- Epiglottitis.
- Otitis media.
- Mastoiditis.
- Sinusitis.
- Acute rheumatic fever.
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
- Toxic shock syndrome.
Complications
Pharyngitis may be caused by bacterial or viral infections. There are numerous viral and bacterial agents that can cause pharyngitis. They include: Viruses are the most common cause of sore throats. Pharyngitis is most commonly caused by viral infections such as the common cold, influenza, or mononucleosis.
Symptoms
What Happens When Strep Throat Goes Untreated?
- Rheumatic Fever. If strep throat goes untreated, the bacteria could continue to grow and, in return, create an ongoing immune response from the body.
- Middle Ear Infection. Untreated strep throat can cause middle ear infection, also called Otitis Media. ...
- Glomerulonephritis. ...
- Toxic shock syndrome. ...
Causes
They include:
- measles
- adenovirus, which is one of the causes of the common cold
- chickenpox
- croup, which is a childhood illness distinguished by a barking cough
- whooping cough
- group A streptococcus
Prevention
A strep throat will usually resolve without treatment but failing to take appropriate antibiotics can permit complications to occur such as a retropharyngeal abscess or septic thrombophlebitis of the neck veins.
Which factor may cause pharyngitis?
What are the dangers of untreated strep throat?
What are the causes of pharyngitis?
What happens if you don't treat strep?
What causes pharyngitis?
What causes pharyngitis in the oropharynx?
How long does it take for pharyngitis to resolve?
How many emergency department visits were there for pharyngitis in 2010?
What is the best treatment for beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis?
Is pharyngitis a retropharyngeal abscess?
Can viruses cause pharyngeal mucosa irritation?
See 4 more
About this website

What can happens if pharyngitis is left untreated?
Left untreated, pharyngitis can, in rare cases, lead to rheumatic fever or sepsis (bacterial blood infection), which are life-threatening conditions.
Can pharyngitis be serious?
Pharyngitis is rarely a serious condition and often occurs alongside colds and the flu. Viral pharyngitis typically clears up on its own within a couple of weeks, but bacterial pharyngitis may require a course of antibiotics to prevent complications. Complications of pharyngitis, such as rheumatic fever, are rare.
Can pharyngitis spread to lungs?
What are the complications of Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis? Pus may collect in pockets in the back of the throat or the Tonsils. Infection from the throat or Tonsils may spread to the ears, lungs and even the brain.
What is the best medicine for pharyngitis?
Penicillin and amoxicillin are the antibiotics of choice for the treatment of pharyngitis.
How long will pharyngitis last?
Viral pharyngitis often goes away in five to seven days. If you have bacterial pharyngitis, you will feel better after you have taken antibiotics for two to three days. You must take your antibiotic even when you are feeling better. If you don't take all of it, your sore throat could come back.
Why is my pharyngitis lasting so long?
Chronic pharyngitis is a persistent sore throat that lingers for a few weeks or returns frequently. Chronic pharyngitis may be caused by infection, environmental pollutants, allergies or acid reflux. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause.
What triggers pharyngitis?
It is usually caused by viral and/or bacterial infections, such as the common cold and flu (both viral infections) or by infection with the Streptococcus bacterium (strep throat). Pharyngitis can also occur with mononucleosis (aka “mono”), a viral infection.
What is the fastest way to get rid of pharyngitis?
Lifestyle and home remediesRest. Get plenty of sleep. ... Drink fluids. Fluids keep the throat moist and prevent dehydration. ... Try comforting foods and beverage. ... Gargle with saltwater. ... Humidify the air. ... Consider lozenges or hard candy. ... Avoid irritants. ... Stay at home until you're no longer sick.
Pharyngitis: soothing the sore throat : The Nurse Practitioner - LWW
Figure. Acute pharyngitis accounts for 12 million healthcare encounters annually in the United States, approximately 1% to 2% of all ED visits, and up to 6% of outpatient appointments. 1-4 Sore throats rank within the top 20 reasons patients present to healthcare providers. 4 In temperate climates, the incidence is highest during the winter and early spring (November to May). 5-7 The most ...
Pharyngitis: Approach to diagnosis and treatment - PubMed
Objective: To provide family physicians with an updated approach to diagnosis and treatment of pharyngitis, detailing key symptoms, methods of investigation, and a summary of common causes. Sources of information: The approach described is based on the authors' clinical practice and peer-reviewed literature from 1989 to 2018. Main message: Sore throat caused by pharyngitis is commonly seen in ...
Pharyngitis (Strep Throat): Information For Clinicians | CDC
Many viruses and bacteria can cause acute pharyngitis. Streptococcus pyogenes, which are also called group A Streptococcus (group A strep), cause acute pharyngitis known as strep throat.. Etiology. Group A strep pharyngitis is an infection of the oropharynx caused by S. pyogenes.S. pyogenes are gram-positive cocci that grow in chains (see figure 1).They exhibit β-hemolysis (complete hemolysis ...
How to prevent pharyngitis?
To prevent pharyngitis: avoid sharing food, drinks, and eating utensils. avoid individuals who are sick. wash your hands often, especially before eating and after coughing or sneezing. use alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap and water aren’t available. avoid smoking and inhaling secondhand smoke.
What is pharyngitis in the back of the throat?
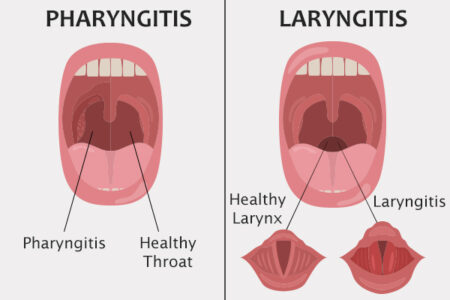
What is pharyngitis? Pharyngitis is inflammation of the pharynx, which is in the back of the throat. It’s most often referred to simply as “sore throat.”. Pharyngitis can also cause scratchiness in the throat and difficulty swallowing.
How long does it take for pharyngitis to develop?
The incubation period is typically two to five days. Symptoms that accompany pharyngitis vary depending on the underlying condition. In addition to a sore, dry, or scratchy throat, a cold or flu may cause: sneezing. runny nose. headache. cough. fatigue. body aches.
How long is a person contagious?
The length of the contagious period will also depend on your underlying condition. If you have a viral infection, you will be contagious until your fever runs its course. If you have strep throat, you may be contagious from the onset until you’ve spent 24 hours on antibiotics.
What is the best medicine for pharyngitis?
For pain and fever relief, consider taking over-the-counter medication such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil). Throat lozenges may also be helpful in soothing a painful, scratchy throat. Alternative remedies are sometimes used to treat pharyngitis.
What is the test for pharyngitis?
This test can determine whether you have mononucleosis. A complete blood count (CBC) test may be done to determine if you have another type of infection.
Do antibiotics help with pharyngitis?
Viral infections don’t respond to antibiotics, and treatment is only necessary to help relieve symptoms. Less commonly, pharyngitis is caused by a bacterial infection. Bacterial infections require antibiotics. The most common bacterial infection of the throat is strep throat, which is caused by group A streptococcus.
What is the most common cause of pharyngitis in all age groups?
The differential diagnosis of acute pharyngitis includes multiple viral and bacterial pathogens. Viruses are the most common cause of pharyngitis in all age groups. Experts estimate that group A strep, the most common bacterial cause, causes 20% to 30% of pharyngitis episodes in children. In comparison, experts estimate it causes approximately 5% to 15% of pharyngitis infections in adults.
What is the name of the virus that causes pharyngitis?
Many viruses and bacteria can cause acute pharyngitis. Streptococcus pyogenes, which are also called group A Streptococcus or group A strep, cause acute pharyngitis known as strep throat.
How does group A strep pharyngitis work?
Shortens the duration of symptoms. Reduces the likelihood of transmission to family members, classmates, and other close contacts. Prevents the development of complications, including acute rheumatic fever. When left untreated, the symptoms of group A strep pharyngitis are usually self-limited.
How old do you have to be to get antibiotics for strep pharyngitis?
Clinicians should confirm group A strep pharyngitis in children older than 3 years of age to appropriately guide treatment decisions. Giving antibiotics to children with confirmed group A strep pharyngitis can reduce their risk of developing sequela (acute rheumatic fever). Testing for group A strep pharyngitis is not routinely indicated for:
How long does it take for strep pharyngitis to develop?
The incubation period of group A strep pharyngitis is approximately 2 to 5 days.
How is strep pharyngitis transmitted?
Typically transmission occurs through saliva or nasal secretions from an infected person. People with group A strep pharyngitis are much more likely to transmit the bacteria to others than asymptomatic pharyngeal carriers.
When is strep pharyngitis most common?
In the United States, group A strep pharyngitis is most common during the winter and spring. CDC does not track the incidence of group A strep pharyngitis or other non-invasive group A strep infections. CDC tracks invasive group A strep infections through the Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) program.
How long does pharyngitis last?
Pharyngitis caused by A streptococcus (GAS) is usually a self-limited condition; symptoms in untreated patients typically last two to five days. Antimicrobial therapy reduces the duration and severity of symptoms byone to two days and prevents spread of infection (Pichichero,2017)
What percentage of otitis media cases are caused by gas?
GAS accounts for less than 5 percent of all cases of acute otitis media (Pinchero, 2017)
What is the abscess behind the throat?
Formation of an abscess behind the throat (retro-pharyngeal abscess) due to untreated or under-treated strep throat infection can lead to severe illness causing pain in throat and neck, difficulty swallowing, and potential respiratory compromise.
What is the condition called when you have a group A strep infection?
There is also a condition called Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorder associated with group A Streptococcus infection ( PANDAS ). This is a somewhat controversial condition linking group A strep infection in children with possible development and/or exacerbation of obsessive compulsive disorders or tic disorders (Tourette's syndrome) in children.
Is strep throat a rheumatic fever?
There is unfortunately no evidence that treatment of strep throat will prevent this condition. Children under the age of seven are at the highest risk of developing PSGN after an episode of strep throat. This condition is more common but less ominous than rheumatic fever. It typically resolves spontaneously after a few, weeks and generally does not lead to permanent kidney damage.
Can heart valves cause rheumatic fever?
The involvement of heart valves can cause damage of the heart valves and potential heart failure. Treatment with appropriate antibiotics, even if started several days after the resolution of the infection, may prevent acute rheumatic fever.
Can antibiotics cause strep throat?
It is thought that if the strep throat infection is untreated or inadequately treated by antibiotics, the bacteria remain in the tonsils and promote a persistent immune response from the body. Certain strains of the bacteria are more likely than others to cause this response. At times, this ongoing immune response may trigger ...
What causes pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oropharynx. In most cases, it is caused by an infection, either bacterial or viral. Other less common causes of pharyngitis include allergies, trauma , cancer, reflux, and certain toxins. This activity reviews the evaluation and treatment of patients with pharyngitis and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in the care of patients with this condition.
What causes pharyngitis in the oropharynx?
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oropharynx. In most cases, the cause is an infection, either bacterial or viral. Other less common causes of pharyngitis include allergies, trauma, cancer, reflux, and certain toxins. [1][2]
How long does it take for pharyngitis to resolve?
Most cases of pharyngitis resolve within 7 to 10 days. Treatment failures are usually due to antibiotic resistance, poor compliance, and untreated close contacts.
How many emergency department visits were there for pharyngitis in 2010?
In 2010, there were 1.814 million emergency department visits for pharyngitis, of which 692,000 were for patients under the age of 15. Most cases of pharyngitis occur in children under the age of 5. Adults can also develop the disorder but at a lower rate. Globally, pharyngitis rates are very high chiefly in countries where antibiotics are overprescribed. [5][6]
What is the best treatment for beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis?
Treatment options for Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis include oral treatment with penicillin V or oral amoxicillin. Cephalosporins, macrolides, and clindamycin may also be used. Intramuscular penicillin is also a treatment option. Resistance may develop during treatment with azithromycin and clarithromycin, and it is not considered a first-line antibiotic for this indication. In patients with a mild penicillin allergy, cephalosporins can be used. In patients with a history of anaphylaxis to penicillin, azithromycin or clindamycin can be used. The disease is no longer infectious after 24 hours of antibiotics. [13]
Is pharyngitis a retropharyngeal abscess?
Pharyngitis symptoms may also be part of the symptom complexes of other serious illnesses, including peritonsillar abscess, retropharyngeal abscess, epiglottitis, and Kawasaki disease. [3][4]
Can viruses cause pharyngeal mucosa irritation?
Bacteria and viruses can cause direct invasion of the pharyngeal mucosa. Certain viruses like rhinovirus can cause irritation secondary to nasal secretions. In almost all cases, there is a local invasion of the pharyngeal mucosa which also results in excess secretion and edema.
