Focusing on the process of understanding and resolving an ethical dilemma, James Rest (1994) developed a theoretical model of ethical decision making that involves four distinct psychological processes: moral awareness, moral judgment, moral intention, and moral action. Rest asserts that, when confronted with an ethical dilemma, individuals engage in a decision-making process that involves working through these four components. Individuals move from moral awareness, the recognition of a moral situation, to moral judgment, the evaluation of choices and outcomes, to moral intention, choosing how one intends to act, and lastly to moral action, the actual behavior in the situation. A failure at any step in the process could result in a failure to make an ethical decision (Rest, 1994).
What are the four steps of ethical decision making?
- Assessment: Make sure you have all the facts about the assessment. ...
- Alternatives: Consider your choices. ...
- Analysis: Identify your candidate decision and test its validity. ...
- Application: Apply ethical principles to your candidate decision. ...
- Action: Make a decision. ...
What are the three main models of ethical decision making?
What are three ethical principles that may provide some guidance for ethical responsibility?
- Management Responsibility.
- Reasonable Occurrence.
- Methods of data processing.
- Limitations.
What are the different types of ethical decision making?
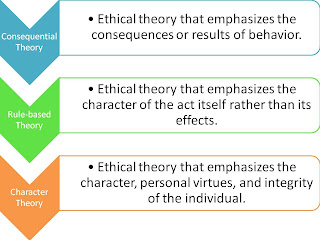
Ethical systems can generally be broken down into three categories: deontological, teleological and virtue-based ethics. The first two are considered deontic or action-based theories of morality because they focus entirely on the actions which a person performs. When actions are judged morally right based upon their consequences, we have ...
What are the rules of ethical decision making?
Decision-Making Models: The Golden Rule. This most basic and useful ethical theory, sometimes called the “ Rule of Reciprocity ,” has a long history: Confucius ( 500 B.C.): “What you do not want done to yourself, do not do to others.”. Aristotle (325 B.C.): “We should behave to others as we wish them to behave to us.”.

What are the 4 components of ethics?
The Fundamental Principles of Ethics. Beneficence, nonmaleficence, autonomy, and justice constitute the 4 principles of ethics.
What are the components of ethical?
Components. Some professional organizations may define their ethical approach in terms of a number of discrete components. Typically these include honesty, trustworthiness, transparency, accountability, confidentiality, objectivity, respect, obedience to the law, and loyalty.
What are the 7 principles of ethical decision making?
In brief these are: 1) modify human practices when possible; 2) justify the need for control; 3) have clear and achievable outcome-based objectives; 4) cause the least harm to animals; 5) consider community values and scientific information; 6) include long-term systematic management; and 7) base control on the ...
What are the 5 steps of ethical decision making?
The Leader's Choice: Five Steps to Ethical Decision Making....Assessment: Make sure you have all the facts about the dilemma. ... Alternatives: Consider your choices. ... Analysis: Identify your candidate decision and test its validity. ... Application: Apply ethical principles to your candidate decision. ... Action: Make a decision.
What is the 4 component model?
The 4-component (4C) model, which divides body weight into fat, water, mineral, and protein, can overcome these limitations.
What are the 3 components of business ethics?
– The concept includes three criteria, namely social, environmental and financial, but it doesn't take into account the factor of time. It's very hard to come up with a win-win strategy, considering that every business action has short-, medium- and long-term consequences.
What is ethical decision making?
Ethical decision-making is based on core character values like trustworthiness, respect, responsibility, fairness, caring, and good citizenship. Ethical decisions generate ethical behaviors and provide a foundation for good business practices.
What are some examples of ethical decision making?
For example, we might say it is ethically obligatory for parents to care for their children, not only because it is right for them to do it, but also because it is wrong for them not to do it. The children would suffer and die if parents did not care for them.
What are the 8 ethical principles?
This analysis focuses on whether and how the statements in these eight codes specify core moral norms (Autonomy, Beneficence, Non-Maleficence, and Justice), core behavioral norms (Veracity, Privacy, Confidentiality, and Fidelity), and other norms that are empirically derived from the code statements.
What are the three main models of ethical decision making?
There are three decision making models that are used when faced with ethical decisions. The are known as the utilitarian model, moral rights model and justice model (Waddell, Jones and George 2012, 133). These ethical decision making models can be used by any manager that is faced with any ethical dilemma.
What is the first step in ethical decision making?
Step 1: Identify the Facts Given that ethical issues often arise because of a lack of sufficient information or evidence, as well as disagreements about the facts, the first step in the ethical decision-making process is an explicit call for identification of the facts.
What are the 7 ethical principles in nursing?
The ethical principles that nurses must adhere to are the principles of justice, beneficence, nonmaleficence, accountability, fidelity, autonomy, and veracity. Justice is fairness.
What are the 7 principles of leadership?
Seven leadership principles to followBelief in the purpose.Taking full responsibility.The ability to move on and forgive.Humility.Optimistic and realistic.Value others' opinions, confidence in your own.Self-acceptance.
What is the purpose of the chapter on ethical decision making?
The purpose of this chapter is to: 1) Outline the decision making process. 2) Explain the nature of ethical decision making. 3) Provide ethical frameworks used in making decision making.
What is decision making?
Decision making is the action or process of thinking through possible options and selecting one (Bright et. al, 2019). A rudimentary framework for how managers engage in the decision making process contains four steps.
How does utilitarianism impact ethical decisions?
Utilitarianism makes ethical decision making easy once the outcomes have been projected. Will this project potentially harm the local water source? What will that cost in terms of clean up or quality of life? Will building a factory create jobs? After asking a series of questions like this, the outcomes are estimated to total impact or good, however that is defined in your ethical dilemma. However, this ethical framework has two primary limitations. First, the concept of utility (or good) is not always easily defined. Financial analysts can project income and net present values of decisions, and these decisions are easy to make once the numbers are in. But how do you estimate how much satisfaction something will bring? If a decision is going to result in the loss of life, how much is a human life worth? How do you estimate the impact a decision has on the community’s culture? Determining utility and then calculating is easy in some cases, but in most it becomes a major challenge to using this framework. The second challenge for utilitarianism is that maximizing the greatest good for most, might result in the sacrifice of a few. A classic example of utilitarianism is the layoff decision. We need to lay off thirty people so that the company stays solvent, and continues to provide jobs for the remaining seventy people. In this case the company stays solvent, but the thirty workers now struggle to provide for their families. Another example is a mass casualty incident. If a trauma ward is overrun with cases, the lead doctor must make decisions about which patients receive immediate care and which ones must be put aside. In this situation, the doctor is trying to save the most human life, which might result in patients with less serious injuries have to wait hours in pain to be treated.
What is the first challenge in decision making?
Identify the Problem. The first challenge in decision making is working to understand what the problem is . Ineffective managers focus on the symptoms without identifying the underlying issues. A child with a runny nose does not have a runny nose problem, she has an infectious disease causing a running nose.
How does an intuitive decision maker make decisions?
The intuitive decision maker simply “knows” what the problem and alternatives are before acting. A manager using analytical tools might uncover new insights from trying to really figure out what the problem is. A democratic manager will rely on the use of the team to work through understanding the problem and figuring out alternative courses of action.
How many decisions do managers make?
Managers make thousands of decisions every day. In most cases they intuit the decision making process and can come to the best solution within nanoseconds of hearing about a problem. These are the types of problems that are routine, and have low consequences.
Who found that managers are in a constant state of making decisions?
Hannaway (1989) found that managers are in a constant state of making decisions as “ [they] switch frequently from task to task, changing their focus of attention to respond to issues as they arise, and engaging in a large volume of tasks of short duration” (p. 39).
How to use ethical decision making model?
Use the three components of the ethical decision-making model (moral awareness, moral judgment, and ethical behavior) found in the Ethical Decision-Making Model media piece in the Resources to analyze the ethical issues. Analyze the factors that contributed to the problem or issue. Identify who is involved or affected by the problem or issue. Describe the factors that contributed to the problem or issue and explain how they contributed. In addition to the readings provided, use the Capella library to locate at least one academic peer-reviewed journal article relevant to the problem or issue that you can use to support your analysis of the situation. Cite and apply the journal article as evidence to support your critical thinking and analysis of the case. Assess the credibility of the information source. Assess the relevance of the information source.
How to describe a case study in health care?
Discuss the effectiveness of the communication approaches present in the case study. Describe how the health care professional communicated with others. Describe the communication and communication strategies that were applied, both in creating and in resolving the problems or issues presented. Assess instances where the professional communicated effectively or ineffectively. Discuss the effectiveness of the approach used by the professional related to any problems or issues involving ethical practice in the case. Describe the actions taken in response to the ethical dilemma or challenge presented in the case study. Summarize how well the professional managed professional responsibilities and priorities to resolve the problem or issue in the case. Discuss the key lessons this case provides for health care professionals. Apply ethical principles to a possible solution to the
What are the resources that are needed to make a decision?
Resources can include people (i.e., a mentor, coworkers, external colleagues, or friends and family) as well professional guidelines and organizational policies and codes. Such resources are critical for determining parameters, generating solutions, clarifying priorities and providing support, both while implementing the solution and dealing with the repercussions of the solution.
What is the purpose of ethics filters?
Their purpose is to surface the ethics considerations and implications of the decision at hand. When decisions are classified as being "business" decisions (rather than "ethics" issues), values can quickly be left out ...
Why is it important for an organization to develop a set of guidelines?
Organizations struggle to develop a simple set of guidelines that makes it easier for individual employees, regardless of position or level, to be confident that his/her decisions meet all of the competing standards for effective and ethical decision-making used by the organization.
What is a formal mechanism?
Providing a formal mechanism (i.e., a code and a helpline, giving employees access to a definitive interpretation of the policies, laws and universal values when they need additional guidance before making a decision).
Do plus filters guarantee ethically sound decisions?
The PLUS filters do not guarantee an ethically-sound decision. They merely ensure that the ethics components of the situation will be surfaced so that they might be considered.
What are the components of ethical action?
Rest developed his Four-ComponentModel by asking: “What must happen psychologically in order for moralbehavior to take place?” He concluded that ethical action is the product ofthese psychological subprocesses: (1) moral sensitivity (recognition); (2) moraljudgment or reasoning; (3) moral motivation; and (4) moral character.1The first half of the chapter is organized around Rest’s framework. I’ll describeeach factor and then offer some tips for improving your performance on thatelement of Rest’s model.
What is the third frame of a decision?
The third frame highlights the likely impacts of decisions . Identifying pos-sible harm to stakeholder groups can help us take steps to prevent damage.Such analysis requires understanding the perspectives of others as well as care-ful reasoning.
What is moral behavior?
Moral behavior is the product of moral sensitivity, moral judgment, moralmotivation, and moral character. You’ll need to master each of these compo-nents in order to make and then implement wise ethical decisions.
What is the fourth stage of moral action?
Moral agents must overcome active opposition, copewith fatigue, resist distractions, and develop sophisticated strategies for reaching their goals. In sum, they must persist in a moral task or action despite obstacles.Persistence can be nurtured like other positive character traits (seeChapter 2), but it is also related to individual differences. Those with a strongwill, as well as confidence in themselves and their abilities, are more likely topersist. So are individuals with an internal locus of control.20Internally ori-ented people (internals) believe that they have control over their lives and candetermine what happens to them. Externally oriented people (externals)believe that life events are beyond their control and are the product of luck orfate. Because internals take personal responsibility for their actions, they aremotivated to do what is right. Externals are more susceptible to situationalpressures. As a consequence, they are less likely to persist in ethical tasks.Successful implementation demands that persistence be complementedwith competence. A great number of skills can be required to take action,including, for instance, relationship building, organizing, coalition building,and public speaking. Pulitzer Prize–winning author and psychiatrist RobertColes discovered the importance of ethical competence during the 1960s.21Coles traveled with a group of physicians who identified widespread malnutri-tion among children of the Mississippi Delta. They brought their report toWashington, D.C., convinced that they could persuade federal officials to providemore food. Their hopes were soon dashed. The secretaries of agriculture andeducation largely ignored their pleas and Southern senators resisted attempts toexpand the food surplus program. The physicians were skilled in medicine, butthey didn’t understand the political process. They only got a hearing when NewYork Senator Robert Kennedy took up their cause. A highly skilled politician,Senator Kennedy coached them on how to present their message to the press andpublic, arranged special committee meetings to hear their testimony, and trav-eled with them to the South to draw attention to the plight of poor children.
What is the purpose of the moral compass?
Harvard ethics professor Lynn Paine offers a four-part “moral compass”for guiding managerial decision making.23The goal of the compass is to ensurethat ethical considerations are factored into every organizational decision.Paine believes that we can focus our attention (and that of the rest of thegroup) on the moral dimension of even routine decisions by engaging in thefollowing four frames of analysis. Each frame or lens highlights certain ele-ments of the situation so that they can be carefully examined and addressed.Taken together, the lenses increase moral sensitivity, making it easier for orga-nizational members to recognize and discuss moral issues.

The Importance of Ethical Standards
An Empirical Approach to An Ethical Decision-Making Model
The Ethical Decision-Making Process
- Before a model can be utilized, leaders need to work through a set of steps to be sure they are bringing a comprehensive lens to handling ethical disputes or problems. 1. Some initial analysis has to happen for leaders to truly understand where they need to bring in ethical principles. Leaders need to decide why an ethical decision needs to be made and the outcomes that are de…
Plus Ethical Decision-Making Model
- PLUS Ethical Decision-Making Modelis one of the most used and widely cited ethical models. To create a clear and cohesive approach to implementing a solution to an ethical problem; the model is set in a way that it gives the leader “ethical filters” to make decisions. It purposely leaves out anything related to making a profit so that leaders can focus on values instead of a potential im…
The Character-Based Decision-Making Model
- While this one is not as widely cited as the PLUS Model, it is still worth mentioning. The Character-Based Decision-Making Model was createdby the Josephson Institute of Ethics, and it has three main components leaders can use to make an ethical decision. 1. All decisions must take into account the impact to all stakeholders– This is very similar t...