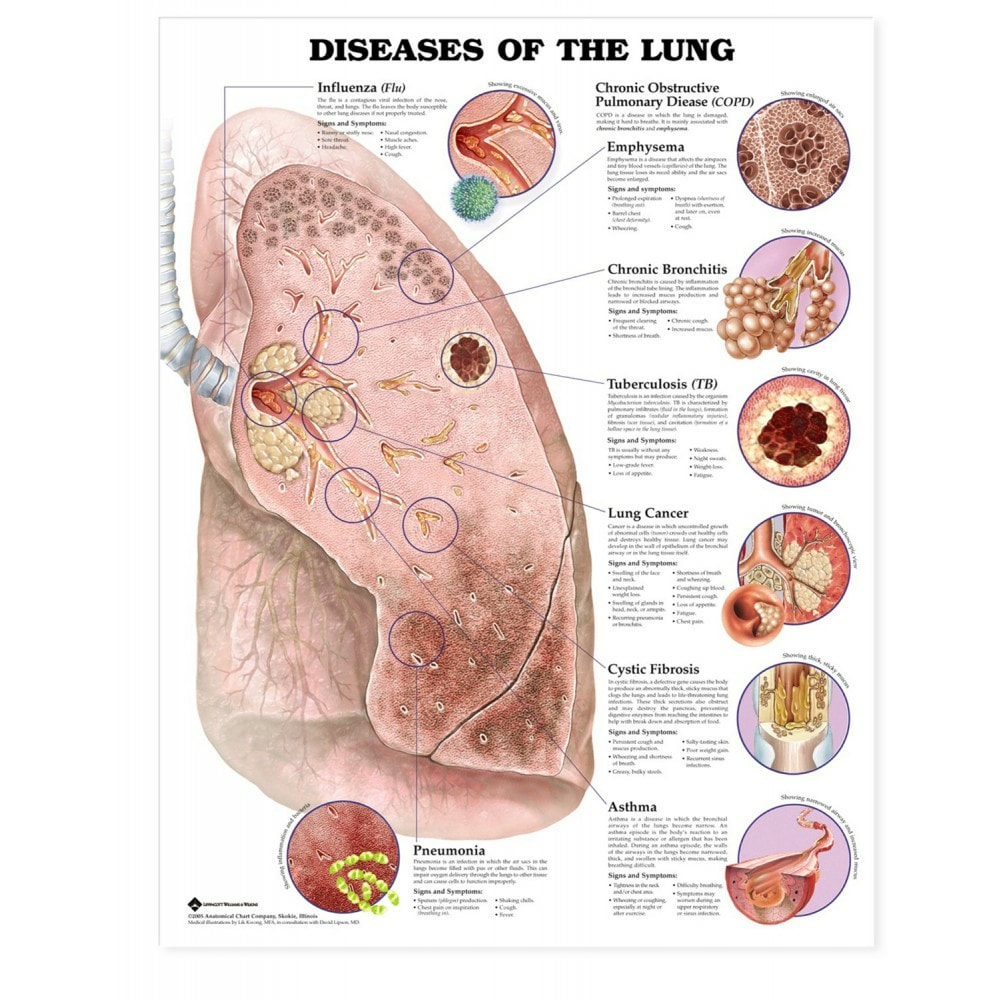
- Asthma.
- Collapse of part or all of the lung (pneumothorax or atelectasis)
- Swelling and inflammation in the main passages (bronchial tubes) that carry air to the lungs (bronchitis)
- COPD.
- Lung cancer.
- Lung infection (pneumonia)
- Abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
What are the most common types of lung disease?
Most common lung diseases fall into one or more of these three categories. Some of the most common diseases include: asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) bronchiectasis; bronchitis
What is the most deadliest lung disease?
- Pulmonary edema
- Pneumonia
- Lung cancer
- Emphysema
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Bronchitis
- Atelectasis – collapse of part and sometimes all (less common) of the lung
- Asthma
What are some serious lung diseases?
What are the most serious lung diseases?
- Asthma.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Chronic Bronchitis.
- Emphysema.
- Lung Cancer.
- Cystic Fibrosis/Bronchiectasis.
- Pneumonia.
- Pleural Effusion.
What are common symptoms of lung disease?
When to book an appointment with your GP?
- It hurts to breathe
- You have a fever (38o C or above)
- You are coughing up a lot of mucus (particularly if it is yellow or green in colour)
- There is blood in the mucus
- Your symptoms are not improving, or they are getting worse
- You have a heart or lung disease, such as heart failure or asthma.
What are the most common lung diseases?
What is lung disease?
What are the different lung categories and diseases?
What makes it difficult for the lungs to work properly?
Why does my airway feel so swollen?
How do doctors classify lung diseases?
How many people died from lung cancer in 2008?
See 4 more
About this website
What is the most common lung disease?
The two most common chronic respiratory diseases are asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These both affect the airways in the lungs.
What are the disease of lungs?
The term lung disease refers to many disorders affecting the lungs, such as asthma, COPD, infections like influenza, pneumonia and tuberculosis, lung cancer, and many other breathing problems. Some lung diseases can lead to respiratory failure.
What are 7 respiratory diseases?
Types of Respiratory DiseasesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD) If you are a smoker or inhale tobacco in any form, you are most likely to suffer from this disease. ... Asthma. ... Emphysema. ... Lung Cancer. ... Pneumonia. ... Pleural Effusion. ... Chronic Bronchitis.
What are the top 5 respiratory diseases?
The Top 8 Respiratory Illnesses and DiseasesAsthma. ... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) ... Chronic Bronchitis. ... Emphysema. ... Lung Cancer. ... Cystic Fibrosis/Bronchiectasis. ... Pneumonia. ... Pleural Effusion.More items...•
What is a lung infection called?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
What can damage your lungs?
Your lungs can be damaged if you breathe in cigarette smoke, air pollution (both outside and inside the home) or dusts and fumes in the workplace over a sustained period of time. If your airways get damaged, you can get more breathless over time. Sometimes, the cause of lung damage is unknown.
What causes lungs problem?
Smoking, infections, and genes cause most lung diseases. Your lungs are part of a complex system, expanding and relaxing thousands of times each day to bring in oxygen and send out carbon dioxide. Lung disease can happen when there are problems in any part of this system.
What lung diseases are incurable?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), is an incurable lung disease in which scars are formed in the lung tissues. It is a devastating condition characterised by increasing breathlessness, disability and death three to four years after diagnosis. Only 25% of people survive for five years.
What can damage your lungs?
Your lungs can be damaged if you breathe in cigarette smoke, air pollution (both outside and inside the home) or dusts and fumes in the workplace over a sustained period of time. If your airways get damaged, you can get more breathless over time. Sometimes, the cause of lung damage is unknown.
What are the first signs of lung disease?
Wheezing: Noisy breathing or wheezing is a sign that something unusual is blocking your lungs' airways or making them too narrow. Coughing up blood: If you are coughing up blood, it may be coming from your lungs or upper respiratory tract. Wherever it's coming from, it signals a health problem.
What are 3 diseases of the respiratory system?
Respiratory diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
What are the symptoms of lungs problem?
Signs of Lung ProblemsChronic cough (eight weeks or longer for adults and four weeks or longer in children)Shortness of breath.Difficulty breathing.Increased mucus production.Pain or tightness in the chest when breathing.
Types of Lung Diseases & Their Causes - WebMD
A common health problem, lung diseases range from mild to severe. WebMD breaks down the information and describes the types and causes of some common lung diseases.
What Are The Most Common Lung Diseases? - HealthPrep.com
Lung disease describes any issue that occurs in the lungs that inhibits them from functioning as they should. The lungs are an element of an intricate mechanism that relaxes and expands thousands of times a day to perform the oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
List of Respiratory Diseases
Common diseases of the respiratory system, types of chronic, acute upper and lower respiratory diseases and disorders, risk factors, prevention
What Types of Lung Disease Are There? - Healthline
Learn the common types of chronic lung disease, their causes, risk factors, what to do to avoid them, and when you need to talk with a doctor.
8 Common Respiratory Diseases - Verywell Health
Verywell Health articles are reviewed by board-certified physicians and healthcare professionals. These medical reviewers confirm the content is thorough and accurate, reflecting the latest evidence-based research. Content is reviewed before publication and upon substantial updates. Learn more. The ...
What is lung disease?
Lung disease describes any issue that occurs in the lungs that inhibits them from functioning as they should. The lungs are an element of an intricate mechanism that relaxes and expands thousands of times a day to perform the oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange. Oxygen is essential for the cells throughout the body to operate properly.
How does airway disease affect the lungs?
Airway diseases have adverse effects on the tubes that carry oxygen in and carbon dioxide out of the lungs. Lung circulation diseases negatively affect blood vessels that run throughout the lungs. Some lung diseases may fall into more than one of these three subclasses.
What is pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion is a condition where the space between an individual's chest cavity wall and the lungs, the pleural space, becomes filled with more fluid than normal. An individual's lung and chest cavity are lined with pleura or special membranes that contain a small amount of fluid that is meant to keep them moist and reduce friction. There are many possible causes of pleural effusion, including kidney or liver disease, autoimmune disorders, pulmonary embolism, cancer, congestive heart failure, certain respiratory infections, and complications from specific medical procedures. A pleural effusion patient may have symptoms such as unproductive cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, inability to take deep breaths, problems with breathing when lying down, fever, and painful breathing. An individual who has common bouts of hiccups that are difficult to diffuse may also have pleural effusion. A diagnosis of pleural effusion is made with a physical examination, x-ray, CT scans, kidney function tests, liver function tests, lung biopsy, bronchoscopy, and echocardiogram. Treatment for this condition may include chest draining, pleurodesis, and surgery.
What are the symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease include shortness of breath, wheezing, chest pain, persistent cough, and chest tightness.
What is pulmonary edema?
Pulmonary edema is a lung condition where excess fluid accumulates in the air sacs or alveoli, causing problems with the function and structure of the organs. Pulmonary edema can be caused by problems with heart structure or function, or it can be caused by nervous system conditions, high altitudes, acute respiratory distress syndrome, adverse drug reaction, pulmonary embolism, smoke inhalation, near drowning, infections, and toxin exposure. Symptoms of pulmonary edema include breathlessness, wheezing, clammy skin, blue-tinted lips, palpitations, rapid weight gain, lower extremity swelling, fatigue, anxiety, productive cough, fever, chest discomfort, headaches, difficulty with exercise, and shortness of breath upon exertion or lying down. Pulmonary edema is diagnosed with the use of a physical examination, pulse oximetry, blood tests, echocardiogram, chest x-rays, cardiac catheterization, and electrocardiogram. Treatment for pulmonary edema may include administration of supplemental oxygen, diuretic medications, morphine, blood pressure medications, and in rare cases, therapy in a hyperbaric chamber.
What causes a person to have a cough?
Pneumonia is a lung disease that affects the alveoli or air sacs in the lungs. Numerous germs can cause an individual to develop pneumonia, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses that come in contact with the lungs. Even small pieces of aspirated food can cause someone to develop pneumonia. The air sacs or alveoli in a patient with pneumonia tend to fill up with purulent material or pus. Symptoms include a cough that produces phlegm or pus, difficulty breathing, chills, chest pain when breathing and coughing, confusion, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, and fever.
What is the term for a disease that causes damage to the bronchi?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a disease that causes damage to the bronchi or larger branches in the lung that carry air to smaller branches. COPD is an umbrella term used to encompass two different long-term diseases that occur concurrently, including the chronic form of bronchitis and emphysema.
What Your Lungs Do
The lungs are not just empty sacs that inflate and deflate with each breath. They are made up of a complete system of filters and membranes that move oxygen into your body and get rid of waste gases like carbon dioxide.
Types of Lung Disease
Your lungs depend on their ability to expand and contract to move oxygen and other gases in and out of your body. Over a lifetime of breathing, many people develop some type of lung disease.
Airway Diseases
Airway diseases are one of the main types of lung diseases. These diseases are grouped together because they affect your body's ability to move air in and out of your lungs. The subgroup is also referred to as obstructive, or reactive, lung diseases.
Lung Tissue Diseases
With lung tissue diseases, parts of your lung tissues are damaged—for example, by scarring or another injury. This subgroup of diseases is sometimes called interstitial lung disease.
Lung Circulation Diseases
After oxygen and other gases pass through the alveoli, your circulatory system is tasked with moving oxygen to all the tissues of the body and bringing back waste products to the lungs for disposal.
Summary
There are many diseases that can affect how well your lungs are able to move oxygen and other gases in and out of your body.
A Word From Verywell
Breathing is one of the most important tasks your body handles and, in most cases, you do not have to think about doing it. However, if your lungs become damaged or weakened, the feeling of not being able to breathe can take over your thoughts and even put your life in danger.
What are the lungs susceptible to?
The lungs are susceptible to an eclectic arrangement of diseases ranging from congenital anomalies (some of which are incompatible with life) to infectious disorders and malignancies. It is important that the astute healthcare professional is able to clinically examine and appropriately investigate patients with pulmonary disorders, ...
What is the shape of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder?
Also look at the shape of the patient’s chest as some individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disorders have a widened or barrel-shaped chest. In this case, the anteroposterior diameter of the chest is greater than the lateral diameter. The sternum may be abnormally elevated or depressed (pectus carinatum or excavatum, respectively). Pay close attention to whether or not the patient has lordotic (abnormal inward curvature of the spine) or kyphotic (abnormal convex curvature of the spine) deformities, as they may also impact the respiratory system based on their severity.
What happens if you get a pneumothorax?
The thoracic cavity is a closed space under negative pressure that houses the lungs and mediastinum. Therefore, if there is an injury to the chest wall that allows communication with the external environment, then air will be pulled into the cavity. Additionally, spontaneous injury to the lung can also result in leakage and accumulation of air into the pleural space. In both cases, the resulting disorder is known as a pneumothorax. This disorder can occur spontaneously or secondary to a lung injury. Spontaneous primary pneumothorax tends to occur in tall individuals with a history of smoking and a predisposition to developing apical blebs (thin-walled air-filled sacs beneath the pleural membrane). The blebs may rupture with increased intrathoracic pressures such as Valsalva maneuvers or changes in atmospheric pressure (pilots and deep-sea divers). Iatrogenic, accidental, or malicious injury to the chest wall often results in a traumatic pneumothorax. These injuries may be associated with blood (hemopneumothorax), pus (empyema), or lymphatic fluid (chylothorax) within the pleural space. Additionally, the lung parenchyma may be compromised by an underlying infection or disease process that results in rupture of the lung parenchyma and leakage of air into the thorax. This is referred to as a secondary pneumothorax.
What are the sounds of breathing?
There are additional breath sounds that can be appreciated in pathological processes. These sounds include but are not limited to crackles and wheezes. Wheezes are musical sounds generated by uninterrupted passage of air within a partially obstructed airway. While it is most commonly associated with asthma, wheezing can also occur as a result of cardiac failure. Crackles, on the other hand, are non-musical and occur due to collapsing peripheral airways. They can occur at any point during the respiratory cycle. When they occur in the early phase, it is indicative of small airway disease such as bronchiolitis. Crackles during the middle of inspiration suggest pulmonary edema; while those occurring in late respiration can be fine, medium or coarse crackles. Late fine crackles suggest pulmonary fibrosis, medium ones indicate pulmonary edema, and coarse crackles are in-keeping with lung abscesses, pneumonia, or tuberculosis. Coarse crackles heard in both inspiration and expiration suggests bronchiectasis.
How to determine if a patient has an obstruction of the airway?
Once the patient is prepared as described above, look for the use of accessory muscles of respiration (contraction of sternocleidomastoid ), nasal flaring, tracheal tugging, subcostal flaring or intercostal recessions. These are all early signs of acute airway obstruction that require urgent attention. Assess the respiratory rate by counting the number of breaths over a 60 second period. In a healthy adult, the normal respiratory rate ranges from 12 – 20 breaths per minute.
What are the effects of a pulmonary embolism?
This chronic pulmonary embolism obstructs the microvascular circulation of the lungs leading to increased pulmonary arterial pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy and subsequent dilatation, tricuspid regurgitation, right atrial hypertrophy and dilation, and subsequent right heart failure. Patients usually complain of shortness of breath on exertion and features of right heart failure (i.e. hepatomegaly, elevated JVP, decreased cardiac output, etc). Later on, in the disease process, the physician may detect a right parasternal heave, loud P2, and other features of right heart failure on clinical examination. A plain chest radiograph shows enlarged right ventricle and pulmonary trunk. This right ventricular enlargement along with the accompanying right heart strain can also be detected on electrocardiography. The arterial blood gas study may be normal at rest but if repeated following formal exercise, the partial pressure of oxygen will be reduced.
How to tell if a patient has carbon dioxide?
Ask the patient to position both upper limbs such that each limb is flexed at the shoulders and extended at the elbows and wrists. Observe the hands for frequent back and forth motions referred to as flapping tremors or asterixis. Another way to elicit asterixis is by asking the patient to squeeze the middle and index fingers together for 30 seconds or more. Patients with a flapping tremor would be unable to maintain their grip for that long. This clinical sign is indicative of carbon dioxide retention and impending respiratory failure as a result of pulmonary or hepatic dysfunction.
Why do we have lung diseases?
Smoking, infections, and genes cause most lung diseases. Your lungs are part of a complex system, expanding and relaxing thousands of times each day to bring in oxygen and send out carbon dioxide. Lung disease can happen when there are problems in any part of this system.
What is the term for a condition caused by inhaling something that injures your lungs?
Pneumoconiosis. This is a category of conditions caused by inhaling something that injures your lungs. Examples include black lung disease from coal dust and asbestosis from asbestos dust.
What causes a long term wet cough?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease( COPD ). With this lung condition, you can’t exhale the way you usually would, which causes trouble breathing. Chronic bronchitis. This form of COPD brings a long-term wet cough. Emphysema. Lung damage allows air to be trapped in your lungs in this form of COPD.
What is the thin lining that surrounds your lung and lines the inside of your chest wall?
The pleura is the thin lining that surrounds your lung and lines the inside of your chest wall. A tiny layer of fluid lets the pleura on your lung's surface slide along the chest wall with each breath. Lung diseases of the pleura include: Pleural effusion. Fluid collects in the space between your lung and the chest wall.
What are the air sacs in the lung called?
Your airways branch into tiny tubes (bronchioles) that end in clusters of air sacs called alveoli. These air sacs make up most of your lung tissue. Lung diseases affecting your alveoli include: Pneumonia. An infection of your alveoli, usually by bacteria or viruses, including the coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
What is interstitial lung disease?
Interstitial lung disease (ILD). This is a group of lung conditions that includes sarcoidosis , idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and autoimmune disease. Pneumonia and pulmonary edema can also affect your interstitium. Lung Diseases Affecting Blood Vessels.
What causes fluid to leak out of the air sacs?
Pulmonary edema. Fluid leaks out of the small blood vessels of your lung into the air sacs and the area around them. One form is caused by heart failure and back pressure in your lungs' blood vessels. In another form, injury to your lung causes the leak of fluid. Lung cancer.
What is the most common lung disease?
Asthma is one of the most common types of chronic lung disease. When triggered, your lungs become swollen and narrow, making it harder to breathe. Symptoms include:
What is the name of the disease that causes the lungs to become inflamed?
Chronic pneumonia. Pneumonia is a lung infection caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Microorganisms grow and thrive in the lungs, creating difficult symptoms. The air sacs become inflamed and may fill up with fluid, which disrupts the flow of oxygen.
What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is a disease in which the cells in your lungs grow abnormally, gradually developing tumors. As the tumors get bigger and more numerous, they can make it more difficult for your lungs to do their job. Eventually, the cancerous cells can spread to other areas of your body.
What is the name of the disease that affects newborns?
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited lung disease that affects newborn children. It changes the makeup of mucus in the body. Instead of being slippery and watery, mucus in a person with cystic fibrosis is thick, sticky, and excessive. This thick mucus can build up in your lungs and make it more difficult to breathe.
What is COPD in lungs?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease in which your lungs become inflamed, making breathing more difficult. The inflammation leads to an overproduction of mucus and a thickening of the lining of your lungs. The air sacs, or alveoli, become less efficient at bringing oxygen in and sending carbon dioxide out.
How many types of interstitial lung diseases are there?
A number of different lung diseases fit under the umbrella term “interstitial lung disease.” Interstitial lung diseases include over 200 types of lung disorders. A few examples:
How does cystic fibrosis affect the body?
Doctors know that cystic fibrosis is caused by a gene mutation that normally regulates the level of salt in cells. The mutation causes this gene to malfunction, changing the makeup of mucus and increasing salt in sweat. There is no cure for the disease, but treatment eases symptoms and slows progression.
What is lung disease?
Any disorder that prevents the lungs from working properly is referred to as lung disease. However, there are different types of lung disease that affect the lungs in different ways. Our lung doctor in Newport Beach and Foothill Ranch, CA, explains more here.
What is the phone number for West Coast Lung?
If you would like to learn more about this and other topics related to lung disease, feel free to contact West Coast Lung by clicking here or by calling 949-274-8030.
What are some examples of lung tissue diseases?
Pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis are examples of lung tissue disease. Lung circulation diseases -- These diseases affect the blood vessels in the lungs. They are caused by clotting, scarring, or inflammation of the blood vessels. They affect the ability of the lungs to take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
What is lung disease?
Definition. Lung disease is any problem in the lungs that prevents the lungs from working properly. There are three main types of lung disease: Airway diseases -- These diseases affect the tubes (airways) that carry oxygen and other gases into and out of the lungs.
What are the diseases that affect the airway?
Airway diseases include asthma, COPD and bronchiectasis. People with airway diseases often say they feel as if they're "trying to breathe out through a straw.". Lung tissue diseases -- These diseases affect the structure of the lung tissue. Scarring or inflammation of the tissue makes the lungs unable to expand fully (restrictive lung disease).
What is the term for a lung infection?
Lung infection (pneumonia)
What are some examples of lung circulation?
An example of a lung circulation disease is pulmonary hypertension. People with these conditions often feel very short of breath when they exert themselves. Many lung diseases involve a combination of these three types. The most common lung diseases include:
What are the most common lung diseases?
Some of the most common diseases include: asthma. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COP D) bronchiectasis. bronchitis. pulmonary fibrosis. sarcoidosis. hypertension.
What is lung disease?
Lung diseases and mortality. Summary. Lung disease is a general term for several disorders that include airway diseases, lung tissue diseases, and lung circulation diseases, some of which may lead to respiratory failure. During the course of a day, a person generally takes a breath nearly 25,000 ...
What are the different lung categories and diseases?
There are three main categories of lung disease, and each affects the lungs in a different way:
What makes it difficult for the lungs to work properly?
Lung tissue diseases: These conditions make it difficult for the lungs to work properly and diffuse oxygen from the airways into the bloodstream.
Why does my airway feel so swollen?
Asthma. When someone has asthma, their airway can become swollen and narrow, making it hard for the person to breathe and making them feel as though they cannot get enough air. Asthma events often happen after the person has been exposed to a “trigger” such as smoke, pollution, or pet hair.
How do doctors classify lung diseases?
Doctors tend to classify lung diseases according to the way they affect the lungs. However, the lungs are complex organs and respiratory conditions may involve more than one lung disease category.
How many people died from lung cancer in 2008?
Lung disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. In 2008, lung infections, lung cancer, and COPD accounted for 9.5 million deaths worldwide.
