
- Components of Neurons A neuron is a nerve cell. ...
- Axons An axon is a fiber rather like a cable. ...
- Dendrites Dendrites are finger like receptors of signals coming from other neurons. ...
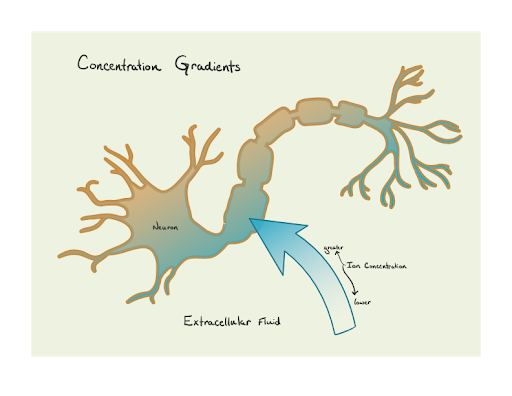
- Synapses Synapses are the gaps between the axons of transmitting neurons and the dendrites of receptor neurons. ...
- Neurotransmitters There are various neurotransmitter chemicals. ...
What are the parts and functions of a neuron?
Types of neurons based on structure include:
- Unipolar neurons: These neurons have a single long axon that is responsible for sending electrical signals. ...
- Multipolar neurons: These neurons are able to receive impulses from multiple neurons via dendrites. ...
- Bipolar neurons: These neurons send signals and receive information from the world. ...
What are the three main parts of a neuron?
What are the 3 parts of a neuron?
- Sensory neurons.
- Motor neurons.
- Interneurons.
- Neurons in the brain.
What parts of a neuron are involved in a synapse?
Synapses are composed of three main parts:
- The presynaptic ending that contains neurotransmitters
- The synaptic cleft between the two nerve cells
- The postsynaptic ending that contains receptor sites
How many types of neurons are there?
Types of neurons
- Sensory neurons. Sensory neurons are the nerve cells that are activated by sensory input from the environment - for example, when you touch a hot surface with your fingertips, the ...
- Motor neurons. ...
- Interneurons. ...
- Neurons in the brain. ...

What are the four main components of a neuron?
A neuron has 4 basic parts: the dendrites, the cell body (also called the "soma"), the axon and the axon terminal.
What are the three main components of a neuron?
Each neuron has three basic parts: cell body (soma), one or more dendrites, and a single axon.Cell Body. In many ways, the cell body is similar to other types of cells. ... Dendrites. Dendrites and axons are cytoplasmic extensions, or processes, that project from the cell body. ... Axon.
What are the 5 parts of a neuron?
Following are the different parts of a neuron:Dendrites. These are branch-like structures that receive messages from other neurons and allow the transmission of messages to the cell body.Cell Body. ... Axon. ... Synapse.
What are the 9 parts of a neuron?
Structure of a neuronNucleus. It is the central part of the neuron. ... Dendrites. Dendrites are the “arms of the neuron”, they form branch extensions that come out of different parts of the neuron. ... Cell body. This is the part of the neuron that includes the nucleus. ... Glial cells. ... Myelin. ... Axon terminal. ... Node of Ranvier. ... Axon.
What are the 3 types of neurons and their functions?
Although there are billions of neurons and vast variations, neurons can be classified into three basic groups depending on their function: sensory neurons (long dendrites and short axons), motor neurons (short dendrites and long axons) and relay neurons (short dendrites and short or long axons).
Which of the following is not a component of a neuron?
The axon, cell body, dendrite, and nodes of Ranvier are all features that can be found on neurons. Neuroglia on the other hand, are a class of cells in the nervous system that are not neurons, but rather serve to provide functional support for neurons. Therefore, the correct answer is (b) Neuroglia.
What are the main structures of a neuron quizlet?
Solutions. A neuron is composed of a body, dendrites, and an axon which at the end of it is the terminals. The dendrites receive information from other nerve cells and pass the information to the cell body, where the cell body determines what is the best response to the information given.
What are the five parts of a neuron quizlet?
Terms in this set (6)Dendrites. A branch like structure that "receives" information and carries it into the neuron.Soma (Cell Body) It's surrounded by dendrites and it is the brain of the neuron.Axon. ... Terminal Buttons. ... Synapse. ... What are the 5 parts of a major neuron?
Which are parts of a neuron quizlet?
Terms in this set (8)Dendrites. rootlike parts of the cell that stretch out from the cell body. ... Soma/Cell body. contains nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life.Axon. ... Myelin sheath. ... Terminal Buttons. ... Synapse. ... Neurotransmitters. ... Synaptic Vesicles.
How many parts are in the neuron?
Neurons have three basic parts: a cell body and two extensions called an axon (5) and a dendrite (3). Within the cell body is a nucleus (2), which controls the cell's activities and contains the cell's genetic material.
What is neuron short answer?
The neuron is the basic working unit of the brain, a specialized cell designed to transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells. Neurons are cells within the nervous system that transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells. Most neurons have a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.
What is a neuron Class 10?
Neuron also known as a nerve cell is the functional and structural unit of the nervous system which has the capability to get excited by electrical or chemical impulse. These cells help in communication inside the body. These cells are found in animals except sponges whereas plants and fungi lack these cells.
What is the most common neuron structure?
Multipolar neurons are the most common neuron in the vertebrate nervous system and their structure most closely matches that of the model neuron: a cell body from which emerges a single long axon as well as a crown of many shorter branching dendrites.
What is a neuron?
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa.
What are synapses in neurons?
Synapse – The junction between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another, through which the two neurons communicate.
What are the 2 types of nerves?
You have two main types of nerves: Sensory nerves carry signals to your brain to help you touch, taste, smell and see. Motor nerves carry signals to your muscles or glands to help you move and function.
What is a neuron?
Neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. All neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body and axon. The n...
What are sensory neurons and motor neurons?
A sensory neuron carries impulses from the receptor to the CNS (brain or spinal cord), while a motor neuron carries impulses from the CNS (brain or...
Name the part of the neuron a) Where information is acquired. b) Through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
a) The part of the neuron which helps in the acquisition of information is known as the dendrite. They are tree-like structures that are designed t...
What is a synapse?
A synapse is the site of transmission of nerve impulses between two nerve cells (neurons) or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell (effector)...
What are the components of a neuron?
(b) It has a cell membrane, cytoplasm, a large vesicular nucleus containing a single prominent nucleolus, numerous rod-like or spherical mitochondria, and a Golgi apparatus.
How many parts does a Schwann cell have?
In this process, the Schwann cells grow round the axon and envelop it completely along its entire length so that cell membrane of the Schwann cell can be divided into two parts—one surrounding the axon, i.e., inner part and other outer part which are connected to one another by the double mesaxon.
What is the membrane of the nerve fibre called?
This set of membranes is known as myelin sheath. (c) Each membrane is composed of two layers of lipid substances sandwiched between layers of protein and they form the myelin sheath of the nerve fibre. (d) The thickness of the myelin sheath is ascertained by the number of membrane layer wrapped round the axon.
Where does the axon come from?
Axon: (a) The axon or nerve fibre arises from the axon-hillock of the perikaryon which is rich in neurofibrillae but has no nissl granules. (b) It consists of a central core of semifluid axoplasm which flows from the cell body to the axon and not in the reverse direction.
Which granules are located on the long axis of the axon?
ADVERTISEMENTS: (c) Axoplasm also contains mito chondria, nissl granules, neurofibrillae running parallel to the long axis of the axon. Axoplasm is bounded by a cell membrane known as axolemma which is continuous with the cell membrane of parent cell body.
Why are myelinated nerves white?
The myelinated nerve fibres are also said to be white nerve fibres on account of the presence of lipids in the myelin sheath. The non-myelinated nerve fibres appear grey for which they are known as grey nerve fibres.
What are the three parts of a neuron?
Neurons vary in size, shape, and structure depending on their role and location. However, nearly all neurons have three essential parts: a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.
How many types of neurons are there?
Given the sheer number of neurons, there are thousands of different types, much like there are thousands of species of living organisms on Earth. In terms of function, scientists classify neurons into three broad types: sensory, motor, and interneurons.
How do action potentials affect other neurons?
In a chemical synapse, action potentials affect other neurons via a gap between neurons called a synapse. Synapses consist of a presynaptic ending, a synaptic cleft, and a postsynaptic ending. When an action potential is generated, it’s carried along the axon to a presynaptic ending.
What is the name of the structure that connects the cell body to the cell body?
Axon. An axon is a long, tail-like structure which joins the cell body at a specialized junction called the axon hillock. Many axons are insulated with a fatty substance called myelin. Myelin helps axons to conduct an electrical signal. Neurons generally have one main axon .
How many dendrites can a neuron have?
Neurons can have more than one set of dendrites, known as dendritic trees. How many they have generally depends on their role. For instance, Purkinje cells are a special type of neuron found in the cerebellum. These cells have highly developed dendritic trees which allow them to receive thousands of signals.
How do neuronal signals work?
Neurons send signals using action potentials. An action potential is a shift in the neuron’s electric potential caused by the flow of ions in and out of the neural membrane. Action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses.
Where are the interneurons located?
Interneurons are neural intermediaries found in your brain and spinal cord. They’re the most common type of neuron. They pass signals from sensory neurons and other interneurons to motor neurons and other interneurons. Often, they form complex circuits that help you to react to external stimuli.
What are the components of a neuron?
It receives signals via chemicals called neurotransmitters. It then transmits the signals, electrically. A neuron consists of a cell body or soma, dendrites, and a single axon. It is one of many units that makes up the brain.
What are the different types of neurotransmitters?
There are various neurotransmitter chemicals. Each serves a different type of neuron. Among them are serotonin, acetylcholine, and dopamine. Serotonin imparts a feeling of well being. It is associated with the central nervous system, blood platelets, and the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the axon of a cell?
An axon is a fiber rather like a cable. It carries electrochemical signals from the soma to other neurons. The axon is surrounded by a series of short, cylindrical myelin sheaths along its length. These lie much like beads on a string. If the sheaths are damaged, the axon cannot transmit signals properly. This can lead to multiple sclerosis.
Where are synapses located?
Synapses are the gaps between the axons of transmitting neurons and the dendrites of receptor neurons. Electrochemical signals are carried across the gap by neurotransmitter molecules. These end up at the receptor proteins located in the ends of dendrites.
What is the brain?
The brain is the cognitive center of the higher animals, and humans. The brain is compared to a computer central processing unit (CPU). The brain has a complex substructure. These include macroscopic, microscopic, and submicroscopic features. Of special significance are neurons. These are typically illustrated in Figure 1.
What is the function of dendrites?
An important function of the dendrite is the integration of various input signals.
Why is it important to know more about the different parts of the neuron?
Knowing more about the different parts of the neuron can help you to better understand how these important structures function as well as how different problems , such as diseases that impact axon myelination, might impact how messages are communicated throughout the body.
What is the role of neuron in the nervous system?
These specialized cells are the information-processing units of the brain responsible for receiving and transmitting information. Each part of the neuron plays a role in communicating information throughout the body. Neurons carry messages throughout the ...
What is the function of dendrites in the cell?
Transmit information to the cell body. Most neurons possess these branch-like extensions that extend outward away from the cell body. These dendrites then receive chemical signals from other neurons, which are then converted into electrical impulses that are transmitted toward the cell body.
What is a dendrite?
Dendrites are tree-like extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses.
What are the connections between axons and other cells?
Axons connect with other cells in the body including other neurons, muscle cells, and organs. These connections occur at junctions known as synapses. The synapses allow electrical and chemical messages to be transmitted from the neuron to the other cells in the body.
How do neurons carry messages?
Neurons carry messages throughout the body, including sensory information from external stimuli and signals from the brain to different muscle groups in the body. In order to understand exactly how a neuron works, it is important to look at each individual part of the neuron. The unique structures of the neuron allow it to receive ...
What are the characteristics of a cell?
Characteristics. Contains numerous organelles involved in a variety of cell functions. Contains a cell nucleus that produces RNA that directs the synthesis of proteins. Supports and maintains the functioning of the neuron. Think of the cell body as a small factory that fuels the neuron.
How many basic functions do neurons have?
If you think about the roles of the three classes of neurons, you can make the generalization that all neurons have three basic functions. These are to:
Which type of neuron receives information from other neurons?
Interneurons. Interneurons, which are found only in the CNS, connect one neuron to another. They receive information from other neurons (either sensory neurons or interneurons) and transmit information to other neurons (either motor neurons or interneurons).
What are the parts of the nervous system?
The human nervous system 1 The central nervous system ( CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It is in the CNS that all of the analysis of information takes place. 2 The peripheral nervous system ( PNS ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS.
How do motor neurons get information?
Motor neurons get information from other neurons and convey commands to your muscles, organs and glands. For instance, if you picked up a hot coal, it motor neurons innervating the muscles in your fingers would cause your hand to let go.
How many input signals do neurons receive?
Most neurons receive many input signals throughout their dendritic trees. A single neuron may have more than one set of dendrites, and may receive many thousands of input signals. Whether or not a neuron is excited into firing an impulse depends on the sum of all of the excitatory and inhibitory signals it receives.
What are the cells that make up the nervous system?
Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ).
Where does the signal from the sensory neurons in your fingertips travel?
For instance, if you picked up a hot coal, the signal from the sensory neurons in your fingertips would travel to interneurons in your spinal cord. Some of these interneurons would signal to the motor neurons controlling your finger muscles (causing you to let go), while others would transmit the signal up the spinal cord to neurons in the brain, where it would be perceived as pain.
Components of Neurons
- A neuron is a nerve cell. It receives signals via chemicals called neurotransmitters. It then transmits the signals, electrically. A neuron consists of a cell body or soma, dendrites, and a single axon. It is one of many units that makes up the brain.
Axons
- An axon is a fiber rather like a cable. It carries electrochemical signals from the soma to other neurons. The axon is surrounded by a series of short, cylindrical myelin sheaths along its length. These lie much like beads on a string. If the sheaths are damaged, the axon cannot transmit signals properly. This can lead to multiple sclerosis.
Dendrites
- Dendrites are finger like receptors of signals coming from other neurons. Although the dendrites do not touch other neurons, they come close, leaving tiny gaps (synapses) to separate them. An important function of the dendrite is the integration of various input signals.
Synapses
- Synapses are the gaps between the axons of transmitting neurons and the dendrites of receptor neurons. Electrochemical signals are carried across the gap by neurotransmitter molecules. These end up at the receptor proteins located in the ends of dendrites.
Neurotransmitters
- There are various neurotransmitter chemicals. Each serves a different type of neuron. Among them are serotonin, acetylcholine, and dopamine. Serotonin imparts a feeling of well being. It is associated with the central nervous system, blood platelets, and the gastrointestinal tract. Acetylcholine relates to the heart and skeletal musculature. Dopamine may occur in increased le…