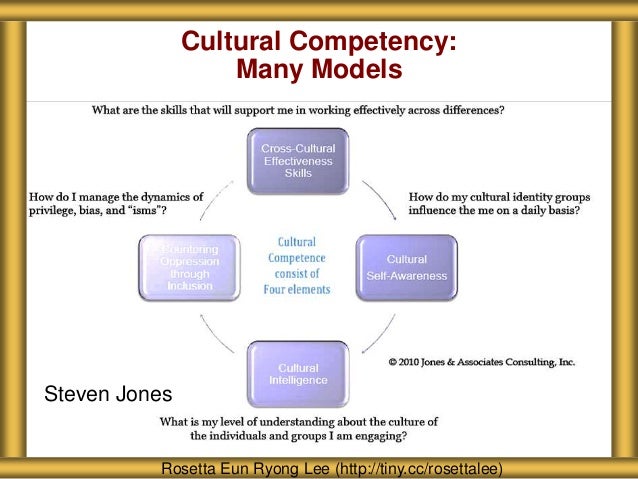
Main cultural components
- Political and civic. Once a society is established, the creation of certain symbols encourages the notion of identity of its members.
- History and customs. History is a fundamental part of the identity of a society; Is to know where they come from and how they have become what they are now.
- Artistic practices and knowledge set. ...
- Language and dialect. ...
What is cultural identity in sociology?
Cultural identities are the distinct identities of people or groups in cultural or subcultural categories and social groups. Categories that make up cultural identities include sexuality, gender, religion, ethnicity, social class, or region. We are often born into our cultural identities.
How is culture and identity formed in our lives?
Your culture and identity are first formed when you learn to speak. Depending on the language that you are born into will help to define who you become. Different cultures speak different languages and even if you are born in the United States, for example, but speak Japanese, this is a cultural identity that you behold.
What shapes your cultural identity?
Important parts of your cultural identity are shaped due to your affiliation with any number of groups or cultural patterns, some of which we (as a culture) assign to you at birth, such as your: Other contributions to your cultural identity occur as you navigate your life and the social constructs (aka social constructions) around you.
How are cultural identity groups expressed through communication?
Additionally, common ways of being and acting within a cultural identity group are expressed through communication. In order to be accepted as a member of a cultural group, members must be acculturated, essentially learning and using a code that other group members will be able to recognize.

What are the elements of cultural identity?
Cultural identities are influenced by several different factors such as ones religion, ancestry, skin colour, language, class, education, profession, skill, family and political attitudes. These factors contribute to the development of one's identity.
What are the 4 cultural identities?
Race, gender, sexuality, and ability are cultural identities that affect our communication and our relationships.
What are the 5 cultural identities?
Cultural identity versus social identity Categories that make up cultural identities include sexuality, gender, religion, ethnicity, social class, or region.
What are the 3 main components of culture?
Components of CultureSurvival. ... Education - the way people in a culture learn what they need to know in order to be successful in their culture.Transportation - the way a culture gets people and goods from one place to another.Communication - the way a culture shares ideas and messages.More items...
What is your cultural identity?
Put simply, your cultural identity is the feeling that you belong to a group of people like you. This is often because of shared qualities like birthplace, traditions, practices, and beliefs. Art, music, and food also shape your cultural identity.
What are the types of identity?
Multiple types of identity come together within an individual and can be broken down into the following: cultural identity, professional identity, ethnic and national identity, religious identity, gender identity, and disability identity.
What are the big 8 identities?
The “Big 8” socially constructed identities are: race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, gender identity, ability, religion/spirituality, nationality and socioeconomic status.
What is the importance of cultural identity?
Cultural identity is an important contributor to people's wellbeing. Identifying with a particular culture gives people feelings of belonging and security. It also provides people with access to social networks which provide support and shared values and aspirations.
What are 7 components of culture?
Social Organization.Language.Customs and Traditions.Religion.Arts and Literature.Forms of Government.Economic Systems.
What are the 10 components of culture?
Terms in this set (10)Values. Beliefs, principles and important aspects of lifestyle.Customs. Holidays, clothing, greetings, typical rituals and activities.Marriage and Family. Type of marriage (i.e. arranged, free, same sex, etc.) ... Government and Law. ... Games and Leisure. ... Economy and Trade. ... Language. ... Religion.More items...
What are the 8 components of culture?
Terms in this set (8)Religion. Beliefs of a society, some traditions.Art. Architecture, style.Politics. Government and laws of a culture (rules and leadership)Language. Communication system of a culture (speech, writing, symbols)Economy. ... Customs. ... Society. ... Geography.
What are examples of identities?
Examples of identities include heterosexual, gay, lesbian, bisexual (people who are attracted to people of two genders), pansexual (a term referring to the potential for attractions or love toward people of all gender identities and sexes), asexual (people who either do not feel sexual attraction or do not feel desire ...
What are the big 8 identities?
The “Big 8” socially constructed identities are: race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, gender identity, ability, religion/spirituality, nationality and socioeconomic status.
What are social and cultural identities?
Social identities are components of self that are derived from our involvement in social groups to which we are interpersonally invested. Cultural identities are components of self based on socially constructed categories that teach us a way of being and include expectations for our thoughts and behaviors.
What are the different social and cultural identities?
Social identity groups are usually defined by some physical, social, and mental characteristics of individuals. Examples of social identities are race/ethnicity, gender, social class/socioeconomic status, sexual orientation, (dis)abilities, and religion/religious beliefs.
What are the components of identity?
Two related but distinct components of our identities are our personal and social identities (Spreckels, J. & Kotthoff, H., 2009). Personal identities include the components of self that are primarily intrapersonal and connected to our life experiences. For example, I consider myself a puzzle lover, and you may identify as a fan of hip-hop music. Our social identities are the components of self that are derived from involvement in social groups with which we are interpersonally committed.
How do social identities differ from personal identities?
Social identities differ from personal identities because they are externally organized through membership. Our membership may be voluntary (Greek organization on campus) or involuntary (family) and explicit (we pay dues to our labor union) or implicit (we purchase and listen to hip-hop music). There are innumerous options for personal and social identities. While our personal identity choices express who we are, our social identities align us with particular groups. Through our social identities, we make statements about who we are and who we are not.
Why do nondominant groups have difficulty valuing differences?
Members of nondominant groups may have difficulty valuing difference due to negative experiences with the dominant group, such as not having their experiences validated. Both groups may be restrained from communicating about difference due to norms of political correctness, which may make people feel afraid to speak up because they may be perceived as insensitive or racist. All these obstacles are common and they are valid. However, as we will learn later, developing intercultural communication competence can help us gain new perspectives, become more mindful of our communication, and intervene in some of these negative cycles.
What is ascribed identity?
Any of these identity types can be ascribed or avowed. Ascribed identities are personal, social, or cultural identities that are placed on us by others, while avowed identities are those that we claim for ourselves (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). Sometimes people ascribe an identity to someone else based on stereotypes. You may see a person who likes to read science-fiction books, watches documentaries, has glasses, and collects Star Trek memorabilia and label him or her a nerd. If the person doesn’t avow that identity, it can create friction, and that label may even hurt the other person’s feelings. But ascribed and avowed identities can match up. To extend the previous example, there has been a movement in recent years to reclaim the label nerd and turn it into a positive, and a nerd subculture has been growing in popularity. For example, MC Frontalot, a leader in the nerdcore hip-hop movement, says that being branded a nerd in school was terrible, but now he raps about “nerdy” things like blogs to sold-out crowds (Shipman, 2007). We can see from this example that our ascribed and avowed identities change over the course of our lives, and sometimes they match up and sometimes not.
How do personal identities change?
Personal identities may change often as people have new experiences and develop new interests and hobbies. A current interest in online video games may give way to an interest in graphic design. Social identities do not change as often because they take more time to develop, as you must become interpersonally invested. For example, if an interest in online video games leads someone to become a member of a MMORPG, or a massively multiplayer online role-playing game community, that personal identity has led to a social identity that is now interpersonal and more entrenched. Cultural identities are based on socially constructed categories that teach us a way of being and include expectations for social behavior or ways of acting (Yep, G. A., 2002). Since we are often a part of them since birth, cultural identities are the least changeable of the three. The ways of being and the social expectations for behavior within cultural identities do change over time, but what separates them from most social identities is their historical roots (Collier, M. J., 1996). For example, think of how ways of being and acting have changed for African Americans since the civil rights movement. Additionally, common ways of being and acting within a cultural identity group are expressed through communication. In order to be accepted as a member of a cultural group, members must be acculturated, essentially learning and using a code that other group members will be able to recognize. We are acculturated into our various cultural identities in obvious and less obvious ways. We may literally have a parent or friend tell us what it means to be a man or a woman. We may also unconsciously consume messages from popular culture that offer representations of gender.
How to define culture?
Define culture. Define personal, social, and cultural identities. Summarize nondominant and dominant identity development. Explain why difference matters in the study of culture and identity. Culture is a complicated word to define, as there are at least six common ways that culture is used in the United States.
What is culture patterned in?
Culture is patterned in that there are recognizable widespread similarities among people within a cultural group.
How is your cultural identity developed?
Whether that be your home life, school life, work-life, etc., what you do, who you hang out with, and how you live are the elements that shape your identity. Without one, you cannot have the other.
What is one of the often forgotten elements of cultural identity?
One of the often forgotten elements of cultural identity is the norms in our everyday lives.
How are values instilled in us?
Values are instilled in us from a young age. Whether it’s our parents, grandparents, or other guardians that raise us, we come to understand that there are certain things in the world that are more important to us than others. These values shape how we think, feel, and act toward others.
What are the things that people know and love?
The answer is, all of these things are conducive to creating the ‘you’ that people know and love. And, the you that you know, even if you don’t understand yourself at times. 1. Language. Your culture and identity are first formed when you learn to speak.
What is cultural identity?
Your cultural identity is a critical piece of your personal identity (and worldview) that develops as you absorb, interpret, and adopt (or reject) the beliefs, values, behaviors, and norms of the communities in your life.
Why is cultural identity important?
Your cultural identity is critical to your success because it influences the way you interpret and react to the world around you. Building an awareness of your identity can help you gain a better understanding of the unique contributions you have to offer, both personally and professionally, while shedding light on your blind spots. For additional insight, we’d invite you to visit our resources page for more exercises.
What Defines and Shapes a Person’s Cultural Identity?
Anytime a group of people unites toward a common objective, a culture begins to form. No matter how large or small the group, there are beliefs, norms, values, and behaviors that emerge.
Why is it important to be aware of your own identity?
Our cultural identity influences how we interpret and react to situations, so it is important that we become aware of our own identity in relation to the world around us. Since we have an innate craving to feel a sense of belonging to a group, when we are under stress we tend to subconsciously revert to whatever behaviors make us “feel” safe and accepted. In doing so, we set up invisible barriers within ourselves and between ourselves and others that impact personal interactions, professional performance, and organizational success .
What makes culture complicated?
What makes culture complicated is that many of these defining characteristics go unspoken. The group unconsciously develops certain standards for what is normal and acceptable based on social cues. Then, through our continual exposure to the group, we begin to accept these standards as part of our cultural identity.
Is cultural identity fixed?
The first myth is that our cultural identity is fixed, which simply isn’t true. It is dynamic and it evolves as we affiliate ourselves with different groups. Think about some of the beliefs you had as a child that have since changed. This happens due to our exposure to new ways of thinking and as we absorb whatever resonates for us into our cultural identity.
What is cultural identity?
Cultural identity is related to the ability to associate and feel as part of a group, based on their culture. Although culture usually refers to language, race, heritage, religion, cultural identity, it is also associated with social class, locality, generation or other types of human groups. Individual identity and culture are linked by experience.
How are identity and culture linked?
Individual identity and culture are linked by experience. A person experiences different processes throughout life and then joins some group and develops a sense of belonging. When enough people share the same beliefs, experiences and values, a culture is outlined. Experiences vary from person to person, and valuation is subjective.
What is transculturation in culture?
Transculturation means more than the transition from one culture to another. It does not consist simply in acquiring another culture-acculturation-or in losing or uprooting an earlier culture -desculturation-rather it fuses these concepts and, in addition, entails the idea of creating new cultural phenomena-enculturation.
What is the process of cultural change and psychological change that results from the reunion between cultures?
Acculturation is the process and conceptual model of cultural change and psychological change that results from the reunion between cultures. The effects of acculturation can be seen at multiple levels in both interacting cultures.
What is social identity in globalized societies?
Social identity in globalized societies. In recognizing the difficulty of establishing the differences or the boundaries between social identity and individual identity Jenkins (1996: 19-20) raises the concept of social identity in the sociological field and states that"if identity is a condition Necessary for social life, ...
What is prime culture?
As for these, what is prime is how the members of a group appropriate the tangible, interpret, and construct meaning they generate.
What is culture in social studies?
Culture is the distinctive feature and knowledge of a particular group of people, made up of language, religion, food and gastronomy, social habits, music, the arts, and so on.