified nucleoside is protected to create a phosphoramidite, which can then be used to obtain analogues not found in nature and/or to synthesize an oligonucleotide.
Prebiotic synthesis of nucleotides
Theories about how life arose require knowledge of chemical pathways that permit formation of life’s key building blocks under plausible prebiotic conditions. The RNA world hypothesis holds that in the primordial soup there existed free-floating ribonucleotides, the fundamental molecules that combine in series to form RNA. Complex molecules like RNA must have arisen from small molecules whose reactivity was governed by physico-chemical processes. RNA is composed of
Unnatural base pair (UBP)
An unnatural base pair (UBP) is a designed subunit (or nucleobase) of DNA which is created in a laboratory and does not occur in nature. Examples include d5SICS and dNaM. These artificial nucleotides bearing hydrophobic nucleobases, feature two fused aromatic rings that form a (d5SICS–dNaM) complex or base pair in DNA. E. coli have been induced to replicate a plasmid containing UBPs through multiple generations. This is the first known example of a living organi…
Medical applications of synthetic nucleotides
Several nucleotide derivatives have been used as antivirals against hepatitis and HIV. Tenofovir disoproxil, Tenofovir alafenamide and Sofosbuvir are examples of NRTI used against hepatitis. Whereas certain drugs like Mericitabine, Lamivudine, Entecavir and Telbivudine for example are nucleosides, but they are metabolized into their bioactive nucleotide forms through phosphorylation.
Length unit
Nucleotide (abbreviated "nt") is a common unit of length for single-stranded nucleic acids, similar to how base pair is a unit of length for double-stranded nucleic acids.
Abbreviation codes for degenerate bases
The IUPAC has designated the symbols for nucleotides. Apart from the five (A, G, C, T/U) bases, often degenerate bases are used especially for designing PCR primers. These nucleotide codes are listed here. Some primer sequences may also include the character "I", which codes for the non-standard nucleotide inosine. Inosine occurs in tRNAs and will pair with adenine, cytosine, or thymine. This character does not appear in the following table, however, because it does not rep…