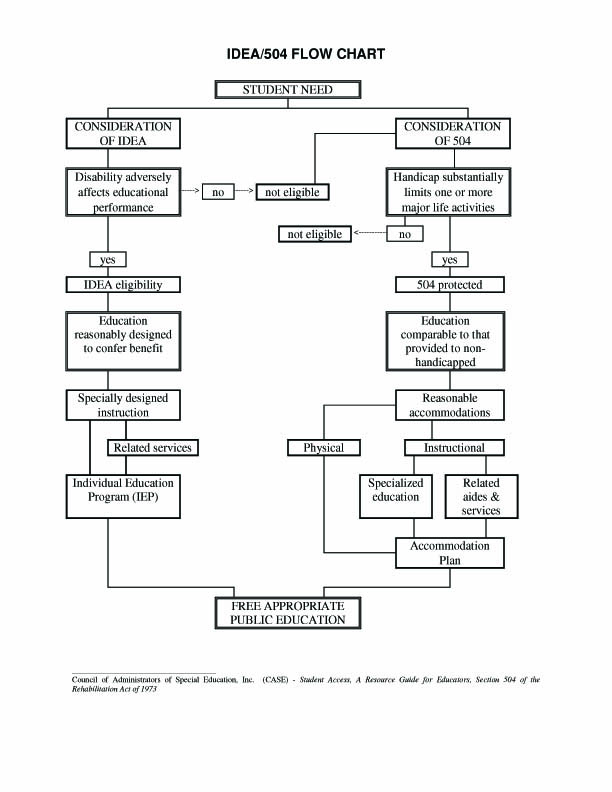
Two criteria exist for an IEP, both of which must be met:
- The student must meet one of the 13 disability categories defined by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, 2004 ( IDEA ).
- The student must need special education; that is, the child requires specifically designed instruction to receive educational benefits
How many goals do you typically write for an IEP?
Writing IEP Goals
- Reading. In 2000, the report of experts on the National Reading Panel explained the research in reading. ...
- Math. After children master math operations skills (adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing), they learn how to use reasoning to solve word problems.
- Writing. Achievement in written language requires many skills. ...
How to qualify for an IEP?
Your Child Must Qualify for an IEP
- Investigate what’s difficult for your child to do in school.
- Find evidence that (or describe how) your child is having trouble, and that the teacher has tried a couple of different methods to teach, the and then
- Write a letter, requesting an IEP, as we describe below. ...
What should an IEP include?
What should be in an IEP?
- The nature of the child or young person’s learning or developmental difficulties
- What help should be given
- Who will give the help, what equipment, programmes or materials will be used
- When, where and how often the help will be given
- The nature of the support required from parents at home
- Any pastoral care or medical requirements
What qualifies a child for an IEP?
The IEP must include:
- Information about your child
- Detailed plan specially designed for your child
- Evaluation of academic performance
- Annual goals
- Special education and any related services
- Accommodations
- State and district test results
- List of needed transition services
- Assessed progress of the child
What are the conditions that qualify for an IEP?
What is a learning disability that can be easily missed?
What is visual impairment?
What is the definition of a child who is deaf?
What are the different types of speech impairments?
What is the importance of IEP?
What are the acronyms for special education?
See 2 more

What is the criteria for IEP goals?
IEP goals include three components that must be stated in measurable terms: (a) direction of behavior (increase, decrease, maintain, etc.) (b) area of need (i.e., reading, writing, social skills, transition, communication, etc.) (c) level of attainment (i.e., to age level, without assistance, etc.)
What are the 5 components of an IEP?
The Components of an Individualized Education ProgramCurrent Performance. In IEP terms, your child's current performance is called the “Present Level of Performance” or PLOP. ... Goals. ... Assessment. ... Services. ... Transition. ... Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) and Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) ... Placement.
What are the 7 components of an IEP?
A Closer Look at Each IEP ComponentAnnual Goals. ... Benchmarks or Short-Term Objectives. ... Measuring and Reporting Progress. ... Special Education. ... Related Services. ... Supplementary Aids and Services. ... Program Modifications for School Personnel. ... Extent of Nonparticipation.More items...
What are the 7 special factors that must be considered in the development of any IEP?
The special factors are:Behavior (Keep scrolling)Limited English proficiency.Blindness or visual impairment.Communication needs/Deafness.Assistive technology.
What are the 3 most important parts of an IEP?
The three parts of an IEP goal: current level of performance, specific and measurable goal, and service delivery all need to support each other.
What is not included in an IEP?
An IEP must include all of the following EXCEPT: a. The present levels of educational performance and how the student's disability affects his or her involvement and progress in the general education curriculum.
What are 3 types of IEP?
Let's take a look at each type of IEP below.Presentation. This changes how the information is presented to the student. ... Response. This alters how the student completes assignments and testing. ... Setting. Some students struggle to learn in a traditional classroom setting. ... Timing and Scheduling.
What are the 6 key parts of an IEP?
Components of the IEPPLAAFP. A statement of your child's Present Level of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP). ... Parent Input. ... Annual Educational Goals. ... Accommodations and Modifications. ... FAPE (Free and Appropriate Public Education). ... Transition Plan.
What are some IEP accommodations?
Common examples of accommodations include extended time to complete assignments, provision of notes or outlines, untimed tests, and reduced number of test questions.
What is the most common reason for an IEP?
Students who are eligible for special education services need an IEP. While there are many reasons that students could be eligible, some common conditions include: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) autism.
What are the three most common disabilities in special education?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Learning Disabilities. Mobility Disabilities.
What 4 elements must be contained in every IEP goal?
Each goal has four elements: a target behavior, the conditions under which the target behavior will be exhibited and measured, the criterion for acceptable performance, and the timeframe within which the student will meet the criterion.
What are the 5 key areas of the disability standards of education?
The Disability Standards cover five specific areas of an educational service: enrolment • participation • curriculum • support services • preventing harassment and victimisation.
What are the 6 elements that should be included in an IEP?
Components of the IEPPLAAFP. A statement of your child's Present Level of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP). ... Parent Input. ... Annual Educational Goals. ... Accommodations and Modifications. ... FAPE (Free and Appropriate Public Education). ... Transition Plan.
What 4 elements must be contained in every IEP goal?
Each goal has four elements: a target behavior, the conditions under which the target behavior will be exhibited and measured, the criterion for acceptable performance, and the timeframe within which the student will meet the criterion.
Which component of IEP is most important?
The PLAAFP Section It is sometimes referred to as “Present Levels.” This may be the most important part of the IEP because it tells you how the school assesses your child's skills. The PLAAFP will focus on your child's needs to help direct his learning.
Qualifying for an IEP: What You Should Know
As kids go back to school, it’s important to know your child’s education options, especially if he or she has disabilities. Children with delayed skills or other disabilities might be eligible for special services that provide individualized education programs in public schools, free of charge to families. Understanding how to access these services can help you as a parent be an effective ...
A Guide to the Individualized Education Program
Contents Introduction / 1 The Basic Special Education Process under IDEA / 2 A Closer Look at the IEP / 5 Contents of the IEP / 5 Additional State and School-System Content / 6
What is mastery criteria in IEP?
The first consideration in IEP mastery criteria is the type of skill the goal is addressing. Different skills lend themselves to different types of mastery. And even within the subject or area of the skill, you could have different needs for mastery. Let's look at reading, math and behavior as examples. Reading.
Why is IEP Mastery Criteria Important?
While IEP mastery criteria seems pretty straightforward, it can trip up an IEP team in many different ways. If it isn’t clear, there may be disagreement among the team about when the skill is or isn’t mastered. If the mastery criteria is written vaguely, there is unlikely to be agreement. And some mastery criteria can seem different depending on the reader.
What happens if the mastery criteria is not clear?
If it isn't clear, there may be disagreement among the team about when the skill is or isn't mastered. If the mastery criteria is written vaguely, there is unlikely to be agreement. And some mastery criteria can seem different depending on the reader.
Why do educators lock themselves into a really complex data system?
Educators often lock themselves into a really complex data system, because of how the IEP goal is written. Think about how you will measure the skill BEFORE you write the goal or you will regret it.
When is IEP mastery critical?
And some mastery criteria can seem different depending on the reader. And, IEP mastery criteria is critical when you go to create your system of data collection.
How is challenging behavior measured?
Challenging behavior is often measured by frequency of behavior over time (e.g., no more than 1 instance of hitting adults per week). However, if I was measuring crying, I might need to have mastery as duration. Because crying for 60 minutes one time a day (i.e., frequency=1) is more significant than crying 10 minutes each time for 3 times a day (i.e., frequency=3). And if the problem was the severity of the behavior, we would need different measures like rating scales.
How often should you take data for 4/5 days?
For instance, if you write that he will do it 4/5 days, you are going to have to take data every day. So you might want to write it as he will demonstrate the skill on 4/5 opportunities on twice weekly samples collected over a period of 3 weeks. Then you take a sample twice a week and use that data.
What is OHI in education?
Other health impairment (OHI) - This means the child has limited strength or alertness to the educational environment related to a health condition. It also can refer to a heightened alertness to stimuli, like in the case of ADD and ADHD. OHI can also include sensory integration dysfunction, anxiety disorder, asthma, sickle cell anemia, diabetes, epilepsy, lead poisoning leukemia, nephritis, food allergies.
What is autism in children?
Autism – Autism is defined as a developmental disability that significantly affects verbal and nonverbal communication and social interactions. Children with autism also typically engage in repetitive activities and stereotyped movements, have great difficulty with change in daily routine and difficulty handling sensory stimuli. Though it is generally diagnosed by age 3, an older child can also be diagnosed with autism if they experience the above characteristics. The autism category can include any of the autism spectrum disorders such as PDD, PDD NOS, and Asperger’s syndrome.
What is a TBI?
The TBI results in a total or partial functional disability, or psychosocial disability, or both. This could be an open or closed head injury that results in impairments in cognition, language, memory, attention, reasoning, abstract thinking, judgment, problem solving, sensory, perceptual and motor abilities, psychosocial behavior, ...
What is considered a disability in special education?
There are also specific requirements under federal guidelines as to who is qualified to diagnose certain disabilities. To be eligible for special education, your child must have an educational disability. An educational disability is defined as one of 13 categories below that adversely affects their educational performance ...
What is a combination of disabilities that are so connected that they cause such a significant disability that the needs cannot be?
Multiple disabilities - This means that there is a combination of disabilities that are so connected that they cause such a significant disability that the needs cannot be met in a special education program designed solely for one of the disabilities. Generally, this would include mental retardation and another disability. For instance, mental retardation and blindness.
What is a visual impairment?
Visual impairment (VI) – This includes partial sightedness and blindness.
How long does it take to write an IEP?
The IEP team then has 30 days to begin writing your child’s individualized education program (IEP). Sometimes this happens at the same time as eligibility is determined ...
What is an IEP eligibility meeting?
IEP Eligibility Meeting. Once your child’s special education evaluations are completed, you will be invited to a meeting. If this is your child’s first IEP, the eligibility meeting is usually held separately from an IEP meeting. Once there is an IEP in place, this meeting is bundled with IEP re-evaluations, per IDEA.
Why should IEP parents not agree to let's just wait and see?
Why IEP Parents Should Never Agree to the “Let’s just Wait and See.”. The team said no to an IEP because we speak Spanish. This is one I see often. Yes, if the child speaks primarily Spanish and does not read English well, the language difference may account for the difficulties.
How long does it take for an IEP to be developed?
If your child is eligible for an IEP, one will be developed. Most states give 30 days for this.
Is IEP eligibility simple?
IEP Eligibility is a complex issue. It’s not as simple as yes or no. If you’ve been told no but your gut is telling you yes, keep advocating. Join our Facebook group for specific questions.
Can a child with poor schooling get an IEP?
The evals come back and confirm–the child is really behind. However, since the child had poor schooling for 5 years prior, he likely will not get an IEP.
Can you be bilingual and dyslexic?
You can be bilingual and dyslexic or have ADHD. If your child is fluent in English and you suspect a reading or learning disability, you’re going to have to keep pushing. Keep advocating. Learn about IEEs and ask for one. Gather up examples, both written and video, of how your child is fluent in both.
Should parents read their state's special education regulations?
Parents should read their state’s special education regulations as well as reputable websites that support your child’s suspected condition (s). This can help a parent better define what they are seeing.
How will we know if Krista is making progress?
The evaluation component of the objective addresses the question: “How will we know whether Krista is making progress?” In this case, the speech pathologist will determine whether Krista is meeting the goal of 85 percent accuracy and send reports to her homeroom teacher and family each week. Other evaluation methods include test-taking, videotaping, peer reports, daily logs, checklists, computer printouts, and worksheets.
How often does Krista receive speech therapy?
OBJECTIVE: “Krista will increase her verbal responses by receiving speech therapy from a licensed speech pathologist at least four times a week, in a one-on-one situation, in the resource room. The sessions will last at least 30 minutes. Krista will verbally answer questions with 85 percent accuracy after receiving both verbal and visual cues. The speech pathologist will send weekly reports, based on record-keeping, to Krista’s parents as well as her homeroom teacher. This therapy shall begin September 1st and continue until June 3rd, excluding pre-determined school holidays.”
What is an IEP program?
A program that is appropriate for one child with autism may not be right for another. The IEP is the cornerstone for the education of a child with a disability.
What is the purpose of an IEP meeting?
The notification must indicate the purpose of the meeting (i.e., to discuss transition services, behavior problems interfering with learning, academic growth).
How often do you have to have an IEP?
108-446), parents now must be included as “members of any group that makes decisions on the educational placement of the child.” IEP meetings must be held at least once annually, but may be held more often if needed. Parents may request a review or revision of the IEP at any time. While teachers and school personnel may come prepared for the meeting with an outline of goals and objectives, the IEP is not complete until it has been thoroughly discussed and all parties agree to the terms of the written document.
Why is it important for students with disabilities to receive related services?
Students with disabilities have a right to related services to help them learn and receive the maximum benefit from their educational programs. Related services, according to IDEIA, consist of “transportation and such developmental, corrective and other supportive services as are required to assist a child with a disability to benefit from special education.” These services are to be determined on an individualized basis, not by the disability or category of the disability.
What is a child's teacher?
The child’s teacher or prospective teacher. A representative of the public agency (local education agency), other than the child’s teacher, who is qualified to provide or supervise the provision of special education. The child, if appropriate.
Writing the IEP Goal Mastery Criteria
There are certain topics that I just can’t help but jump on a soapbox about. Once you get me talking, it’s hard for me to stop. IEP goal mastery criteria is one of those topics. This isn’t because I absolutely love writing IEP goals. This is because I see the mastery criteria frequently mishandled. It’s often an after thought.
1. What does mastery of this skill really look like?
Now get big picture for me. Think beyond the child. Think about the skill. What does true mastery of this skill look like? If I told that Johnny has mastered letter identification, what would that mean to you? That Johnny knows some of the letters? All of the letters? All of the time? Some of the time? Think about why you are teaching this skill.
2. What timeline do I have to accomplish this goal?
Yes, we have our annual IEP deadline but think about the details. When is winter break? When is summer break? Think about other contributing factors that the success of the goal.
3. How will I collect data on this goal?
Beyond what does mastery really look, the 80% mastery criteria bugs me because that isn’t how we teach or collect data. I can’t quickly do the math in my head on what 11 correct out of 13 possible is. I also don’t know if 80% is in regards to 5 problems or 50 problems and that’s a big difference.
What is traumatic brain injury?
Traumatic Brain Injury means an acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in a total or partial functional disability or psychological impairment, or both, that adversely affects a child’s educational performance. The term applies to open or closed head injuries resulting in impairments in one or more areas, such as cognition; language; memory; attention; reasoning; abstract thinking; judgment; problem solving; sensory, perceptual and motor abilities; psychosocial behavior; physical functions; information processing; and speech. The term does not apply to brain injuries that are congenital or degenerative, or brain injuries caused by birth trauma.
What is the definition of blindness?
(Refer to eligibility criteria for Deafness and for Visual Impairment) The impairment adversely affects the student’s educational performance, and requires special education to meet the student’s needs.
How does disability affect education?
The disability adversely affects the student’s educational performance , and requires special education to meet the student’s needs. Alternative method: Inadequate achievement measured against expectations for a child’s age or the grade level standards set by the state.
How does hearing impairment affect language development?
The hearing impairment adversely affects the development of expressive and/or receptive language and communication. The hearing impairment adversely affects the student’s educational performance, and requires special education to meet the student’s needs.
How does impairment affect students?
The impairment adversely affects the student’s educational performance, and requires special education to meet the student’s needs.
What is the responsibility of an IEP team?
It is the IEP team’s responsibility to determine if a student has a disability. If the student has more than one disability the team must determine the primary disability. Student must meet one of the eligibility and must also need related service (s). Possible related services could be:
What is limited alertness?
Limited strength, vitality, or alertness including a heightened alertness to environmental stimuli, that results in limited alertness with respect to the educational environment.
What is the IEP team?
It means that under the law, the IEP team has the flexibility to determine if a child qualifies for services. Criteria states that to qualify for special education services, a child must have one of the 13 disabilities as defined by IDEA AND the impact of the disability must create a need for services.
What is the IDEA for autism?
With regards to ADHD and autism spectrum disorders, IDEA allows school districts to add classifications at their discretion. This means that if a disorder is severe, the IEP team can determine that a child needs special education services.
What are some examples of adverse impacts?
Examples of adverse impacts include: Problems with fine or gross motor skills. For example, if a child is developmentally and chronologically ten years old but continues to read at a first grade level, the adverse effect would be a limited progression in reading.
Can a child be cut and dry?
If your child’s performance is NOT hindered by their disability, they may not qualify for services, even if they have one of the thirteen disabilities. Consequently, determining if a child is eligible is not cut and dry.
Is it cut and dry to determine if a child is eligible for special education?
Consequently, determin ing if a child is eligible is not cut and dry. It really depends on the child and their specific situation. Fortunately, IDEA was written to support this flexibility. If you are in disagreement with your IEP team on whether your child should receive special education eligibility, you should read the sections on collaboration, ...
What are the conditions that qualify for an IEP?
Disabilities or Conditions listed in this category are: ADD (Attention Deficit Disorder), ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder), Asthma, Diabetes, Epilepsy, Heart conditions, Hemophilia, Lead Poisoning, Leukemia, Nephritis (A kidney inflammation disorder), Rheumatic Fever, Sickle Cell Anemia and Tourette’s Syndrome . With any of these, there must be clear signs that educational outcome is affected.
What is a learning disability that can be easily missed?
Specific Learning Disability: This is another one that can be easily missed that includes dyslexia, perceptual disabilities, brain injury (including those that cause minimal brain dysfunction), and developmental aphasia (also known as word blindness ).
What is visual impairment?
Visual Impairment (including Blindness): This covers any impairment with a child’s vision whether it can be corrected or not that also affects a child’s educational outcome.
What is the definition of a child who is deaf?
Deafness: A child would need to be completely deaf or the hearing must be so bad that they cannot function at an educational level appropriate to their age, with or without technical assistance or amplification.
What are the different types of speech impairments?
Speech or Language Impairment: These would be listed as a communication disorder with the following types of conditions- stuttering, a voice or language impairment, or an impaired articulation . Once again, educational outcome must be affected.
What is the importance of IEP?
The important thing to remember for any IEP is that the condition MUST affect a child’s educational outcome. If they are brilliant and have no problems whatsoever with learning or adapting to a classroom environment affecting the ability to learn, chances are they may not qualify. This is a very important thing for parents to remember.
What are the acronyms for special education?
In the world of special education, teachers, special education departments and administrators live by acronyms. They will refer to FAPE, IEP, IDEA, and other terms all the time. If you aren’t familiar with these terms, it can get very confusing for a parent. So it is worth it to brush up on these prior to any IEP meeting.