What are the basic components of the nervous system?
What are the basic elements of the nervous system?
- Neurons. Nerve cells, the basic elements of the nervous system.
- Dendrite. A cluster of fibers at one end of a neuron that receives messages from other neurons.
- Axon.
- Terminal buttons.
- Myelin Sheath.
- All-or-none law.
- Resting State.
- Action Potential.
What are two integrated parts of the autonomic nervouse system?
These include the following[2][4][30][31]:
- Dorsal nucleus: provides parasympathetic output to the viscera
- Nucleus ambiguus: produces motor fibers and preganglionic neurons that innervate the heart
- Nucleus solitarius: receives afferents of taste sensation and that from viscera, and lastly
How long can you live with autonomic dysfunction?
MSA is a fatal form of autonomic dysfunction. Early on, it has symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease. But people with this condition usually have a life expectancy of only about 5 to 10 years...
What do autonomic nerves system send signals to?
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) also called autonomic motor or visceral motor system. processes regulated below conscious level. transmits signals from CNS to heart, smooth muscle, glands. responds to visceral sensory inputs (from blood vessels) (these sensory neurons are not considered part of ANS) Functions to maintain homeostasis (keep ...
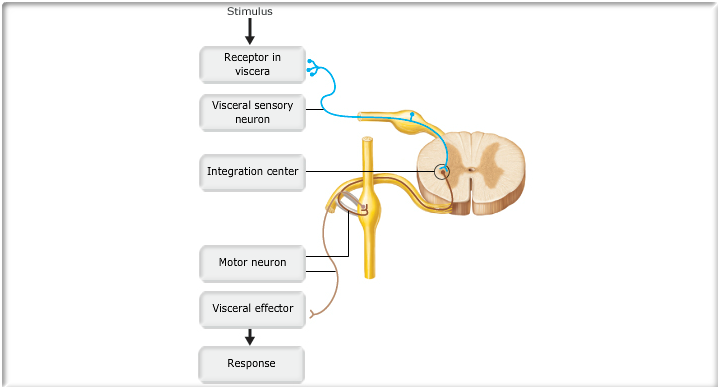
What are the two components of the autonomic nervous system?
What does the autonomic nervous system do?Sympathetic nervous system: This system activates body processes that help you in times of need, especially times of stress or danger. ... Parasympathetic nervous system: This part of your autonomic nervous system does the opposite of your sympathetic nervous system.More items...•
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Summary. Your autonomic nervous system is the part of your nervous system that controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart and the widening or narrowing of your blood vessels. When something goes wrong in this system, it can cause serious problems, including: Blood pressure problems. Heart problems.
Which of the following are components of the autonomic nervous system quizlet?
c) The motor (output) division of the autonomic nervous system has three divisions: parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic.
What are the 7 major components of the nervous system?
The central nervous system (defined as the brain and spinal cord) is usually considered to have seven basic parts: the spinal cord, the medulla, the pons, the cerebellum, the midbrain, the diencephalon, and the cerebral hemispheres (Figure 1.10; see also Figure 1.8).
What is an example of autonomic nervous system?
It operates automatically, and is generally considered to be outside the realm of voluntary control. Examples of the types of functions controlled by the ANS are salivating, sweating, changing pupil size, managing heart rate, crying, and secreting hormones.
What are the functions of the autonomic nervous system quizlet?
What is the function of the autonomic nervous system? a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal.
What is the correct order of the five components of an autonomic reflex arc?
So, the correct answer is 'Receptors - Sensory neuron - Spinal cord - Motor neuron - Muscle'
What are the basic structural components of an autonomic plexus quizlet?
What are the basic structures from an autonomic plexus? Collections of sympathetic postganglionic axons and parasympathetic preganglionic axons as well as some visceral sensory axons.
Which division of the nervous system is composed of the autonomic and somatic nervous systems quizlet?
The role of the PNS is to relay messages from the CNS to the rest of the body. It consists of two components: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
What are the 3 main components of the nervous system?
The human nervous system is made up of three basic parts: the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system, and the autonomic nervous system.
What are the major components of the nervous system and describe their functions?
The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and a complex network of nerves. This system sends messages back and forth between the brain and the body. The brain is what controls all the body's functions. The spinal cord runs from the brain down through the back.
What are the four major components of the central nervous system?
The CNS has three main components: the brain, the spinal cord, and the neurons (or nerve cells)....Spinal Cord8 cervical nerves.12 thoracic nerves.5 lumbar nerves.5 sacral nerves.1 coccygeal nerve.
What is the autonomic nervous system controlled by?
The hypothalamus is the key brain site for central control of the autonomic nervous system, and the paraventricular nucleus is the key hypothalamic site for this control.
Is the autonomic nervous system voluntary or involuntary?
involuntaryThe autonomic nervous system (ANS) is also called the vegetative nervous system. It controls the involuntary functions and influences the activity of internal organs.
What triggers the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is one of the major neural pathways activated by stress. In situations that are often associated with chronic stress, such as major depressive disorder, the sympathetic nervous system can be continuously activated without the normal counteraction of the parasympathetic nervous system.
What is another name for autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies smooth muscle and glands, and thus influences the function of internal organs.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Your autonomic nervous system is a part of your overall nervous system that controls the automatic functions of your body that you need to survive. These are processes you don’t think about and that your brain manages while you’re awake or asleep.
Where does the autonomic nervous system fit in the overall structure of the nervous system?
Central nervous system: This includes your brain (your retina and optic nerve in your eyes are considered part of your brain, structure-wise) and spinal cord.
What does the autonomic nervous system do?
Your autonomic nervous system breaks down into three divisions, each with its own job:
How does the autonomic nervous system help with other organs?
Much like a home needs electrical wiring to control lights and everything inside that needs power, your brain needs the autonomic nervous system’s network of nerves. These nerves are the physical connections your brain needs to control almost all of your major internal organs.
What are some interesting facts about the autonomic nervous system?
Your sympathetic and parasympathetic systems create a balancing act. Your sympathetic nervous system activates body processes, and your parasympathetic deactivates or lowers them. That balance is key to your body's well-being and your ongoing survival.
Where is it located?
Your autonomic nervous system includes a network of nerves that extend throughout your head and body. Some of those nerves extend directly out from your brain, while others extend out from your spinal cord, which relays signals from your brain into those nerves.
What is it made of?
Your autonomic nervous system has a similar makeup to your overall nervous system. The main cell types are as follows, with more about them listed below:
Which nervous system interacts with the gut?
And of course, the enteric and sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems also have interactions in the gut. So, the gut is really, hard to understand in any kind of a simple way. There’s an example of what I am talking about.
What are the components of the ANS?
In this video Dr. Goldstein discusses important components of the ANS including the vagus nerve, gastroduodenal parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves and the enteric nervous system.
What are the chemical messengers of the enteric nervous system?
So, the enteric nervous system – nobody knows what the chemical messengers are of the enteric nervous system, how they’re organized…it’s very complex. There are numerous putative transmitters. They interact. And of course, the enteric and sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems also have interactions in the gut. So, the gut is really, hard to understand in any kind of a simple way. There’s an example of what I am talking about. These are enteric nerves, but they are impinged on by parasympathetic postganglionic neurons. Now the parasympathetic ganglia are near or even inside the target organ, so very different from sympathetic postganglionic innervation where these are very long wispy fibers that come from the ganglia. Here most of the parasympathetic innervation is preganglionic, it’s myelinated, the vagus nerve is myelinated, and it is only very short postganglionic fibers that go to the target organ.
Which nerves are preganglionic parasympathetic?
You’ve got the vagus nerve and pelvic nerves that are preganglionic parasympathetic nerves. You have got ganglia that use acetylcholine as the chemical messenger…that’s true for all the parts of the autonomic nervous system.
Which nerve supplies the heart?
The main parasympathetic nerve outside the brain is the vagus nerve, that’s the tenth cranial nerve, and importantly it supplies the heart and it supplies most of the GI tract – not all because of that sacral innervation – but most of the GI tract as well as the lungs and splanchnic organs such as the pancreas and spleen.
Which nervous system has chemical messengers?
So, the enteric nervous system – nobody knows what the chemical messengers are of the enteric nervous system, how they’re organized…it’s very complex. There are numerous putative transmitters. They interact. And of course, the enteric and sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems also have interactions in the gut.
Which nerves increase the tone of the stomach?
First of all, you’ve got the enteric nerves that are in the walls of the gut and then you have parasympathetic innervation which in general increases the tone of those organs…of the stomach, and sympathetic inhibition. It’s kind of interesting to think about sympathetic inhibition.
Why is it important to know the autonomic nervous system?
In order to fully understand disease and health , it's important to know how the autonomic nervous system works.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is one of the most incredible parts of the human body. Your nervous system takes in all the information in the world around you and sends a message to your muscles, allowing you to make your way through the world. Your autonomic nervous system also controls all of your vital functions, many of which you aren't consciously aware ...
What is the name of the clump of nerves that synapse before the message is transmitted to?
One of the interesting things about the autonomic nervous system is that, almost without exception, the nerves synapse in a clump of nerves called a ganglion before the message is transmitted to the target organ, such as a salivary gland. This allows for another level of communication and control.
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic system is the emergency system and performs life saving flight or fight responses.
Which neurotransmitter is responsible for communication in the autonomic nervous system?
Neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and norepinephrine are primarily responsible for communication in your autonomic nervous system. For both parasympathetic and sympathetic parts of the autonomic system, acetylcholine is released at the level of the ganglia. The acetylcholine receptors in ganglia are nicotinic and may be blocked by drugs such as ...
Where do parasympathetic nerves travel?
Many nerves of the parasympathetic autonomic nervous system begin in the nuclei in your brainstem. From there, they travel through cranial nerves such as the vagus nerve, which slows the heart rate, or the oculomotor nerve, which constricts the pupil of the eye. Parasympathetic are what causes your eyes to tear and your mouth to salivate. Other parasympathetic terminate in the walls of thoracic and abdominal organs like the esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, pharynx, heart, pancreas, gallbladder, kidney, and ureter. The sacral parasympathetic synapse in ganglia in the walls of the colon, bladder, and other pelvic organs.
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for the fight or flight response?
Your autonomic nervous system lies almost entirely outside of the central nervous system and involves two main parts: the craniosacral part (parasympathetic), and the thoracolumbar part (sympathetic). These are sometimes thought of as being opposite to each other, ultimately striking a balance within the body. The parasympathetic is associated with relaxation, digestion, and generally taking it easy. The sympathetic is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system ( ANS ), formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies smooth muscle and glands, and thus influences the function of internal organs. The autonomic nervous system is a control system ...
What are the three branches of the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system has three branches: the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system . Some textbooks do not include the enteric nervous system as part of this system. The sympathetic nervous system is often considered the " fight or flight " system, while the parasympathetic nervous ...
What are the cells of the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system consists of cells with bodies in the lateral grey column from T1 to L2/3. These cell bodies are "GVE" (general visceral efferent) neurons and are the preganglionic neurons. There are several locations upon which preganglionic neurons can synapse for their postganglionic neurons:
Where are sympathetic ganglia located?
Preganglionic sympathetic neurons are located in the spinal cord, at the thorax and upper lumbar levels. Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are found in the medulla oblongata where they form visceral motor nuclei; the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve; the nucleus ambiguus, the salivatory nuclei, and in the sacral region of the spinal cord.
Where are motor neurons located?
Motor neurons of the autonomic nervous system are found in ‘’autonomic ganglia’’. Those of the parasympathetic branch are located close to the target organ whilst the ganglia of the sympathetic branch are located close to the spinal cord.
Which subsystem of neurons is a non-cholinergic transmitter?
There are inhibitory and excitatory synapses between neurons. A third subsystem of neurons has been named as non-noradrenergic, non-cholinergic transmitters (because they use nitric oxide as a neurotransmitter) and are integral in autonomic function, in particular in the gut and the lungs.
Who was the first person to describe the autonomic nervous system?
The specialised system of the autonomic nervous system was recognised by Galen. In 1665, Willis used the terminology, and in 1900, Langley used the term, defining the two divisions as the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Where is the sympathetic nervous system located?
Sympathetic nervous system. The cell bodies of the SNS lays within the intermediolateral columns of the spinal cord gray matter (T1-L2/L3). In a transverse section of the spinal cord, the intermediolateral columns can be seen as the lateral horns of the spinal cord.
What are the two types of neurotransmitters?
In terms of physiology, a couple of things are important: 1 All preganglionic fibers of the ANS release acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter 2 Postganglionic PSNS fibers release acetylcholine, while postganglionic SNS fibers release norepinephrine (noradrenalin) (except for those that supply the sweat glands which release acetylcholine)
What is the ganglion in the brain?
A ganglion is a neural tissue outside of the CNS which comprises of the neuronal bodies of the second-order neurons whose axons (postganglionic fibers) provide autonomic innervation to the organs. SNS ganglia are found close to the SNS centers, in contrast with PSNS ganglia which are farther from the PSNS centers.
What is the central part of the ANS?
Anatomy. The central part of the ANS consists of centers within the brainstem and the spinal cord , while the peripheral part is made up of autonomic fibers and ganglia of the PNS. SNS centers are found within the thoracic and lumbar segments of the spinal cord, which is why it is also called the thoracolumbar division.
Where does sympathetic innervation come from?
Sympathetic innervation of the head and neck comes from the postganglionic fibers of the superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic trunk and form multiple periarterial plexuses around the branches of the carotid arteries. Sympathetic innervation of the thoracic viscera comes from the cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves, which contribute to cardiac, esophageal, and pulmonary plexuses. They are postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic trunk.
What is the ANS in the CNS?
Together with endocrine glands, the ANS affects important body functions without an obvious involvement of the cerebral cortex. Morphologically, the ANS is divided ...
Where are preganglionic neurons located?
Preganglionic (first-order) neurons are found within the gray matter of the CNS. Their axons (preganglionic fibers) synapse with the bodies of the postganglionic (second-order) neurons, which are found within autonomic ganglia.
How does the autonomic nervous system work?
How It Works. The autonomic nervous system operates by receiving information from the environment and from other parts of the body. The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems tend to have opposing actions in which one system will stimulate a response where the other will inhibit it. 2 .
What are the functions of the autonomic system?
Functions. The autonomic system controls a variety of internal processes including: 1 . The autonomic nerve pathways connect different organs to the brain stem or spinal cord. There are also two key neurotransmitters, or chemical messengers, that are important for communication within the autonomic nervous system:
What are the three branches of the nervous system?
This system is further divided into three branches: the sympathetic system, the parasympathetic system, and the enteric nervous system. 1
What is the diagnosis of autonomic disorder?
Diagnosis of an autonomic disorder requires a doctor's evaluation, which may include a physical examination, recording blood pressure when the patient is both lying down and standing, testing of the sweat response, and an electrocardiogram.
Which division of the nervous system is responsible for controlling the bladder?
The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system helps maintain normal body functions and conserves physical resources. This division also performs such tasks as controlling the bladder, slowing down heart rate, and constricting eye pupils.
Why is the nervous system important?
This system also helps prepare the body to cope with stress and threats, as well as returning the body to a resting state afterward. Learning more about this part of the nervous system can give you a better understanding of the processes that underlie many human behaviors and responses.
Which neurotransmitter is used in the parasympathetic system to inhibit the parasympathetic response?
There are also two key neurotransmitters, or chemical messengers, that are important for communication within the autonomic nervous system: Acetylcholine is often used in the parasympathetic system to have an inhibiting effect.
Overview
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies smooth muscle and glands, and thus influences the function of internal organs. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, digestion, r…
Structure
The autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic division emerges from the spinal cord in the thoracic and lumbar areas, terminating around L2-3. The parasympathetic division has craniosacral “outflow”, meaning that the neurons begin at the cranial nerves (specifically the oculomotor nerve, facial nerve, gloss…
Function
Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions typically function in opposition to each other. But this opposition is better termed complementary in nature rather than antagonistic. For an analogy, one may think of the sympathetic division as the accelerator and the parasympathetic division as the brake. The sympathetic division typically functions in actions requiring quick responses. The parasym…
History
The specialised system of the autonomic nervous system was recognised by Galen. In 1665, Willis used the terminology, and in 1900, Langley used the term, defining the two divisions as the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Caffeine effects
Caffeine is a bioactive ingredient found in commonly consumed beverages such as coffee, tea, and sodas. Short-term physiological effects of caffeine include increased blood pressure and sympathetic nerve outflow. Habitual consumption of caffeine may inhibit physiological short-term effects. Consumption of caffeinated espresso increases parasympathetic activity in habitual caffeine consumers; however, decaffeinated espresso inhibits parasympathetic activity in habitu…
See also
• Dysautonomia
• Feeling
• International Society for Autonomic Neuroscience
• Polyvagal Theory
• Medullary ischemic reflex
External links
• Autonomic nervous system article in Scholarpedia, by Ian Gibbins and Bill Blessing
• Division of Nervous System