
What are facts about the cerebrum?
- The dendrites of neurons in the cerebellar cortex grow in a tangential direction toward the pial surface (the boundary separating gray matter and cerebrospinal fluid) but also toward the excitatory ...
- All excitatory fibers (i.e. ...
- Inhibitory fibers also grow parallel to the pial surface but tangentially to the direction of the excitatory fibers.
What happens if the cerebrum is damaged?
These symptoms include, but not are limited to, the following:
- Difficulty in planning basic tasks, such as making a cup of coffee or restocking toilet paper.
- Apathy or a complete loss of interest in life.
- Loss of thinking flexibility.
- Difficulty focusing or a complete lack of attention.
- Difficulty speaking in social settings.
- Often repeating actions without any awareness of doing so.
What are the responsibilities of the cerebrum?
There are several key functions of the cerebellum, including: 3
- Balance and posture
- Mental function
- Movement
- Motor learning
- Vision
What are the five parts of the brainstem?
Understanding the Five Major Areas of the Brain
- Frontal Lobe. The frontal lobe is the last portion of the brain that fully develops and is not fully “grown” until after a person passes from adolescence into adulthood.
- Parietal Lobe. ...
- Occipital Lobe. ...
- Temporal Lobe. ...
See more
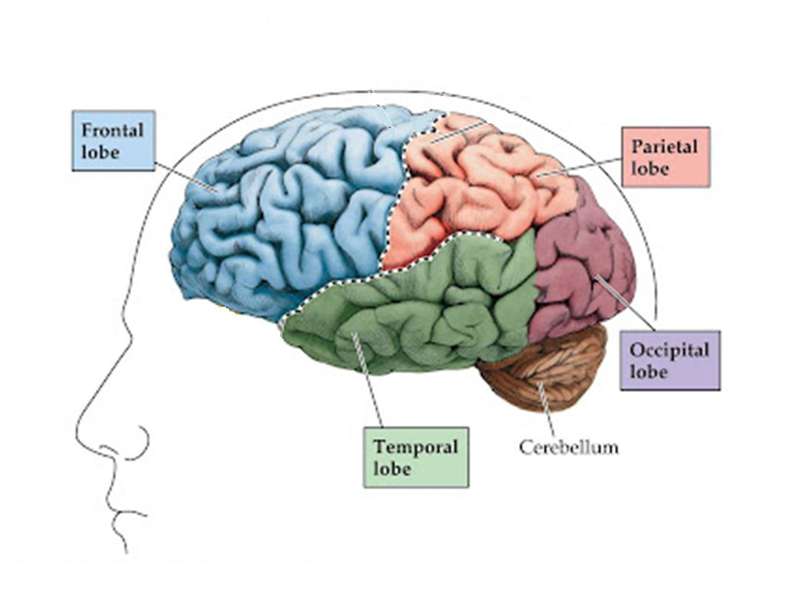
What are the main parts of the cerebrum?
Lobes of the Brain and What They Control Each brain hemisphere (parts of the cerebrum) has four sections, called lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Each lobe controls specific functions.
What are the 3 parts of the cerebrum?
The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain. The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum (1).
How many parts make up the cerebrum and what are they?
The cerebrum is divided into four regions called lobes that control senses, thoughts, and movements. The four lobes are the occipital, temporal, frontal, and parietal lobes. Although each lobe has a different task to perform, they all must work together.
What is the main function of the cerebrum?
Your cerebrum is the largest part of your brain and handles conscious thoughts and actions. Different areas within your cerebrum also have different responsibilities like language, behavior, sensory processing and more.
Which of the following covers the cerebrum?
The cerebral cortex serves as the outer layer of the cerebrum and it consists of mostly of gray matter, which is a type of tissue labeled on the basis of its color [8]. Four lobes make up the cerebral cortex: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the occipital lobe.
What are the 5 lobes of the cerebrum?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes, four of which have the same name as the bone over them: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe. A fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil, lies deep within the lateral sulcus.
What are the 4 lobes of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum consists of two cerebral hemispheres the outer layer called the cortex (gray matter) and the inner layer (white matter). There are four lobes in the cortex, the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe. This review article will focus on the functions of the cerebral cortex.
What are the three parts of the cerebellum?
There are three functional areas of the cerebellum – the cerebrocerebellum, the spinocerebellum and the vestibulocerebellum. Cerebrocerebellum – the largest division, formed by the lateral hemispheres.
What are the lobes of cerebrum?
The cerebrum consists of two cerebral hemispheres the outer layer called the cortex (gray matter) and the inner layer (white matter). There are four lobes in the cortex, the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe.
What is the cerebrum also known as?
The cerebrum, or telencephalon, is the large upper part of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres . In the human skull, the cerebrum sits atop the brainstem, with the cerebellum underneath the rear portion.
How many lobes are in the cerebrum?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes, four of which have the same name as the bone over them: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe.
What are the two types of tissue in the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is comprised of two different types of tissue – grey matter and white matter:
Where does the cerebrum drain?
Venous drainage of the cerebrum is via a network of small cerebral veins. These vessels empty into the dural venous sinuses – endothelial lined spaces between the outer and inner layers of dura mater.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, located superiorly and anteriorly in relation to the brainstem. It consists of two cerebral hemispheres (left and right), separated by the falx cerebri of the dura mater. Embryologically, the cerebrum is derived from the prosencephalon.
Which lobe is responsible for visual perception?
The parieto-occipital sulcus separates the occipital lobe from the parietal and temporal lobes anteriorly. The primary visual cortex (V1) is located within the occipital lobe and hence its cortical association area is responsible for vision. By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 1.2 – The lobes of the cerebral cortex.
Which structure separates the frontal and parietal lobes?
The two cerebral hemispheres are connected by a white matter structure, called the corpus callosum. Central sulcus – groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes. Lateral sulcus – groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. Lunate sulcus – groove located in the occipital cortex.
How many lobes are there in the cerebral cortex?
Lobes of the Cerebrum. The cerebral cortex is classified into four lobes, according to the name of the corresponding cranial bone that approximately overlies each part. Each lobe contains various cortical association areas – where information from different modalities are collated for processing.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for personality and behavioural changes?
Frontal lobe – a diverse range of presentations, often personality and behavioural changes occur and an inability to solve problems develops.
What are the three major parts of the brain?
There are three major components of the brain. The cerebrum is the largest component, extending across the top of the head down to ear level. The cerebellum is smaller than the cerebrum and located underneath it, behind the ears toward the back of the head. The brain stem is the smallest and is located under the cerebellum , extending downward and back toward the neck.
Why is the cerebellum important?
The cerebellum creates automatic programs so we can make complex movements without thinking. The brain stem is located underneath the temporal lobes and extended down to the spinal cord. It is critical for survival because it connects the brain with the spinal cord.
What is the brain stem?
The brain stem is located underneath the temporal lobes and extended down to the spinal cord. It is critical for survival because it connects the brain with the spinal cord. The top portion of the brainstem is called the midbrain. The midbrain is a small portion of the brain stem located at the top of the brain stem. Just below the midbrain is the pons, and below the pons is the medulla. The medulla is the part of the brain stem closest to the spinal cord. The medulla, with its critical functions, lies deep within the head, where it is well-protected from injuries by an extra-thick section of overlying skull. When we are asleep or unconscious, our heart rate, breathing and blood pressure continue to function because they’re regulated by the medulla.
What is the part of the brain that lies deep within the head?
Just below the midbrain is the pons, and below the pons is the medulla. The medulla is the part of the brain stem closest to the spinal cord. The medulla, with its critical functions, lies deep within the head, where it is well-protected from injuries by an extra-thick section of overlying skull.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for visual processing?
The occipital lobe analyzes visual information from the retina and then processes that information. If the occipital lobe becomes damaged, a person could become blind, even if his or her eyes continue to function normally. The cerebellum is located at the back of the head underneath the occipital and temporal lobes.
How many neurons are there in the brain?
The brain is composed of more than a thousand billion neurons. Specific groups of them, working in concert, provide us with the capacity to reason, to experience feelings, and to understand the world. They also give us the capacity to remember numerous pieces of information.
Which part of the brain controls the most complex intellectual thoughts?
The cerebral cortex is the outside portion of the cerebrum, also called the “gray matter”. It generates the most complex intellectual thoughts and controls body movement. The cerebrum is divided into left and right sides, which communicate with each other through a thin stalk of nerve fibers.
Why do the lobes of the cerebrum work together?
Different lobes in the cerebrum will receive and control different bodily functions, though the lobes also work together to carry out many functions. Dysfunction may occur in one or more areas due to injury or a chronic health condition. The cerebrum is not the entire brain itself.
How does the cerebellum work?
It works directly with the structures in the cerebrum to coordinate functions such as posture and balance. It also sends signals to control muscle movements. Sustaining damage to the cerebellum may therefore result in balance or gait difficulties. Learn more about the cerebellum here.
How many lobes does the cerebrum have?
The cerebrum itself houses the four major lobes, and each lobe as its own set of functions. So although the cerebrum as a whole controls numerous functions in the body, this is mainly due to the function of each individual lobe and the interplay between them.
How are the lobes divided?
These lobes each have two sections, divided by the central fissure in the brain. As there are no other distinct separations in the brain, neuroscientists divide the lobes roughly based on the major folds in the area. Major folds include the: Central sulcus: This divides the frontal and parietal lobes.
What is the white matter in the cerebral cortex?
Beneath the cerebral cortex lie the deeper structures, often known as white matter. This includes connecting structures such as nerve fibers called axons, which help connect and transmit to various areas of the cerebral cortex.
What is the brain and cerebrum?
Click on it to learn more about the brain and its various parts. The cerebrum, or telencephalon, is the large upper part of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres. In the human skull, the cerebrum sits atop the brainstem, with the cerebellum underneath ...
What is the outermost layer of the cerebrum?
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the cerebrum, or its gray matter. In humans, this gray matter has an uneven surface with many folds. Ridges called gyri and valleys, or folds, called sulci help increase the surface area of the cerebral cortex.
What are the two lobes of the cerebrum?
CEREBRUM: composed of the two (left and right) cerebral hemispheres and their cortices (singular, cortex --the outermost layer of grey matter ), and the underlying regions of white matter. The fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres ...
What are the folds in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex surface contains folds to increase the surface area available to allow more neurons. These folds create gyri (singular, gyrus --raised area) and sulci (singular, sulcus --low area).
What are the four ventricles of the brain?
VENTRICLES: The ventricles of the brain are a set of four connected cavities where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced by the choroid plexus , a web of specialized glial cells known as ependymal cells. The ependymal cells line all four ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord, which is connected to the fourth ventricle.
What is the largest white matter-based structure in the brain?
It is a very busy place, consuming 25% of the body's total glucose supply. CORPUS CALLOSUM : a broad, wide, and flat band of nerve fibers that join the two sides of the brain at the longitudinal fissure that separates the two hemispheres. It is the largest white matter-based (myelinated axon) structure in the brain.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest and most superior portion of the brain, made up of the. ventricles. The cerebrum is responsible for processing of sensory information and motor control of the body. The majority of the cerebrum is divided into named lobes which will be reviewed in a different section.
How did the limbic system help us survive?
The Limbic System allowed our survival as a species by generating and orchestrating the innate drives, desires, and emotions, ability to remember and learn, and sexual inclinations--crucial features of living and surviving.
Which fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres?
The fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres is known as the longitudinal fissure.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
Where is the cerebellum located?
The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a fist-sized portion of the brain located at the back of the head, below the temporal and occipital lobes and above the brainstem. Like the cerebral cortex, it has two hemispheres. The outer portion contains neurons, and the inner area communicates with the cerebral cortex.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
How many nerves are in the cranium?
Inside the cranium (the dome of the skull), there are 12 nerves, called cranial nerves:
What organ controls memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger, and every other process?
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
What is gray matter made of?
Gray matter is primarily composed of neuron somas (the round central cell bodies), and white matter is mostly made of axons (the long stems that connects neurons together) wrapped in myelin (a protective coating). The different composition of neuron parts is why the two appear as separate shades on certain scans.
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back.
What does it mean when you feel like you are spinning?
Vertigo: Vertigo is the sensation of spinning. You may feel as if you’re spinning or that your surroundings are spinning. Many cases of vertigo are caused by inner ear problems. But there are instances where vertigo can be caused by damage to the cerebellum or brain stem.
What part of the brain works with sensory input from your eyes and ears to keep you upright and steady?
Balance and posture: Your cerebellum works with sensory input from your eyes and ears to keep you upright and steady.
What is the term for uncoordinated movement, trouble with fine motor tasks, and changes in speech?
Ataxia : Ataxia is characterized by uncoordinated movement, trouble with fine motor tasks, and changes in speech.
How are the lobes of the cerebellum separated?
The cerebellum is divided up into three different parts called lobes. These lobes are separated from each other by deep grooves called fissures. There are two major components of the cerebellum:
Which part of the brain contains the most nerve cells?
The cerebellum only accounts for about 10 percent of your brain’s total size. Although it’s much smaller than the cerebrum, it contains significantly more nerve cells.
How to take care of cerebellum?
You can take care of your cerebellum by making some lifestyle changes. Protecting your head, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol, and not smoking can all help lower your risk of injury or disease that can affect the cerebellum and the rest of your brain.
What is autism spectrum disorder?
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD): ASD is a developmental condition characterized by impairments in communication and social interaction as well as repetitive or restricted behaviors.
