
Neurotransmitters can be classified as follows:
- Amines : They are neurotransmitters that derive from different amino acids such as, for example, tryptophan. ...
- Amino acids : Unlike the previous ones (that derive from different amino acids), these are amino acids. ...
- Purines : Recent research indicates that purines such as ATP or adenosine also act as chemical messengers.
- Gases : Nitric oxide is the main neurotransmitter of this group.
What are the 4 classes of neurotransmitters?
What are the types of neurotransmitters quizlet?
- Acetylchline (Ach) involved in voluntary motor control; found in synapses where axons connect to muscles and body organs; contributes to regulation of attention, learning, sleeping, dreaming, and memory.
- Dopamine. …
- Glutamate. …
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) …
- Norepinephrine. …
- Serotonin. …
- endorphins.
What are all the types of neurotransmitters?
Understanding 7 Major Neurotransmitters
- Glutamate
- GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)
- Dopamine
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
- Serotonin
- Oxytocin
- Acetylcholine
What is the most common neurotransmitter?
The list of neurotransmitters include
- Rapidly acting type. These neurotransmitters act very fast, like in a fraction of seconds. ...
- Slow acting type. From specific tissues. ...
- Classical neurotransmitters. ...
- Acetylcholine. ...
- Dopamine. ...
- Norepinephrine. ...
- Epinephrine. ...
- Serotonin. ...
- Glutamate. ...
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) GABA is another neurotransmitter present predominantly in the brain. ...
What are the criteria for a neurotransmitter?
the criteria are: (i) a neurotransmitter must be synthesized in a neuron and released from a presynaptic terminal, (ii) a neurotransmitter should reproduce the specific responses that are evoked by the stimulation of presynaptic neurons at the postsynaptic neuron or effector cells, (iii) the effect of the chemical should be blocked by antagonists …
What are the 3 classes of neurotransmitter?
Classification of Neurotransmitters The major types of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, biogenic amines, and amino acids.
What are the 4 major types of neurotransmitters?
Four neurotransmitters come under the chemical classification of biogenic amines. These are epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin.
What are the 6 classes of neurotransmitters?
Although there are several different minor and major neurotransmitters, we will focus on these major six: acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, GABA, and glutamate.
How many classes of neurotransmitters are there?
To date, scientists have identified more than 60 distinct types of neurotransmitters in the human brain, and most experts say there are more left to discover. These powerful neurochemicals are at the center of neurotransmission, and, as such, are critical to human cognition and behavior.
What are the neurotransmitters and their functions?
Neurotransmitters are often referred to as the body's chemical messengers. They are the molecules used by the nervous system to transmit messages between neurons, or from neurons to muscles. Communication between two neurons happens in the synaptic cleft (the small gap between the synapses of neurons).
Which of the following is not a functional classification of neurotransmitters?
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous TissueQuestionAnswerWhich of the following is FALSE regarding chemical synapses?They transmit nerve impulses directly from one neuron to another.Which of the following is NOT a functional classification of neurotransmitters?chemical50 more rows
What are the five major neurotransmitters?
From our point of view the most important neurotransmitters are, in alphabetical order, acetylcholine (associated with Alzheimer's disease and myasthenia gravis), dopamine (Parkinson's disease), glutamate and GABA (epilepsy and seizures), and serotonin (major depression; although this is arguably the domain of ...
What are neurotransmitters Class 10?
A neurotransmitter is the body's chemical messenger. They are molecules that transmit signals from neurons to muscles, or between different neurons. The transmission of signals between two neurons occurs in the synaptic cleft.
What are neurotransmitters quizlet?
Definition of neurotransmitter. A chemical that is released from a nerve cell which thereby transmits an impulse from a nerve cell to another nerve, muscle, organ, or other tissue. A neurotransmitter is a messenger of neurologic information from one cell to another.
What are two neurotransmitters?
Types of NeurotransmittersAcetylcholine. Acetylcholine (Ach) was the first neurotransmitter discovered. ... Dopamine. ... Glutamate. ... Serotonin. ... Norepinephrine. ... gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) ... Other Neurotransmitters.
What are neurotransmitters in psychology?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the body. Their job is to transmit signals from nerve cells to target cells. These target cells may be in muscles, glands, or other nerves. Neurotransmitters are part of the nervous system. They play a crucial role in human development and many bodily functions.
Which neurotransmitters are classified as monoamines?
Monoamines (also known as "biogenic amines") include three classes of neurotransmitters:Catecholamines. ... Indolamines. ... Histamine.
What are 2 neurotransmitters?
Examples of excitatory neurotransmitters include glutamate, epinephrine and norepinephrine. Inhibitory. Inhibitory neurotransmitters block or prevent the chemical message from being passed along any farther. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine and serotonin are examples of inhibitory neurotransmitters.
What are the 5 brain chemicals?
Getting to Know Your 5 Essential Brain ChemicalsGlutamate & GABA. Glutamate and GABA can be thought of as mainstay neurotransmitters. ... Serotonin. Serotonin is all about serenity and hopefulness in moods. ... Dopamine. Dopamine is our arousal and stimulation neurotransmitter. ... Endorphins. ... Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
How many neurotransmitters are in the brain?
The total number of neurotransmitters is not known, but is well over 100. Despite this diversity, these agents can be classified into two broad categories: small-molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides.
What are neurotransmitters quizlet?
Definition of neurotransmitter. A chemical that is released from a nerve cell which thereby transmits an impulse from a nerve cell to another nerve, muscle, organ, or other tissue. A neurotransmitter is a messenger of neurologic information from one cell to another.
What is the function of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are substances which neurons use to communicate with one another and with their target tissues in the process of synaptic transmission (neurotransmission). Neurotransmitters are synthetized in and released from nerve endings into the synaptic cleft. From there, neurotransmitters bind to receptor proteins in ...
What are the most important neurotransmitters in the nervous system?
There are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; some of the most important are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, serotonin, and histamine.
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters?
Classification of neurotransmitters. Excitatory neurotransmitters function to activate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and enhance the effects of the action potential, while inhibitory neurotransmitters function to prevent an action potential.
Which neurotransmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic cells?
So, the type of the synapse and the response of the target tissue depends on the type of neurotransmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters cause depolarization of the postsynaptic cells and generate an action potential; for example acetylcholine stimulates muscle contraction.
What is the name of the hormone that regulates neurotransmission?
Vasopressin; also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH) In this article, we are going to discuss the mechanism of neurotransmission, the classification of neurotransmitters, and some clinical notes about disorders associated with both excess and shortage of some neurotransmitters.
How does repeated synaptic activity affect the receptor neuron?
Repeated synaptic activities can have long-lasting effects on the receptor neuron, including structural changes such as the formation of new synapses, alterations in the dendritic tree , or growth of axons . An example of this is the learning process – the more you study and repeat, the more synapses are created in your brain and enable you to retrieve that information when needed.
Why is norepinephrine important?
It acts to stimulate the processes in the body. For example, it is very important in the endogenous production of epinephrine. Norepinephrine has been implicated in mood disorders such as depression and anxiety, in which case its concentration in the body is abnormally low.
What is Neurotransmitter?
A neurotransmitter is the body’s chemical messenger. They are molecules that transmit signals from neurons to muscles, or between different neurons. The transmission of signals between two neurons occurs in the synaptic cleft. The electrical signals that travel along the axon are briefly converted into chemical signals through neurotransmitters.
What are the diseases of the neurotransmitter system?
The common neurotransmitter diseases include: Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease. Depression. Neurotransmitter diseases are genetically inherited from their parents.
How is the Activity of the Neurotransmitter Stopped?
The activity of the neurotransmitter can be stopped in the following ways:
Which neurotransmitter increases the chances of the neuron firing an action potential?
These type of neurons increase the chances of the neuron firing an action potential. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are the two excitatory neurotransmitters.
How to determine if a chemical is a neurotransmitter?
Because of this, neuroscientists have developed a number of guidelines for determining whether or not a chemical should be defined as a neurotransmitter: 1 . Presence of the chemical within the cell. The chemical is either synthesized in the neuron or otherwise found in it. Stimulus-dependent release.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in the body?
Influencing Drugs. A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that carries, boosts, and balances signals between neurons (also known as nerve cells) and target cells throughout the body. These target cells may be in glands, muscles, or other neurons.
What happens to the neurotransmitter after release?
After release, the neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic gap and attaches to the receptor site on the other neuron, either exciting or inhibiting the receiving neuron depending on what the neurotransmitter is.
How do neurotransmitters affect our brain?
Billions of neurotransmitter molecules work constantly to keep our brains functioning, managing everything from our breathing to our heartbeat to our learning and concentration levels. They can also affect a variety of psychological functions such as fear, mood, pleasure, and joy. Verywell / Jessica Olah.
What hormone is produced by the hypothalamus?
Oxytocin: This powerful hormone acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain. It is produced by the hypothalamus and plays a role in social recognition, bonding, and sexual reproduction. 6 Synthetic oxytocin such as Pitocin is often used as an aid in labor and delivery. Both oxytocin and Pitocin cause the uterus to contract during labor.
Which neurotransmitter increases the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential?
Excitatory neurotransmitters : These types of neurotransmitters have excitatory effects on the neuron, meaning they increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential. Some of the major excitatory neurotransmitters include epinephrine and norepinephrine.
What neurotransmitter is responsible for memory and learning?
Glutamate: The most plentiful neurotransmitter found in the nervous system, glutamate plays a role in cognitive functions such as memory and learning. Excessive amounts of glutamate can cause excitotoxicity resulting in cellular death. This excitotoxicity caused by glutamate build-up is associated with some diseases and brain injuries including Alzheimer's disease 5 , stroke, and epileptic seizures.
How many neurotransmitters are there in the human body?
Overall, over 40 neurotransmitters exist within the human central nervous system (CNS), each having a specific and vital function for human behavior.
What is the balance of neurotransmitters in the body?
The balance of neurotransmitters in our body is the key to proper mood, cognition, energy, and overall health.
What happens when neurotransmitters inhibit the neuron?
This type of neurotransmitter will have inhibitory effects on the neuron. When they inhibit the neuron, it will be less likely to fire an action potential.
How many amino groups are in monoamine?
A monoamine contains one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain.
Which neurotransmitter is most important for learning and memory?
Glutamate is the most common neurotransmitter in the frontal cortex, and it plays a significant part in cognitive functions, including learning and memory.
Is acetylcholine an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
Acetylcholine is different from other neurotransmitters and acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter in the neuro muscular junction in skeletal muscle but is inhibitory in the heart.
What are some examples of neurotransmitters?
Examples of these types of neurotransmitter are epinephrine and norepinephrine. Inhibitory neurotransmitters – in contrast to excitatory neurotransmitters, inhibitory neurotransmitters have the opposite effect, inhibiting/hindering the neurons.
Which amino acid is the most abundant neurotransmitter?
Another amino acid is glutamate, which supports cognitive functions such as memory formation and learning. This is known as the most abundant neurotransmitter, which is found in the central nervous system.
What is the effect of serotonin on the brain?
Instead, it balances out the excessive excitatory neurotransmitter effects. A deficit in serotonin can be linked to depression, sadness, fatigue, suicidal thoughts, and anxiety.
What is a neuromodulator?
Modulatory neurotransmitters – these are often called neuromodulators. If a neurotransmitter is a neuromodulate, this means it can affect a large number of neurons at the same time, as well as being able to influence the effects of other neurotransmitters. Neuromodulators do not directly activate the receptors of neurons but work together with neurotransmitters to enhance the excitatory or inhibitory responses of the receptors.Examples of these types of neurotransmitter are serotonin and dopamine.
How do neurotransmitters affect neurons?
A neurotransmitter can influence neurons in one of three ways: it can excite, inhibit, or modulate them. Excitatory neurotransmitters – these types have an excitatory/stimulating effect on the neurons. If a neurotransmitter is excitatory, it will increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire action potential.
What happens to the neurotransmitter after neurotransmission?
After neurotransmission, the signal is terminated, allowing the neurons to return to a resting state. When neurotransmitters get released into the synapse, not all are able to be attached to the receptors of the postsynaptic neuron. However, the gap between the neurons needs to be clearer of neurotransmitters at signal termination.
What is the name of the space between two neurons?
A neurotransmitter signal travels from a neuron, across the synapse, to the next neuron. The synapse is the name given to the space between the two neurons.
What are the four neurotransmitters?
By the 1950s, the list of neurotransmitters (defined by the criteria described in Box A) had expanded to include four amines—epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin —in addition to ACh. Over the following decade, three amino acids—glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glycine—were also shown to be neurotransmitters. Subsequently, other small molecules were added to the list, and considerable evidence now suggests that histamine, aspartate, and ATP should be included (Figure 6.3). The most recent class of molecules discovered to be transmitters are a large number of polypeptides; since the 1970s, more than 100 such molecules have been shown to meet at least some of the criteria outlined in Box A.Figure 6.3Examples of small-molecule and peptide neurotransmitters. Small-molecule transmitters can be subdivided into acetylcholine, the amino acids, purines, and biogenic amines. The catcholamines, so named because they all share the catechol moiety (i.e., a hydroxylated benzene ring), make up a distinctive subgroup within the biogenic amines. Serotonin and histamine contain an indole ring and an imidazole ring, respectively. Size differences between the small-molecule neurotransmitters and the peptide neurotransmitters are indicated by the space-filling models for glycine, norepinephrine, and methionine enkephalin. (Carbon atoms are black, nitrogen atoms blue, and oxygen atoms red.)
How many amino acids are in a neuropeptide?
Neuropeptides vary in length, but usually contain between 3 and 36 amino acids. Note that one peptide can include the sequence of other neuroactive peptides. For example, β-endorphin contains both α-endorphin and methionine enkephalin (more...)
Which neurotransmitter is the most extensive set of neurotransmitters?
d) Cholines. Monoamines: These are also called biogenic amines. They form the most extensive set of neurotransmitters (NT’s) and control many vital functions in the body. Examples; Norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, and histamine.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in the nervous system?
Neurotransmitters are the chemical messengers which are part of the nervous system. They help the brain and spinal cord to control and regulate the whole body.
Which molecules are choline based?
Choline based: These have a choline moiety in them bound to an organic acid. These include Acetylcholine, butyrylcholine. Both of them are chemical transmitters in the parasympathetic system. But acetylcholine forms a significant portion of it.
Which amino acid regulates stress?
While histamine plays a crucial role in wound healing and allergy. Whereas serotonin regulates stress and even emotions like anxiety, depression, memory, etc. Aminoacids: These are the ones which are essential aminoacids but have the neurotransmitter function. Ex: glutamine, glycine, GABA.
Is glycine a transmitter?
The glycine and GABA are an inhibitory type of transmitters. Peptides: These are large molecule NT’s in the body. Their chemical structure is a polymer of amino acids. They are vast and limited and specific function in the body.
What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are molecules synthesized by neurons, the specialized cells that make up the functional part of the nervous system, which function as messengers, that is, they transmit information from one neuron to another without losing any information, keeping the nerve impulse constant with the message. This process is called a synapse.
What are the main types of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are endogenous molecules (synthesized by our own body) that are released into the synaptic space, that is, the tiny region that separates neurons from the network of the nervous system.
1. Dopamine
Dopamine is one of the best known neurotransmitters, although it is more famous for its role as a hormone than for its actual role as a transmitter of electrical impulses. Dopamine is generated only in the brain and performs very important functions.
2. Adrenaline
Adrenaline is a neurotransmitter that is synthesized when we are in stressful situations.
3. Serotonin
As with the previous two, serotonin also functions as a hormone.
4. Noradrenaline
Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter very similar to adrenaline that also functions as a stress hormone. Norepinephrine focuses on regulating the heart rate and enhancing our attention span when we feel that we are in danger. Similarly, norepinephrine also regulates motivation, sexual desire, anger, and other emotional processes.
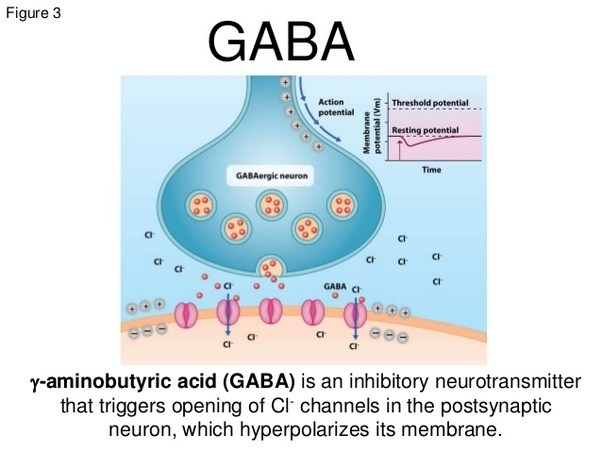
5. GABA
Unlike the previous ones, the neurotransmitter Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) is inhibitory, that is, it reduces the level of excitation of neurons.

How Neurotransmitters Work
Criteria
- The actual identification of neurotransmitters can actually be quite difficult. While scientists can observe the vesicles containing neurotransmitters, figuring out what chemicals are stored in the vesicles is not quite so simple. Because of this, neuroscientists have developed a number of guidelines for determining whether or not a chemical should be defined as a neurotransmitter:1 1…
Classification
- Neurotransmitters play a major role in everyday life and functioning. Scientists do not yet know exactly how many neurotransmitters exist, but more than 60 distinct chemical messengers have been identified.2 Neurotransmitters can be classified by their function:3 1. Excitatory neurotransmitters: These types of neurotransmitters have excitatory effects on the neuron, mea…
Types
- There are a number of different ways to classify and categorize neurotransmitters. In some instances, they are simply divided into monoamines, amino acids, and peptides.4 Neurotransmitters can also be categorized into one of six types:
When Neurotransmitters Do Not Work Right
- As with many of the body's processes, things can sometimes go awry. It is perhaps not surprising that a system as vast and complex as the human nervous system would be susceptible to problems. A few of the things that might go wrong include: 1. Neurons might not manufacture enough of a particular neurotransmitter 2. Neurotransmitters may be reabsorbed too quickly 3. T…
Drugs That Influence Neurotransmitters
- Perhaps the greatest practical application for the discovery and detailed understanding of how neurotransmitters function has been the development of drugs that impact chemical transmission. These drugs are capable of changing the effects of neurotransmitters, which can alleviate the symptoms of some diseases. 1. Agonists vs Antagonists: Some drugs are known as agonists an…
A Word from Verywell
- Neurotransmitters play a critical role in neural communication, influencing everything from involuntary movements to learning to mood. This system is both complex and highly interconnected. Neurotransmitters act in specific ways, but they can also be affected by diseases, drugs, or even the actions of other chemical messengers.