The findings
- The low carbohydrate group showed an increased energy expenditure with a range of 209-278 calories/day compared with the high carbohydrate group. ...
- The increased metabolic effect with the low carbohydrate diet was most significant in people who had high insulin secretion at the start of the study, with an increased energy expenditure ...
- A hormone that works to increase appetite, ghrelin, decreased significantly on the low carbohydrate diet, which could help with weight loss maintenance. Another appetite-regulating hormone, leptin, also decreased. ...
How does obesity affect carbohydrate metabolism?
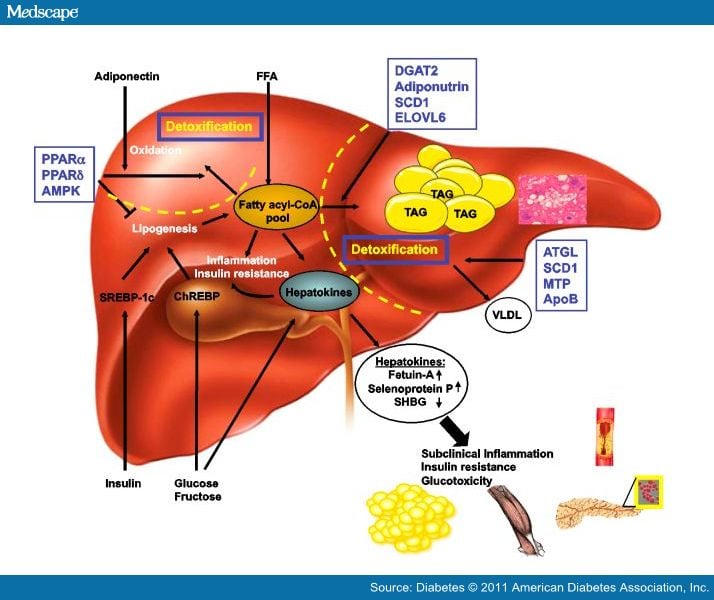
Effect of obesity on carbohydrate metabolism The action of insulin in lowering blood glucose levels results from the suppression of hepatic glucose production and the increased glucose uptake into muscle and adipose tissue viaGLUT4.
What is a carbohydrate metabolism disorder?
Definition. Carbohydrate metabolism disorders are a group of metabolic disorders. Normally your enzymes break carbohydrates down into glucose (a type of sugar). If you have one of these disorders, you may not have enough enzymes to break down the carbohydrates. Or the enzymes may not work properly.
How does a high-carbohydrate diet affect metabolic parameters?
Suggestive Mechanism of the Effects by a High-Carbohydrate Diet on Metabolic Parameters Fat has a high energy density with more than twice the number of calories per gram compared to carbohydrate; high-fat foods are highly palatable and seem to induce a relatively weak sense of satiety [83].
What is the difference between carbohydrate metabolism and glucose metabolism?
Glucose makes up about 80% of the simple sugars initially produced, and is the major and preferred fuel used by the body for energy. Therefore, carbohydrate metabolism essentially refers to glucose metabolism. Glucose must be transported into cells to be available for immediate energy needs.

What does carbohydrate metabolism affect?
Carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental biochemical process that ensures a constant supply of energy to living cells. The most important carbohydrate is glucose, which can be broken down via glycolysis, enter into the Kreb's cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP.
What are the symptoms of carbohydrate metabolism disorder?
Symptoms may include failure to gain weight satisfactorily, vomiting, hypoglycemia, liver dysfunction, and kidney defects. Older children with HFI tend to avoid sweet foods and may have teeth notable for the absence of caries. Children with the disorder do very well if they avoid dietary fructose and sucrose.
What are the end products of carbohydrate metabolism?
In cellular (aerobic) respiration, glucose and oxygen are metabolized to release energy, with carbon dioxide and water as endproducts.
What happens if you have a carbohydrate deficiency?
Your body can store extra carbohydrates in your muscles and liver for use when you're not getting enough carbohydrates in your diet. A carbohydrate-deficient diet may cause headaches, fatigue, weakness, difficulty concentrating, nausea, constipation, bad breath and vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
What diseases are caused by carbohydrates?
Chapter 3 - Dietary carbohydrate and diseaseObesity. The frequency of obesity has increased dramatically in many developed and developing countries. ... Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) ... Cardiovascular disease. ... Cancer. ... Gastrointestinal diseases other than cancer. ... Dental caries. ... Other conditions.
What are metabolic problems?
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that occur together, increasing your risk of heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include increased blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
What regulates carbohydrate metabolism?
Insulin is the key hormone of carbohydrate metabolism, it also influences the metabolism of fat and proteins. It lowers blood glucose by increasing glucose transport in muscle and adipose tissue and stimulates the synthesis of glycogen, fat, and protein.
What is carbohydrate metabolism called?
This process is called cellular respiration. In carbohydrate metabolism, the breakdown starts from digestion of food in the gastrointestinal tract and is followed by absorption of carbohydrate components by the enterocytes in the form of monosaccharides.
What are the 4 stages of carbohydrate metabolism?
The enzyme reactions that form the metabolic pathways for monosaccharide carbohydrates (Chapter 2) include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation as the main means to produce the energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What can be the effects of deficiency and over consumption of carbohydrates?
Over time, ketosis may result in dehydration, altered chemical balance in the blood and perilously low blood sugar levels. Other long-term effects are unclear, but lack of fiber intake can cause constipation and nutritional deficiencies can result from low consumption of fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
What are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. Glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. The complex sugars are also called polysaccharides and are made ...
What happens to glucose molecules when oxygen is available?
When oxygen is available, the pyruvate molecules will then be converted to acetyl CoA which enters the mitochondria and enters the citric acid cycle.
How many ATP molecules are produced by glucose?
This equation states that glucose, in combination with ATP (the energy source), NAD + (a coenzyme that serves as an electron acceptor), and inorganic phosphate, breaks down into two pyruvate molecules, generating four ATP molecules—for a net yield of two ATP—and two energy-containing NADH coenzymes.
What is the process of transferring glucose from ADP to ATP?
Cells in the body take up the circulating glucose in response to insulin and, through a series of reactions called glycolysis , transfer some of the energy in glucose to ADP to form ATP ( Figure 24.2.2 ). The last step in glycolysis produces the product pyruvate.
What is the name of the enzyme that converts glucose to fructose?
Glycolysis begins with the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase to form glucose-6-phosphate. This step uses one ATP, which is the donor of the phosphate group. Under the action of phosphofructokinase, glucose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose-6-phosphate.
How many carbons does glucose have?
The glucose molecule then splits into two three-carbon compounds, each containing a phosphate. During the second phase, an additional phosphate is added to each of the three-carbon compounds. The energy for this endergonic reaction is provided by the removal (oxidation) of two electrons from each three-carbon compound.
Which cycle is pyruvate metabolized by enzymes?
The pyruvate molecules generated during glycolysis are transported across the mitochondrial membrane into the inner mitochondrial matrix, where they are metabolized by enzymes in a pathway called the Krebs cycle ( Figure 24.2.4 ).
What happens if you have a metabolic disorder?
If you have a metabolic disorder, something goes wrong with this process. Carbohydrate metabolism disorders are a group of metabolic disorders. Normally your enzymes break carbohydrates down into glucose (a type of sugar). If you have one of these disorders, you may not have enough enzymes to break down the carbohydrates.
What is the process of breaking down food into sugars and acids?
Chemicals in your digestive system (enzymes) break the food parts down into sugars and acids, your body's fuel. Your body can use this fuel right away, or it can store the energy in your body tissues. If you have a metabolic disorder, something goes wrong with this process. Carbohydrate metabolism disorders are a group of metabolic disorders.
Can genetic disorders be fatal?
These disorders are inherited. Newborn babies get screened for many of them, using blood tests. If there is a family history of one of these disorders, parents can get genetic testing to see whether they carry the gene.
How many calories do low carbs consume?
The low carbohydrate group showed an increased energy expenditure with a range of 209-278 calories/day compared with the high carbohydrate group. The moderate carbohydrate group showed a smaller increase in expenditure of about 100 calories compared with the high carbohydrate group. This trend was consistent throughout the 20-week period.
What did the high carbohydrate group eat?
The types of foods in each diet group were designed to be as similar as possible, but varying in amounts: the high carbohydrate group ate more whole grains, fruits, legumes, and low fat dairy products. In contrast, the low carbohydrate group ate more fat but eliminated all grains and some fruits and legumes. Participants followed the diets ...
Which hormones are responsible for weight loss?
A hormone that works to increase appetite, ghrelin, decreased significantly on the low carbohydrate diet, which could help with weight loss maintenance. Another appetite-regulating hormone, leptin, also decreased. Leptin regulates energy balance and works to keep body weight stable.
Is losing weight hard?
Losing weight is hard work, but many people who have lost weight may agree that keeping the weight off can be an even greater challenge. A lack of self-control or a few too many dietary indulgences are often cited as reasons for regaining weight. But a new study in the November issue of BMJ questions this conventional view, ...
Does obesity cause leptin resistance?
However, some forms of obesity/overweight may lead to “leptin resistance” when the body has high levels of leptin. In this scenario, the brain does not receive an alert that leptin levels are already high, so it continues to send strong hunger signals while conserving body fat stores.
What are the health consequences of being overweight?
Health consequences linked to being overweight or obese include Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, arthritis, depression, and some cancers. An infatuation with sugary foods and refined grains likely contributes to the epidemic proportion of people who are overweight or obese in this country, but so do the consumption ...
How much sugar was consumed in 2008?
The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) reports that sugar consumption in the American diet in 2008 was, on average, 28 teaspoons per day (Figure 4.13 “Sugar Consumption (in Teaspoons) from Various Sources”).
What are added sugars?
Added sugars do not include sugars that occur naturally in whole foods (such as an apple), but do include natural sugars such as brown sugar, corn syrup, dextrose, fructose, fruit juice concentrates, maple syrup, sucrose, and raw sugar that are then added to create other foods (such as cookies).
Is it bad to eat whole grains?
While excessive consumption of simple carbohydrates is potentially bad for your health, consuming more complex carbohydrates is extremely beneficial to health. There is a wealth of scientific evidence supporting that replacing refined grains with whole grains decreases the risk for obesity, Type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Whole grains are great dietary sources of fiber, vitamins, minerals, healthy fats, and a vast amount of beneficial plant chemicals, all of which contribute to the effects of whole grains on health. Eating a high-fiber meal as compared to a low-fiber meal (see Figure 4.14 “Fibers Role in Carbohydrate Digestion and Absorption”) can significantly slow down the absorption process therefore affecting blood glucose levels. Americans typically do not consume the recommended amount of whole grains, which is 50 percent or more of grains from whole grains.
Does sugary soft drink cause weight gain?
There is consistent scientific evidence that consuming sugary soft drinks increases weight gain and disease risk. An analysis of over thirty studies in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition concluded that there is much evidence to indicate higher consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages is linked with weight gain and obesity. [2] . ...
Does high carbohydrate diet increase weight gain?
There is much disagreement over whether high-carbohydrate diets increase weight-gain and disease risk, especially when calories are not significantly higher between compared diets. Many scientific studies demonstrate positive correlations between diets high in added sugars with weight gain and disease risk, but some others do not show ...
What happens if you have a metabolic disorder?
If you have a metabolic disorder, something goes wrong with this process . Carbohydrate metabolism disorders are a group of metabolic disorders. Normally your enzymes break carbohydratesdown into glucose (a type of sugar). If you have one of these disorders, you may not have enough enzymes to break down the carbohydrates.
What is metabolic process?
Research Protocol. Archived . October 5, 2011. Definition. Metabolism is the process your body uses to make energy from the food you eat. Food is made up of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Chemicals in your digestive system (enzymes) break the food parts down into sugars and acids, your body's fuel. Your body can use this fuel right away, ...
5.3 Health Consequences and Benefits of High-Carbohydrate Diets
University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa Food Science and Human Nutrition Program
The Most Notorious Sugar
Before high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) was marketed as the best food and beverage sweetener, sucrose (table sugar) was the number-one sweetener in America.
Do Low-Carbohydrate Diets Affect Health?
Since the early 1990s, marketers of low-carbohydrate diets have bombarded us with the idea that eating fewer carbohydrates promotes weight loss and that these diets are superior to others in their effects on weight loss and overall health. The most famous of these low-carbohydrate diets is the Atkins diet.
Health Benefits of Whole Grains in the Diet
While excessive consumption of simple carbohydrates is potentially bad for your health, consuming more complex carbohydrates is extremely beneficial to health. There is a wealth of scientific evidence supporting that replacing refined grains with whole grains decreases the risk for obesity, Type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
