Compact bone is hard and forms the outer layer of any bone. On the other hand, spongy bone is softer, and forms the inner layer of bones while covering a large surface area. The main function of compact bone is to support the whole body, whereas spongy bones support the body structure.
What is the function of spongy bone?
Spongy bone is used for more active functions of the bones, including blood cell production and ion exchange. However, compact bones also serve a function in storing and releasing calcium to the body when needed.
What is the function of the compact bone?
However, compact bones also serve a function in storing and releasing calcium to the body when needed. The compact bone also provide strong mechanical levers, against which the muscles can create movement. This function is supported by the joints created by spongy bone and connective tissues, such as tendons and ligaments.
What is the difference between compact and spongy bone?
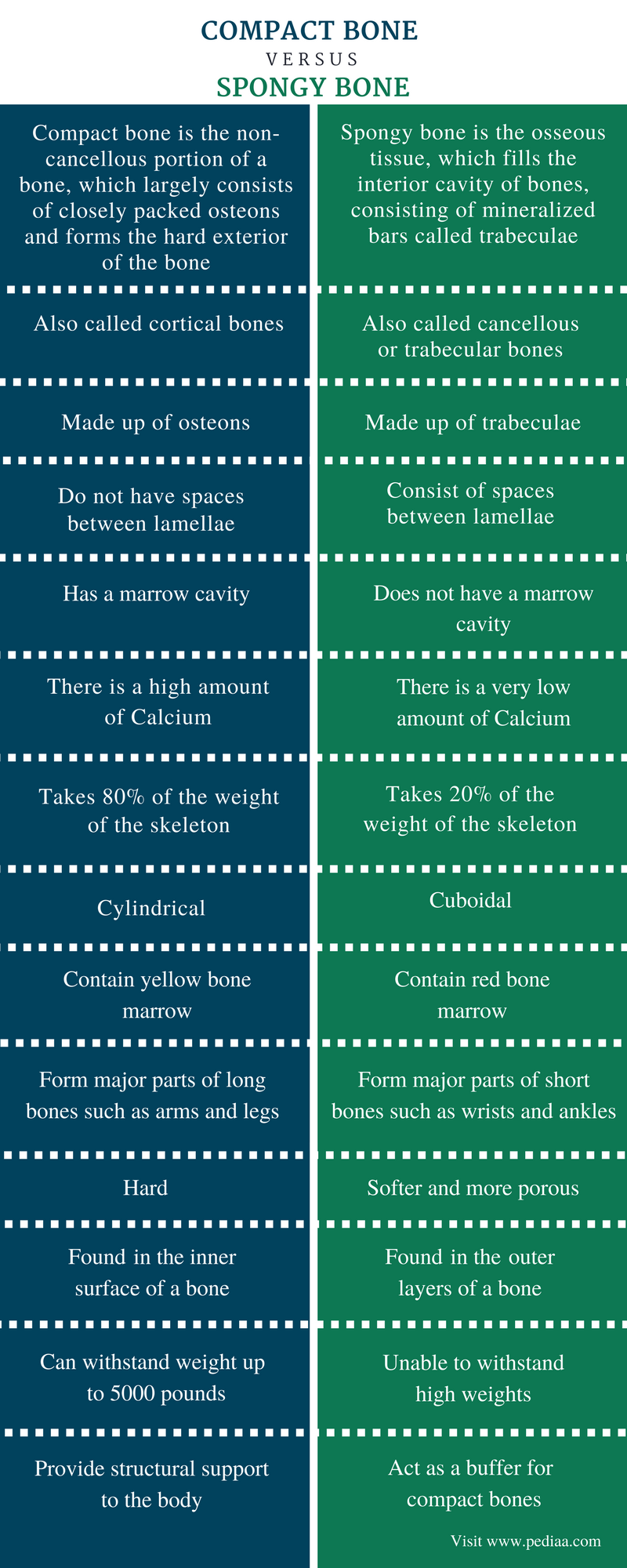
Compact Bone. Compact bone, also called cortical bone, surrounds spongy bone and makes up the other 80% of the bone in a human skeleton. It is smooth, hard and heavy compared to spongy bone and it is also white in appearance, in contrast to spongy bone which has a pink color. Compact bone is made up of units called lamellae which are sheets ...
What are the functional units of compact bone tissue?
Osteons – Functional units of compact bone, created by a network of bone cells and blood vessels. Osteocyte – A cell which function to maintain and repair bone tissue. Osteoblast – Cells which lay down new bone tissue, adding the matrix.

What is the difference in function of compact and spongy bone?
Spongy and compact bones are two basic structural bone types. They make up the long bones in the body. Long bones are dense hard bones that provide strength, structure and mobility....Spongy vs Compact Bones.Spongy BonesCompact BonesThey are made up of trabeculaeThey are made up of osteons6 more rows
What are the functions of spongy bone?
Adds Strength and Flexibility to Bones The trabeculae of spongy bone tend to form along lines of stress, giving the bone strength and flexibility in that area. Spongy bone is also present in the joints of the body and acts as a shock absorber when we walk, run and jump.
What is the difference between compact bone and spongy bone quizlet?
Compact bone has more bone matrix and less space due to osteons. Spongy bones have less bone matrix and more space due to trabeculae.
What is the function of the spongy bone quizlet?
What is a function of spongy bone? What does spongy bone contain instead of capillaries and venules in its matrix? It fills spaces between the trabeculae, forms blood cells, supplies nutrients to osteocytes, and removes wastes.
What is the spongy bone?
Spongy (cancellous) bone is lighter and less dense than compact bone. Spongy bone consists of plates (trabeculae) and bars of bone adjacent to small, irregular cavities that contain red bone marrow. The canaliculi connect to the adjacent cavities, instead of a central haversian canal, to receive their blood supply.
What is the major difference between compact and spongy bone quizlet patho?
What is the major difference between compact and spongy bone? The major difference between the two types of tissue is the organization of the elements. The differences in location in the body, chemical activation, or types of minerals contained are not as relevant.
How will you differentiate compact and spongy bones in terms of their cell arrangement?
Whereas compact bone tissue forms the outer layer of all bones, spongy bone or cancellous bone forms the inner layer of all bones. Spongy bone tissue does not contain osteons that constitute compact bone tissue. Instead, it consists of trabeculae, which are lamellae that are arranged as rods or plates.
What are the major structures found in compact bone and spongy bone quizlet?
MatchCompact Bone. - firmer outer layer of bone tissue. ... Spongy Bone. - softer inner layer of bone tissue. ... Osteon (Haversian System) the structural unit of compact bone, ellongated cylinders parallel to the long axis of the bone.Central (Haversian) Canal. ... Perforating (Volkmann's) Canal. ... Endosteum. ... Lamellae. ... Concentric Lamella.More items...
How does the structure of spongy bone relate to its function?
Spongy bone has a spongy or lattice-like structure, which allows for this portion of bone to hold bone marrow. This structure also makes bone less dense, which allows for flexibility when stress is applied to a bone.
What are the advantages of spongy bone over compact bone?
The advantages of Spongy bones is it's lighter than compact bone yet still strong and they follow the lines of stress which helps with support. Which type of free movable joint allows for the most range of motion? Disks of rubbery cartilage are formed between the individual bones in the spinal column.
What are the 2 other terms for spongy bone?
cancellous bone, also called trabecular bone or spongy bone, light, porous bone enclosing numerous large spaces that give a honeycombed or spongy appearance.
Where is the spongy bone?
Spongy bone is found mostly at the ends of bones and contains red marrow. Bone marrow is found in the center of most bones and has many blood vessels. There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow.