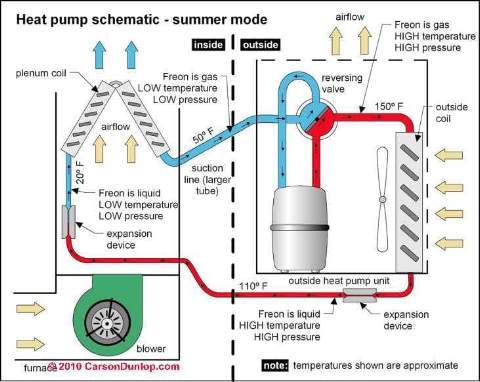
Important Components of a Heat Pump System
- Outdoor Unit. The outdoor unit contains a coil and a fan. ...
- Indoor Unit. Like the outdoor unit, the indoor unit, commonly referred to as the air handler unit, contains a coil and a fan.
- Refrigerant. The refrigerant is the substance that absorbs and rejects heat as it circulates throughout the heat pump system.
- Compressor. ...
- Reversing Valve. ...
- Expansion Valve. ...
What are the main parts of a heat pump?
- Crankcase heater. ...
- ECM. ...
- Reversing valve. ...
- Expansion device. ...
- Electronic control. ...
- Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) Thermostatic Expansion Valve is found on all fan coils and furnace coils and is designed to adjust to changing load conditions by maintaining a preset superheat ...
- Thermostats. ...
- Defrost system. ...
- Fan. ...
- Motors. ...
What are the operating principles of a heat pump?
- Total building energy cost reduction can amount to 60%
- The payback period can be 6-8 years
- Typical COP of a geothermal heat pump for heating and cooling is 3-4
How does a heat pump resemble a refrigeration system?
A heat pump resembles a refrigeration system in various ways – they both possess indoor fans, refrigerants, compressors, and copper coils. They also remove heat from the inside air, making the room cooler. Before we go into the similarities between heat pumps and refrigeration systems, let’s take a look at how both systems work.
Which two components produce the highest heat in a system?
Solar thermal power/electric generation systems collect and concentrate sunlight to produce the high temperature heat needed to generate electricity. All solar thermal power systems have solar energy collectors with two main components: reflectors (mirrors) that capture and focus sunlight onto a receiver. In most types of systems, a heat ...

What are the components of a heat pump HVAC system?
A heat pump consists of two main components: an indoor air handler and an outdoor unit similar to a central air conditioner, but referred to as a heat pump. The outdoor unit contains a compressor that circulates refrigerant that absorbs and releases heat as it travels between the indoor and outdoor units.
What are the two main parts of a heat pump?
A typical air source heat pump system consists of two major components, an outdoor unit (which looks just like the outdoor unit of a split-system air conditioning system) and an indoor air handler unit.
What is the most important part of a heat pump?
Compressor is the one of the most important parts of the heat pump. Inside the compressor the refrigerant is compressed to extremely high pressures, where its temperature is also increased.
What is the inside unit of a heat pump called?
A heat pump consists of two major parts – a “wall cassette” that is mounted inside your home, and a condenser unit that stays on the outside of your home. The heat pump's wall cassette and condenser units are connected by refrigerant line.
What is the outside part of a heat pump called?
In summer, a heat pump is just an air conditioner. The outdoor unit has the compressor and the condensing coil. In winter, though, it has the compressor and the evaporator coil. So if you see the outdoor unit of a heat pump and call it the condenser or condensing unit, you're wrong.
How does heat pump system work?
0:103:57How Does a Heat Pump Work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHow does a heat pump. Work. All air-conditioning systems including heat pumps rely on theMoreHow does a heat pump. Work. All air-conditioning systems including heat pumps rely on the refrigerants pressure temperature. Relationship when a refrigerant evaporates or boils it absorbs heat at a
What are the 3 main parts of the entire HVAC system?
HVAC stands for heating, ventilation and air conditioning, and the well-integrated system will include all these parts. Smooth operation of your HVAC unit can maximize energy efficiency and ensure that maintenance is rarely required.
Does a heat pump have an evaporator coil?
Heat pumps – like air conditioners — have two coils, an indoor coil, known as the evaporator coil, and an outdoor coil, known as the condenser coil. Without these coils, your heat pump can't heat or cool your house. The evaporator coil is filled with a very cold refrigerant that absorbs heat.
What are the parts of an HVAC system called?
Some of the most important parts of your HVAC system are your heat exchanger, blower motor, combustion chamber, condenser, evaporator, and thermostat.
Does a heat pump have a condenser?
The condenser is a main component of the heat pump cycle. Once heat from outside is compressed, it passes into a water heating circuit that flows around your home's radiators. This transfer of heat from the heat pump cycle to the water system takes place in the heat pump condenser.
Does a heat pump require a condenser?
A heat pump can switch from air condition mode to heat mode by reversing the refrigeration cycle, making the outside coil function as the evaporator and the indoor coil as the condenser. The refrigerant flows through a closed system of refrigeration lines between the outdoor and the indoor unit.
What is the difference between a heat pump and HVAC?
A heat pump can heat and cool, but an air conditioner cannot, which is the primary difference between the two HVAC systems.
What is a heat pump?
What is a heat pump? This is a very common question for HVAC professionals, as heat pumps are an often misunderstood marvel of engineering and desi...
What does a heat pump do?
A heat pump is both a heating and cooling system, extracting heat from the air and moving it via an air handler to another location. In the summer...
Where do heat pumps work best?
Heat pumps work best in moderate climates, where the outside temperature during colder months does not drop near or below freezing on a regular bas...
How does a heat pump work?
A heat pump simply reverses the refrigeration process and moves the heat in a different direction when in heating mode. If you have read about refrigeration on High Performance HVAC then you know the process of refrigeration is moving heat. Refrigeration uses mechanical processes to absorb heat.
How does a heat pump work in air conditioning?
That is when in air conditioning mode, the heat pump transfers the heat outside from inside. When in the heating mode, it moves the heat inside from the outside. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the air. It then moves the heat in the direction where it is not wanted or where it is wanted.
How to separate heat pump from air conditioner?
To separate a heat pump from an air conditioner, the heat pump needs a way to reverse the process of refrigeration. This process moves the heat in the opposite direction that an air conditioner moves the heat. That is when in air conditioning mode, the heat pump transfers the heat outside from inside.
How does a heat pump thermostat work?
If you have a heat pump then you have a heat pump thermostat. The thermostat controls the heating mode through the reversing valve or the 4-way valve. The heat pump thermostat reverses the refrigeration process when the heat pump thermostat is set to heating mode.
What is the difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner?
The two major differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner are the controls and the refrigeration circuit. While there are many different types of heat pumps and air conditioners the methods and means these two types of heating and cooling systems use are basically the same.
Why do heat pumps have accumulators?
Because the heat pump operates in cold weather, there is a chance the compressor can eat some liquid when it is operating in cold weather. For this reason, heat pump condensers have accumulators installed in the refrigeration circuit. The accumulator collects liquid refrigerant and allows it to boil into a vapor before it enters the compressor. That prevents the liquid slugging of the compressor.
How does a defrost valve work?
The sequence for defrost mode is timed for defrost mode. When the defrost mode initiates , the defrost control shifts the reversing valve to the air conditioning mode. That makes the condenser coils hot, so the frost or ice will melt off the condenser. After the defrost, the time has expired, the reversing valve shifts back to its heating position. The system is now a heater and not an air conditioner. When the unit is in defrost mode, you want the unit to continue to provide heating. However, how does it do this if it shifted to air conditioning mode when in the defrost mode?
What is the difference between a heat pump and an air compressor?
Compressors for heat pumps and air conditioners operate in much the same principle as an air compressor. The major difference is these compressors pump refrigerant instead of air and the system is sealed. Compressors have a high pressure outlet and a low pressure inlet. The low pressure inlet is the larger of the two copper tubes attached to ...
When should a heat pump compressor run?
In the winter , the compressor should run as long as there is a demand for heating.
Why does my heat pump fan cycle off?
But, the fan may cycle off occasionally when the defrost board determines there is ice or frost on the coil. When the defrost cycle begins, the fan quits, the reversing valve reverses the flow of refrigerant, and your heat pump goes into the cooling mode. In the cooling mode the outdoor coil becomes the hot coil and melts the ice.
What is slugging in heat pump?
Slugging is a common problem with heat pumps. Compressors are designed to pump vapor. When liquid refrigerant enters the suction line (low pressure inlet) it can have devastating effects on a compressor. Most heat pumps have another component called an accumulator.
What is the copper line coming in at the bottom of a compressor?
The copper line coming in at the bottom is always the high pressure from the compressor. On top the middle line is always the return to the compressor. A slide inside the the main part of the valve goes back and forth to divert the flow of refrigerant from inside coil to outside coil.
What are refrigeration coils made of?
Made out of aluminum fins and copper tubing, refrigeration coils are quite fragile. Kids with bikes and hail storms bend the fins and close the gaps reducing the efficiency. The more fins that are bent or the more cotton wood tree stuff gets sucked into the coils the less air moves through them to transfer heat.
Can a heat pump be pumped up in snow?
These holes allow for drainage. If your heat pump is flat on the pad it makes it hard to drain. Heat pumps should be pumped up or raised above anticipated snow levels. If snow is not a factor in your region then keeping your unit up at least a few inches help to keep it drained at least.
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is part of a heating and cooling system and is installed outside your home. Like an air conditioner, it can cool your home, but it’s also capable of providing heat. In cooler months, a heat pump pulls heat from the cold outdoor air and transfers it indoors, and in warmer months, it pulls heat out of indoor air to cool your home.
What is a ground source heat pump?
Ground-source heat pumps, sometimes called geothermal heat pumps, transfer heat between the air inside your home and the ground outside. These are more expensive to install but are typically more efficient and have a lower operating cost due to the consistency of the ground temperature throughout the year.
What is the difference between a heat pump and a ground source heat pump?
Air-source heat pumps transfer heat between indoor air and outdoor air, and are more popular for residential heating and cooling. Ground-source heat pumps, sometimes called geothermal heat pumps, transfer heat between the air inside your home and the ground outside.
Can a heat pump be combined with a furnace?
In colder regions, they can also be combined with furnaces for energy-efficient heating on all but the coldest days. When the temperature outside drops too low for the heat pump to operate effectively, the system will instead use the furnace to generate heat.
Do heat pumps burn fossil fuel?
In colder climates, an electric heat strip can be added to the indoor fan coil for additional capabilities. Heat pumps do not burn fossil fuel like furnaces do, making them more environmentally friendly.
Do heat pumps create heat?
Heat pumps do not create heat. They redistribute heat from the air or ground and use a refrigerant that circulates between the indoor fan coil (air handler) unit and the outdoor compressor to transfer the heat. In cooling mode, a heat pump absorbs heat inside your home and releases it outdoors.
The Basic Anatomy of a Heat Pump
Heat pumps have three major components: the compressor, air handler and thermostat. All of these work together to provide warm air to your home.
How Do Heat Pumps Work?
Heat pumps utilize the same compression/decompression cycle as air conditioners. A standard cooling cycle generates cold air by “pumping” warm air from the room to coils where cool refrigerant passes through.