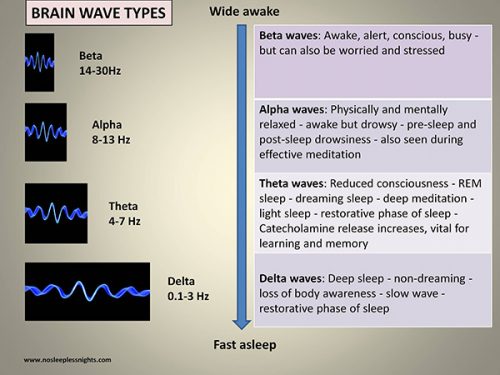
Types of Brain Waves
- Alpha Waves: At 8 to 12 Hz, alpha waves are involved in how we think, feel, communicate, sleep and generally function.
- Delta Waves: At 0.5 to 3 Hz, delta waves are the slowest brain waves and occur in the deepest states of sleep.
- Theta Waves: At 3 to 8 Hz, theta waves also occur during sleep, and have been observed in very deep states of meditation.
What kind of brain waves are produced during sleep?
The Different Types of Brain Waves
- Beta Waves. This is one categorization system that doesn’t start with a— or, in this case, alpha. ...
- Alpha Waves. In contrast to beta waves, alpha waves are associated with a relaxed or resting state. ...
- Theta Waves. Our next category of brainwaves takes us even deeper into unconsciousness. ...
- Delta Waves. ...
How does poor sleep affect your brain?
Sleep deprivation makes us moody and irritable, and impairs brain functions such as memory and decision-making. It also negatively impacts the rest of the body – it impairs the functioning of the immune system, for example, making us more susceptible to infection.
How bad is sleep deprivation for your brain?
This severely impairs your cognitive performance, causing symptoms like:
- impaired memory
- difficulty learning new information
- behavioral changes
- impaired decision-making
- difficulty processing social cues
- slow reaction time
- increased errors
What happens to your body and brain without sleep?
Brain functions including memory, decision-making, reasoning, and problem-solving worsened, along with reaction time and alertness. 5. You forget stuff. Not only can missed sleep make you more ...

What are the 4 types of brain waves?
Figure 2.1. Brain wave samples with dominant frequencies belonging to beta, alpha, theta, and delta bands and gamma waves. Various regions of the brain do not emit the same brain wave frequency simultaneously. An EEG signal between electrodes placed on the scalp consists of many waves with different characteristics.
How are brain waves different when we are sleeping?
Generally, brain waves are faster and have higher frequencies during wakefulness. Brain waves become slower when a person is drowsy and slow down further during deeper stages of sleep. However, in REM sleep7, brain wave patterns resemble those of someone who is awake.
What are the 5 brain frequencies?
Definitions. The EEG (electroencephalograph) measures brainwaves of different frequencies within the brain. ... Recommended Books.Brain Wave Frequencies:DELTA (0.1 to 3.5 Hz) The lowest frequencies are delta. ... THETA (4-8 Hz) The next brainwave is theta. ... ALPHA (8-12 Hz) ... BETA (above 12 Hz) ... GAMMA (above 30 Hz)
Are theta waves safe?
Between these ages, the brainwave frequencies of children typically oscillate in the Alpha and Theta brainwave cycles. Listening to binaural beats in these frequencies should, therefore, be safe for children to listen to.
Are theta waves good for sleep?
Theta waves are also associated with drowsiness and meditation. Studies show that listening to binaural beats at a 6 Hz frequency can induce a meditative state10.
Which frequency is best for brain?
6 Hz beat enhances all area of the brain within 10 minutes. 8 Hz and 25 Hz beats have no clearly responses while 40 Hz beat enhances the responses in frontal lobe. These brain responses can be used for brain modulation application to induce the brain activity in further studies.
What do brain waves tell you?
EEGs, which measure electrical signals in the brain, pick up each of these wavelengths and give us insights into our brain activity. EEGs can determine if brain activity is normal or unusual, which can lead to the diagnosis of a particular physical or mental health condition.
What is the best brain wave?
Gamma brain waves are the fastest brain waves produced inside your brain. Although they can be hard to measure accurately, they tend to measure above 35 Hz and can oscillate as fast as 100 Hz. Your brain tends to produce gamma waves when you're intensely focused or actively engaged in solving a problem.
What do brain waves look like during REM sleep?
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is characterized by darting movements of the eyes under closed eyelids. Brain waves during REM sleep appear very similar to brain waves during wakefulness.
Which brain waves are irregular and associated with stage 1 sleep?
In terms of brain wave activity, stage 1 sleep is associated with both alpha and theta waves.
Is laying down with eyes closed same as sleeping?
Conclusion. Resting your eyes is a good way to relax your body and replenish your eyes before it needs to take on more tasks, but it is in no way a substitute for sleep. Your body needs the replenishing benefits of sleep to function properly and restore itself.
How do brain waves change as a sleeper progresses from stage 1 to REM sleep?
The brain waves become slower. In general terms, how do brain waves change as a sleeper progresses from stage 1 sleep to stage 4 sleep? The brain waves become slower. Their amplitude decreases.
How many different types of brain waves are there?
Your brain produces five different kinds of brain waves, each of which operates at a different speed. From fastest to slowest, the five different types of brain waves include: gamma. beta. alpha. theta. delta. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at theta brain waves, their function, and how they differ from other types of brain waves.
Which brain wave is the fastest?
Gamma waves are the fastest of all the brain waves. They oscillate all the way up to the 100 Hz range and possibly even faster, since they can be challenging to measure accurately. Your brain produces gamma waves when you’re intensely focused on something, or fully engaged in solving a problem.
How to influence theta waves?
One possible way to influence your brain and its production of theta waves is by listening to binaural beats.
Why are theta waves important?
Experts believe that theta waves are important for processing information and making memories. And, as researchers learn more about how they work and how they’re linked to different types of learning, this knowledge may come in handy when determining the best way to help people learn.
What does it feel like to have a theta wave?
However, if you experience high levels of theta waves while you’re awake, you might feel a little sluggish or scattered.
What are the delta waves?
Delta. All the way at the bottom of the spectrum of brain waves — below theta waves — are the low, deep, slow delta waves. Both delta waves and theta waves occur when you’re asleep, but delta waves are the waves that dominate when you’re in a period of deep, restorative sleep. They measure in the 0.5 and 4 Hz range.
When do theta waves occur?
They may occur when you’re drifting off to sleep or suspended in that light phase of sleep, just before you wake up. Theta brain waves can also occur when you’re awake, but in a very deeply relaxed state of mind;
What waves do you get when you are fast asleep?
If you’re fast asleep and mid-REM cycle, you’ll be exhibiting higher levels of Delta and Theta waves.
What are the slowest brain waves?
Delta Waves. Delta waves are associated with deep levels of relaxation and restorative sleep, to remember this simply think of ‘Delta’ for ‘Deep’. They are the slowest recorded brain waves in humans and higher levels are more commonly found in young children. During the aging process, lower Delta waves are produced.
How many brain waves does Lucid have?
Something we hear quite often within the Lucid team is the expression, “I’ve just had a brainwave!”. Well the truth is that your brain actually has 5 brainwaves, each one a distinct electrical pattern which operates even when you’re fast asleep. For years, doctors and scientists have studied these brain waves using an EEG or electroencephalograph, a complex device which tracks the neuro activity known as brainwaves over 5 different channels. Lately, these devices have been simplified into consumer devices by our friends at Emotiv. Read more about the Emotiv hardware here.
Why do we feel theta waves?
Theta waves are also linked to us experiencing and feeling deep and raw emotions, therefore too much theta activity may make people prone to bouts of depression. Theta does however has its benefits of helping improve our creativity, wholeness and intuition, making us feel more natural.
Why do beta waves restrict alpha?
In this scenario, the Beta waves restrict the production of alpha because we because our body is reacting positively to the increased Beta activity, usually in a state of heightened cognitive arousal. Frequency range: 8 Hz to 12 Hz. High levels: Too much daydreaming, over-relaxed state or an inability to focus.
How do you increase beta waves?
Beta waves increased by drinking common stimulants such as caffeine or L-Theanine, or by consuming Nootropics or cognitive enhancers such as Lucid. Think of Beta as the ‘get shit done’ state of mind. Frequency range: 12 Hz to 40 Hz. High levels: Anxiety, inability to feel relaxed, high adrenaline levels, stress.
Why are theta waves considered suggestive waves?
Theta Waves. Theta waves known as the ‘suggestible waves’, because of their prevalence when one is in a trance or hypnotic state. In this state, a brain’s Theta waves are optimal and the patient is more susceptible to hypnosis and associated therapy.
What Happens When Brain Waves Are Out Of Balance?
When our brainwaves are out of balance, there will be corresponding problems in our emotional or neuro-physical health. Research has identified brainwave patterns associated with all sorts of emotional and neurological conditions. Over-arousal in certain brain areas is linked with anxiety disorders, sleep problems, nightmares, agitated depression, chronic nerve pain and spasticity.
What is the slowest band of brain waves?
Delta waves are emitted during deep and during dreamless sleep when there is unconsciousness. Delta is the slowest band of brainwaves. You do not dream in this state and are completely unconscious. 4.
What is the brain made of?
Our brain is made up of billions of brain cells called neurons. The combination of neurons sending signals at once, produces an enormous amount of electrical activity in the brain. These synchronized electrical pulses from masses of neurons communicating with each other produces ‘Brainwaves’. Brainwave speed is measured in Hertz (cycles per second) ...
What frequency is Alpha wave?
Alpha Waves. With a frequency range from 8hz – 12hz, Alpha is emitted when we are in a state of physical and mental relaxation (awake, but not processing much information). Studies show that Alpha states significantly increase beta-endorphin, noroepinephrine and dopamine.
What is brainwave state?
Knowledge of brainwave states enhances a person’s ability to make use of the specialized characteristics of those states: these include being mentally productive across a wide range of activities , such as being intensely focused, relaxed, creative and in restful sleep. Advertisements.
What frequency is beta?
This is the brainwave for the fight-flight response. With a frequency range from 12hz – 27hz, beta waves are emitted when we are consciously alert or we feel agitated, tense and afraid. Many people lack sufficient beta activity, which can cause mental or emotional disorders such as depression and insomnia. 2
What is theta wave?
Present in a frequency range from 3hz – 8hz, these waves offer a state of somnolence with reduced consciousness, light sleep or extreme relaxation. Theta is also a very receptive mental state that has proven useful for hypnotherapy as well as self-hypnosis using recorded affirmations and suggestions. 3
What is the fastest brain wave?
Gamma waves (38 to 42 Hz) Gamma brainwaves are the fastest of brain waves (high frequency, like a flute), and relate to simultaneous processing of information from different brain areas. Gamma brainwaves pass information rapidly and quietly. The most subtle of the brainwave frequencies, the mind has to be quiet to access gamma.
What is the frequency of beta waves?
Beta waves (12 to 38 Hz) Beta brainwaves dominate our normal waking state of consciousness when attention is directed towards cognitive tasks and the outside world. Beta is a ‘fast’ activity, present when we are alert, attentive, engaged in problem solving, judgment, decision making, or focused mental activity.
How to change your brainwave state?
Over the long term, traditional eastern methods (such as meditation and yoga) train your brainwaves into balance. Of the newer methods, brainwave entrainment is an easy, low-cost method to temporarily alter your brainwave state.
What is delta wave?
Delta waves (.5 to 3 Hz) Delta brainwaves are slow, loud brainwaves (low frequency and deeply penetrating , like a drum beat). They are generated in deepest meditation and dreamless sleep. Delta waves suspend external awareness and are the source of empathy. Healing and regeneration are stimulated in this state, ...
How are brainwaves detected?
Brainwaves are detected using sensors placed on the scalp. They are divided into bandwidths to describe their functions (below), but are best thought of as a continuous spectrum of consciousness; from slow, loud and functional - to fast, subtle, and complex. It is a handy analogy to think of brainwaves as musical notes - ...
What is theta in meditation?
Theta brainwaves occur most often in sleep but are also dominant in deep meditation. Theta is our gateway to learning, memory, and intuition. In theta, our senses are withdrawn from the external world and focused on signals originating from within.
What is infra low brainwaves?
Infra-Low brainwaves (also known as Slow Cortical Potentials), are thought to be the basic cortical rythms that underlie our higher brain functions. Very little is known about infra-low brainwaves. Their slow nature make them difficult to detect and accurately measure, so few studies have been done.
What waves do you experience when you are asleep?
When you are asleep, you experience theta waves and delta waves. These waves promote dreamless, deep and restorative slumber.
What are the different types of brain waves?
There are five different types of brain waves ranging from low to high frequency: 1 Delta brain waves happen to be the slowest and are generated when in deep meditation and dreamless sleep. It contains healing and regeneration abilities when the individual is in this state. 2 Theta waves also occur when you are asleep and during relaxation. These brain waves are indicative of dreams, inner focus as well as vivid imagery 3 Alpha waves of occur in your thoughtful and quiet times. They indicate that the brain is in a state of resting. 4 Beta waves are probably the most common pattern in the normal waking state. It’s often present when a person is alert, focused or in a problem-solving state of mind 5 Gamma waves are the fastest and are associated with higher levels of consciousness.
Can you control alpha brain waves?
Alpha waves are linked with relaxed mental states and this is why lots of experts believe that increasing alpha waves can help reduce anxiety and stress.
How to increase alpha waves?
Relaxation techniques such as meditation and mindfulness will help increase your alpha waves.
What does it mean when you have alpha waves?
Alpha waves of occur in your thoughtful and quiet times. They indicate that the brain is in a state of resting.
Why do we use brain waves?
Although a brainwave is a figure of speech used to describe your thoughts, clinicians and scientists use literal brain waves measured on the top of your head to help them understand the functioning of the human brain.
Which brain waves are the slowest?
Delta brain waves happen to be the slowest and are generated when in deep meditation and dreamless sleep. It contains healing and regeneration abilities when the individual is in this state. Theta waves also occur when you are asleep and during relaxation.
What is the meaning of brain waves?
Brain Waves. Brain waves are defined as rhythmic fluctuation of electric potential between parts of the brain as seen on an electroencephalogram (EEG). To measure brain waves electrodes are placed onto the scalp using the EEG. There are four types of brainwaves: Beta. Alpha.
How many Hz are beta waves?
Beta brain waves occur between 14 - 30 H z but during intense mental activity can reach 50 Hz i.e., Beta waves characterize the conscious waking state at 14 cycles per second and up.
What is delta brainwave?
Delta brainwaves occur below 3.5 Hz i.e., brain wave activity in the delta state ranges from 0 - 4 cycles per second. This is total unconsciousness, deep, dreamless sleep. When we are asleep and not dreaming, the brain generates delta waves.
What is the alpha wave?
Alpha brain waves occur between 8 - 13 Hz i.e. ,the alpha state operates at a lower cycle, 7-14 cycles per second level. In general, the alpha rhythm is the prominent EEG wave pattern of an adult who is awake but relaxed with eyes closed.
Why do delta waves increase?
Delta brain waves may increase during difficult mental activities requiring concentration . In general, the occurrence and amplitudes of delta and theta rhythms are highly variable within and between individuals.
What does the beta wave represent?
So, the beta wave represents excitement of the cortex to a higher state of alertness or tension.
Where do alpha waves come from?
Each region of the brain has a characteristic alpha rhythm but alpha waves of the greatest amplitude are recorded from the occipital and parietal regions of the cerebral cortex. Psychic experiences can happen in the alpha state. Both daydreaming and sleep dreaming occur while in the alpha state.
What Are Alpha Brain Waves?
Alpha brain waves are the main brain wave pattern that develops when a person becomes drowsy 3 and transitions from wakefulness to sleep. They continue during the early phase of sleep until they are replaced by slower theta waves.
How Is Alpha Activity Measured?
Electrical activity in the brain, including alpha brain waves, is measured with an electroencephalogram (EEG). An EEG is a common component 8 of a sleep study. Studying brain waves with an EEG helps health care professionals diagnose sleep disorders such as narcolepsy. Doctors also use EEGs to diagnose brain conditions such as epilepsy.
How Do Alpha Waves Affect Sleep?
Alpha wave activity is a normal part of falling asleep. But alpha waves may also play a role in certain sleep disorders and disturbances, notably insomnia and alpha-delta sleep.
