Anaemia, Anemia : Causes, Morphology, Symptoms, Classification & Treatment
- Definition. Anemia (Anaemia) is defined as a reduction in the oxygen-transporting capacity of blood, which usually stems from a decrease in the red cell mass to subnormal levels.
- Pathophysiology. Subnormal level of haemoglobin causes lowered oxygen carrying capacity of the blood. ...
- Clinical symptoms. ...
What are the three classifications of anemia?
The Different Types of Anemia
- Symptoms of Anemia. Common symptoms associated with anemia include fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, headache, feeling cold, and pale or yellowish skin. ...
- Types of Anemia. ...
- Anemia of Chronic Disease vs Iron-Deficiency Anemia. ...
- Anemia of Chronic Disease. ...
What are some names of the different types of anemia?
Types of Anemia
- Iron-deficiency anemia. This type is the most common of the various types of anemia. ...
- Vitamin deficiency anemia. This type arises when the body has neither enough folic acid nor vitamin B12 that are necessary for red blood cells production.
- Aplastic anemia. ...
- Anemia of inflammation. ...
- Hemolytic anemia. ...
What does being 10 on the anemia scale mean?
What does being 10 on the anemia scale mean. Sep 17, 2008. ... deltalicious--It means a few different things; that you are below range with a Hgb of 10, indicating anemia, classed as a grade 1 borderline mild to moderate anemia, you are pulling from your iron stores (ferritin) in the bone marrow and organs. All of which is corrected with iron ...
What are the different types of anemias?
Types of Anemia Scientifically
- Aplastic anemia This is a condition with damage to the red bone marrow of long bones. ...
- Megaloblastic Anemia As the name indicates, the cells formed are very large. Image showing large-sized RBC cells among normal RBC cells. ...
- Genetic or hereditary anemia This condition is less common, but the patient suffers the issue for entire life. ...

What are the 6 types of anemia?
They include:Iron deficiency anemia. This most common type of anemia is caused by a shortage of iron in your body. ... Vitamin deficiency anemia. ... Anemia of inflammation. ... Aplastic anemia. ... Anemias associated with bone marrow disease. ... Hemolytic anemias. ... Sickle cell anemia.
WHO classification anemia in adults?
The World Health Organization (WHO) criterion for anemia in adults is a hemoglobin (Hb) value of less than 12.5 g/dL. Children aged 6 months to 6 years are considered anemic at Hb levels less than 11 g/dL, and children aged 6-14 years are considered anemic when Hb levels are less than 12 g/dL.
What are the 3 types of anemia?
Many types of anemia exist, such as iron-deficiency anemia, pernicious anemia, aplastic anemia, and hemo- lytic anemia. The different types of anemia are linked to various diseases and conditions. Anemia can affect people of all ages, races, and ethnici- ties.
How many types are anemia?
Anemia Types and Causes. There are more than 400 types of anemia, and they're divided into three groups: Anemia caused by blood loss.
Why do we classify anaemia?
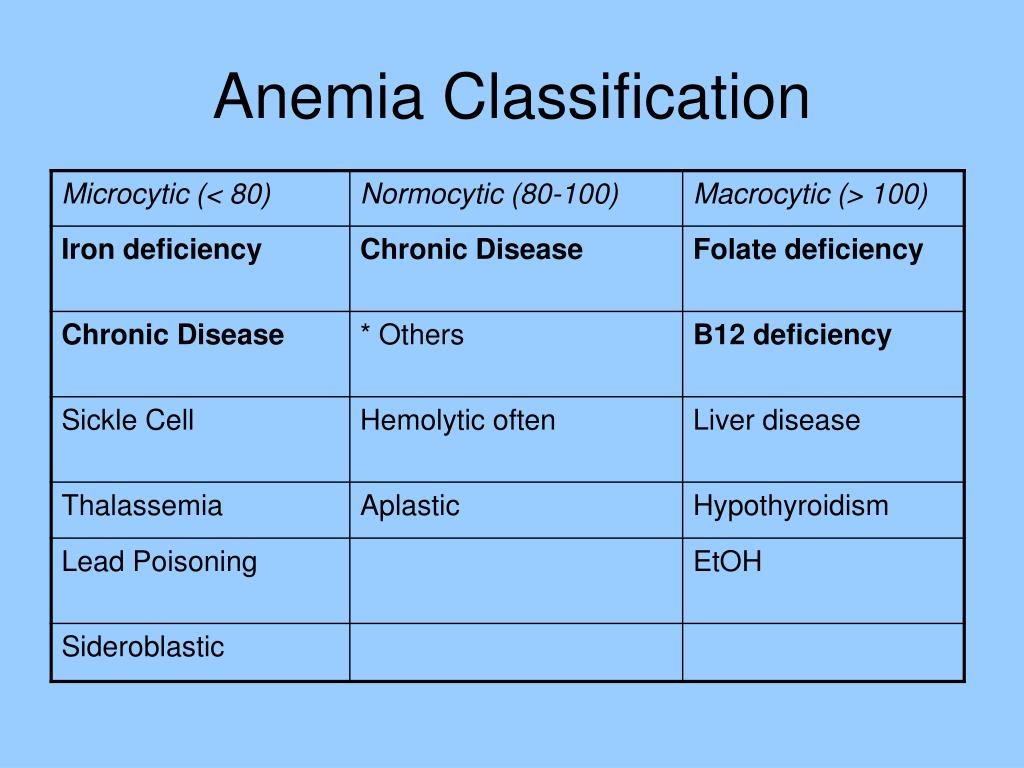
Anemia can also be classified based on the size of the red blood cells and amount of hemoglobin in each cell. If the cells are small, it is called microcytic anemia; if they are large, it is called macrocytic anemia; and if they are normal sized, it is called normocytic anemia....AnemiaFrequency2.36 billion / 33% (2015)8 more rows
What are the 3 main causes of anemia?
Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein that gives the red color to blood. It carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Anemia has three main causes: blood loss, lack of red blood cell production, and high rates of red blood cell destruction.
What is the most common type of anemia?
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia.
What are 3 symptoms of anemia?
Iron deficiency anemia signs and symptoms may include:Extreme fatigue.Weakness.Pale skin.Chest pain, fast heartbeat or shortness of breath.Headache, dizziness or lightheadedness.Cold hands and feet.Inflammation or soreness of your tongue.Brittle nails.More items...•
What are the 21 symptoms of anemia?
Symptoms of AnemiaWeakness.Dizziness.Pale skin.Headache.Numbness or coldness in hands and feet.Low body temperature.Shortness of breath on exertion.
How are different types of anemia diagnosed?
Complete blood count (CBC). A CBC is used to count the number of blood cells in a sample of your blood. For anemia, your doctor will likely be interested in the levels of the red blood cells contained in your blood (hematocrit) and the hemoglobin in your blood.
What defines anemia?
Anemia is a condition that develops when your blood produces a lower-than-normal amount of healthy red blood cells. If you have anemia, your body does not get enough oxygen-rich blood. The lack of oxygen can make you feel tired or weak.
What are the medicine for anemia?
What is the best medication for anemia?Drug nameDrug classAdministration routeFeosol(ferrous sulfate)Iron SupplementOralSlow FeIron SupplementOralVitamin B-12 (cyanocobalamin)Vitamin B-12 supplementOral, injectionFolic Acid (folate)Folate supplementOral, injection4 more rows•Nov 17, 2021
Who anemia diagnostic criteria?
The World Health Organization defines anemia as blood hemoglobin values of less than 7.7 mmol/l (13 g/dl) in men and 7.4 mmol/l (12 g/dl) in women. Typically, the evaluation of the cause of anemia includes a complete blood cell count, peripheral smear, reticulocyte count, and serum iron indices.
WHO guideline for anemia in pregnancy?
Center of Disease Control (CDC) defines anemia as pregnancy hemoglobin less than 11 g/dl (Hematocrit;{Hct} < 33%) in the first and third trimester and less than 10.5 g/dl (Hct < 32%) in the second trimester while World Health Organisation (WHO) defines anemia in pregnancy as Hb values less than 11gm/dl [3, 4].
Who anemia criteria mild moderate severe?
At this point patients were categorized into mild, moderate and severe anemia according to World Health Organization classification, i.e mild anemia (hemoglobin 9.0–10.9 g/dL), moderate anemia (hemoglobin 7.0–8.9 g/dL), and severe anemia (hemoglobin less than 7.0 g/dL).
How do cell size and content determine classification of anemia and what are 6 types of anemia?
Anemias are classified, according to the size of the red cell, as being normocytic (normal MCV), macrocytic (increased MCV), or microcytic (decreased MCV). Microcytic anemias were also often described as being hypochromic based on peripheral smear examination and MCHC when this value was determined manually.
What is the classification of anemia?
Pathophysiological Classification. Anemia is also classified through pathophysiological classification. This classification is based on anemia due either to increased loss or destruction of red blood cells or a decreased production of red blood cells.
How is anemia classified?
Anemia is classified in two ways, either morphological classification or pathophysiological classification. The morphological classification is based on the size or volume of the red blood cell and may also be classified by the hemoglobin content of the red blood cell. A red blood cell of a normal size or volume is said to be normocytic.
What is the morphological classification of anemia?
A morphological classification of anemia can also be normochromic, which we know from our terminology lesson means red blood cells with normal hemoglobin content. Or they could be hypochromic, meaning low hemoglobin content, or hyperchromic, meaning high hemoglobin content.
What does "normo" mean in anemia?
Let's look at a few more terms that will come in handy. Some classifications of anemia deal with the size or volume of the red blood cell, so we use prefixes such as 'normo' to mean normal, 'micro' to mean small and 'macro' to mean large. The hemoglobin content of the red blood cell can also be a factor with anemia.
What is pathophysiological classification?
Pathophysiological classification is based on either anemia due to increased loss or destruction of red blood cells as would be expected in a person with a recent history of hemorrhaging, or a decreased production of red blood cells as would be expected in a person experiencing bone marrow failure. Learning Outcome.
Why is it important to categorize anemia?
The reason is because categorizing an anemia is useful in determining what is going on in the body and, therefore, defining the underlying condition. For example, if tests reveal small red blood cells ( microcytic) and low hemoglobin content ( hypochromic ), then the physician would have a good indication that this patient might be dealing with iron-deficiency anemia and could prescribe an appropriate treatment plan. It might help you to recall this fact by remembering that iron helps make blood cells, so if iron is deficient, then the cell volume and hemoglobin will be deficient, giving us microcytic, hypochromic cells.
What is the term for a decrease in red blood cells?
Anemia is associated with a decrease in red blood cells, or hemoglobin concentration. Ways of classifying anemia depend on the size and hemoglobin content of the red blood cells (morphological) or the mechanism (pathophysiological). Create an account.
What are the symptoms of anaemia?
Four most common presenting symptoms are weakness, dyspnoea, paraesthesia and sore tongue. Apart from pallor, the most common sign is atrophic glossitis. Fever is seen in some percentage (22%) of cases and spleen is seldom enlarged.
What causes anemia in the body?
Anaemia results from repeated loss of small amounts of blood. Common causes are bleeding peptic ulcer, piles, carcinoma, ankylostomiasis or menorrhagia. Frequent medication with aspirin can also cause alimentary bleeding. Frequent and persistent blood loss can cause a progressive fall in Hb.
How old is too old to have iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency is frequently found between the ages of 6 months and 5 years, the highest incidence being at the age of 12 months. There are two factors which predispose to iron deficiency in infancy, name y, inadequate iron stores at birth and inadequate amount of iron in the diet. Prolonged milk feeding especially breast-fed and artificially fed infants become anaemic due to iron deficiency.
How much iron is needed for pregnancy?
Pregnancy Total iron requirement during pregnancy is as follows—Foetal need is about 280 mgmof iron. Expanding maternal red cell mass requires about 200 mgm of iron and a further 125 mgm of ironfor blood loss and placenta during delivery. Although, basal iron losses are offset by amenorrhoea, to this must be added an average daily loss of 162-370 mgm of iron throughout pregnancy.
How much iron is in the human body?
There are about 4 to 5 gms of iron in the adult human body. About two-thirds of it are found.in the red cells. One ml of red cell contains approximately 1 mgm of iron, so that an adult has about 2 gms of iron in the red cell mass. About 0.15 gm is present as myoglobin and respiratory enzymes.
Does iron absorption decrease with anemia?
Body iron stores a decrease of body iron induces increased iron absorption from the alimentary tract. This may occur in iron deficiency state without anaemia . Conversely, iron absorption is diminished if states of iron overload.
Can iron deficiency cause refractory anaemia?
Abnormal utilisation of iron with failure of haem synthesis by the marrow may cause a refractory anaemia. In this condition, there is a peripheral blood picture of chronic iron deficiency anaemia with excessive accumulation of iron containing granules in the erythroblasts and reticulocytes of the bone marrow and haemosiderosis of the liver and other tissues.
What are the symptoms of anemia?
Common symptoms associated with anemia include fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, headache, feeling cold, and pale or yellowish skin . 2 You can experience a combination of these symptoms, but you might not notice any symptoms of anemia.
What is the rarest type of anemia?
Aplastic anemia: This rare type of anemia develops when the body stops producing sufficient numbers of red blood cells. Viral infections, exposure to toxic chemicals, autoimmune diseases, and certain drugs are among the causes. 4
What diseases interfere with the production of red blood cells?
Anemia of chronic disease: Cancer, kidney disease, liver disease, thyroid disease, and RA, can interfere with the production of red blood cells. 1
What causes low RBCs?
Vitamin-deficiency anemia: Low levels of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body cause macrocytic anemia (enlarged RBCs) and low numbers of RBCs. Vitamin B12 deficiency often develops when this vitamin is not well-absorbed. Pernicious anemia is one of many causes of B12 deficiency.
Why do people get anemia?
Anemia can develop due to nutritional deficits, blood loss, or chronic diseases. Anemia of chronic disease is a specific type of anemia that's associated with inflammation. 1 And anemia is common in people with inflammatory types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) .
How is anemia detected?
Often, the condition is first detected with a blood test , especially if the anemia is mild.
What is the condition where there is a low number of red blood cells?
There are many different types of anemia, a condition in which there is a low number of red blood cells (RBCs) or a low hemoglobin concentration in the body. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein in the RBCs that binds to oxygen, transporting it to tissues throughout the body. Anemia can develop due to nutritional deficits, blood loss, ...
What are the symptoms of anemia?
Several signs and symptoms occur in all types of anemia, such as fatigue, shortness of breath and feeling cold. Others include:
How many people are affected by anemia?
Anemia affects more than two billion people globally, which is more than 30% of the total population. It is especially common in countries with few resources, but it also affects many people in the industrialized world. Within the U.S., anemia is the most common blood condition.
Why is anemia genetic?
This genetic form of anemia happens because the shape of the red blood cells is faulty. They are sickle shaped, which means that they can clog the blood vessels and cause damage. The hemoglobin does not work correctly. This type of anemia is most often, but not always, found in African Americans.
Why are my red blood cells low?
Red blood cell levels are low due to one of the following reasons: Your body cannot make enough hemoglobin ( low hemoglobin ). Your body makes hemoglobin, but the hemoglobin doesn't work correctly.
How do you know if you are lacking iron?
Other signs that you might be lacking in iron include having brittle or spoon-shaped nails and possible hair loss. You might find that your sense of taste has changed, or you might experience ringing in your ears.
How to tell if you have anemia?
Your healthcare provider can perform blood tests to tell if you have anemia. The main test is a complete blood count test, also called the CBC. The CBC can tell you how many red blood cells you have, how big they are and what shape they are. Blood tests can also tell you if you are low in vitamins B12 and B9 and how much iron your body has stored.
What causes red blood cells to not form?
Chronic conditions causing your body to not have enough hormones to create red blood cells. These include hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, advanced kidney disease, lupus and other long-term diseases. Blood loss related to other conditions such as ulcers, hemorrhoids or gastritis.
What causes aplastic anemia?
Causes of aplastic anemia include infections, certain medicines, autoimmune diseases and exposure to toxic chemicals. Anemias associated with bone marrow disease. A variety of diseases, such as leukemia and myelofibrosis, can cause anemia by affecting blood production in your bone marrow.
How to prevent anemia?
Treatments for anemia range from taking supplements to undergoing medical procedures. You might be able to prevent some types of anemia by eating a healthy, varied diet.
How to avoid iron deficiency anemia?
But you can avoid iron deficiency anemia and vitamin deficiency anemias by eating a diet that includes a variety of vitamins and minerals, including: Iron. Iron-rich foods include beef and other meats, beans, lentils, iron-fortified cereals, dark green leafy vegetables, and dried fruit. Folate.
What causes low red blood cells?
Vitamin deficiency anemia. Besides iron, your body needs folate and vitamin B-12 to produce enough healthy red blood cells. A diet lacking in these and other key nutrients can cause decreased red blood cell production. Some people who consume enough B-12 aren't able to absorb the vitamin. This can lead to vitamin deficiency anemia, also known as pernicious anemia.
What is the best vitamin for red blood cells?
Besides iron, your body needs folate and vitamin B-12 to produce enough healthy red blood cells. A diet lacking in these and other key nutrients can cause decreased red blood cell production. Also, some people who consume enough B-12 aren't able to absorb the vitamin.
Why do pregnant women have anemia?
Your bone marrow needs iron to make hemoglobin. Without adequate iron, your body can't produce enough hemoglobin for red blood cells. Without iron supplementation , this type of anemia occurs in many pregnant women.
What is the red blood cell?
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin — an iron-rich protein that gives blood its red color . Hemoglobin enables red blood cells to carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body and to carry carbon dioxide from other parts of the body to your lungs to be exhaled.