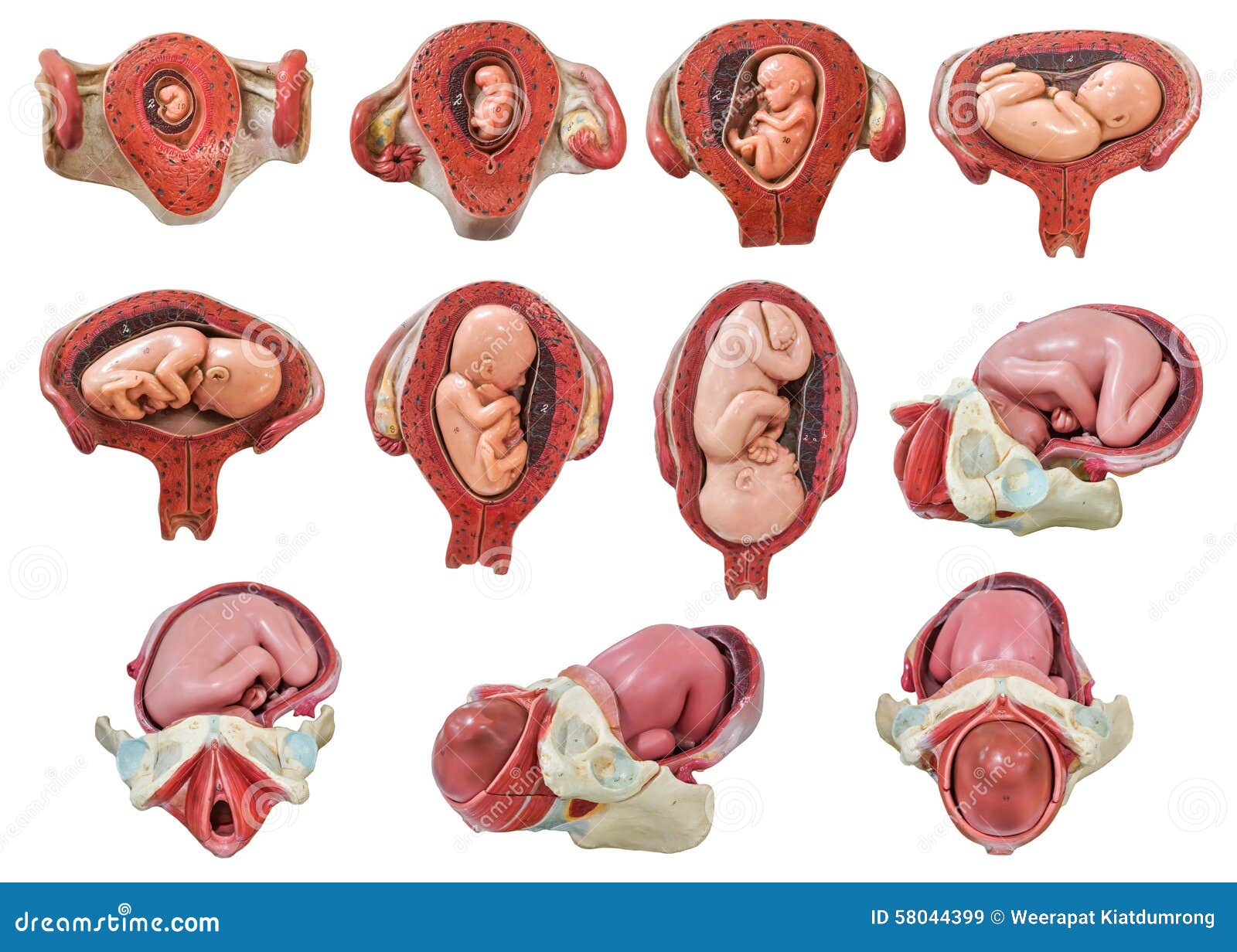
What is the most common uterine position?
The most common position of the uterus is anteverted (cervix angles forward) and anteflexed (body is flexed forward). The position of the uterus in the adult is liable to considerable variation, depending chiefly on the condition of the bladder and rectum.
What is the normal uterine position?
- The first part is verticle and runs parallel Wolfian duct on its lateral side.
- The second part of Mullerian ducts lies horizontally and crosses the ipsilateral Wolfian duct anteriorly.
- The third part is vertical, which joins its counterpart in the midline.
Where is the uterus located on the body?
The uterus is located within the pelvic region immediately behind and almost overlying the bladder, and in front of the sigmoid colon. The human uterus is pear-shaped and about 7.6 cm (3.0 in) long, 4.5 cm (1.8 in) broad (side to side), and 3.0 cm (1.2 in) thick.
What is anteversion of uterus?
Your uterus is a reproductive organ that plays a key role during menstruation and holds a baby during pregnancy. If your doctor tells you have you an anteverted uterus, it means that your uterus tilts forward at your cervix, toward your abdomen. Most women have this type of uterus.
What is the position of the uterus?
Normally, the human uterus lies in anteversion and anteflexion. In most women, the long axis of the uterus is bent forward on the long axis of the vagina, against the urinary bladder. This position is referred to as anteversion of the uterus.
How do you tell if a uterus is Anteverted or retroverted?
The opening of the U is your cervix (the opening to the uterus from the vagina). If your uterus is retroverted, your cervix is aimed toward your belly. It's more typical for the curved part of the U to be aimed toward your belly and your cervix to be pointed toward your rectum (this is called an anteverted uterus).
What is Anteverted position of uterus?
An anteverted uterus describes the position of the uterus within a person's pelvis. When you have an anteverted uterus, it tilts forward towards your abdomen. It's a typical position for the uterus to be in and doesn't cause any health concerns.
What is the most common uterine position?
The normal position of the uterus is known as the anteverted position where the uterus tips forward at the cervix. The uterus is a reproductive organ responsible for different functions, such as menstruation, pregnancy, and labor and delivery.
Does a tilted uterus mean smaller bump?
A tilted uterus can definitely contribute to a smaller (or later) bump—including cases in which people didn't know they were pregnant—but there are so many other elements at play that it's hard to boil it down to just the uterus.
Can a retroverted uterus affect bowel movements?
That's called a retroverted uterus. Women with retroverted uteruses are more at risk for a range of bladder and bowel problems, from prolapse (when the uterus drops into the vagina) to constipation (from pressure on the neighboring bowel).
Does your uterus change positions?
Your uterus may shift as you get older or after a pregnancy, which can alter its position in your body and reduce cramping.
What are the four types of uterus?
Bicornuate uterus: A heart-shaped uterus. Arcuate uterus: Similar to a bicornuate uterus but with less of a dip or heart shape. Septate uterus: When your uterus is divided into two parts by a membrane. Unicornuate uterus: When you have one fallopian tube and an irregularly shaped uterus.
Is retroverted uterus a problem?
Generally, a retroverted uterus does not cause any problems. If problems do occur, it will probably be because the woman has an associated disorder like endometriosis. A disorder like this could cause the following symptoms: Painful sexual intercourse.
What causes retroverted uterus?
In most cases, a retroverted uterus is a normal finding. However, in some cases it may be caused by endometriosis, salpingitis, or pressure from a growing tumor.
Which type of uterus is best for pregnancy?
Positions of the Uterus In most cases, a retroverted or tilted uterus does not interfere with a person's ability to become pregnant or carry a pregnancy to term. In some cases, for some people, it can increase miscarriage risk.
Can you fix a tilted uterus?
If your uterus is tipped and it's causing problems for you, your doctor may be able to prescribe exercises, a support device, or a surgical procedure to correct the angle of your uterus and relieve your symptoms. Ameer MA, et al. (2020).
What causes a tilted uterus?
Weakening of the pelvic muscles: After menopause or childbirth, the ligaments supporting the uterus can become lax or weakened. As a result, the uterus falls in a backward or tipped position. Enlarged uterus: An enlarged uterus due to pregnancy, fibroids, or a tumor can also cause the uterus to become tilted.
Can I get pregnant with a tilted uterus?
Yes, women can get pregnant with a tilted uterus. About 20 to 25 percent of women have a retroverted uterus.
What are the causes of a tilted uterus?
Most women are born with a tilted uterus. In rare cases, a tilted uterus may be caused by various conditions, which include:
What is a benign tumor of the uterus called?
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors of the uterus (the womb) and the single most common indication for hysterectomy. See a picture of Uterine Fibroids and learn more about the health topic.
What is the uterus called when it tilts forward?
This normal presentation of the uterus is called an anteverted position , however, an anteverted uterus may only be found in 50 percent of women, while the rest of the female population have a different uterine position.
What is the normal position of the uterus?
The normal position of the uterus is known as the anteverted position where the uterus tips forward at the cervix.
What is the term for the condition where the cells that grow in the uterus grow outside them?
Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the cells that grow in the uterus grow outside them. These cells can stick the uterus to other organs, causing it to tilt.
What is a myomectomy?
Myomectomy is a surgical procedure that removes fibroids from the uterus. Fibroids (also called leiomyoma) are noncancerous growths that commonly develop in women of childbearing age over the years. These may or may not cause symptoms, such as heavy bleeding during periods and feelings of heaviness, in the lower abdomen or pelvic region.
What does a bicornuate uterus look like?
It can also appear like a pair of horns or points. During pregnancy, this shape of uterus restricts the space that a fetus has to grow and develop. 1
What are Müllerian abnormalities?
The most common Müllerian abnormalities are for a uterus to be missing completely (known as agenesis) or severely underdevelop ed (hypoplasia). 1 In these cases, a person cannot carry a pregnancy.
How is the uterus held in position?
The uterus is held in position by various ligaments. For about half of women, the uterus is tilted slightly forward, toward the front of their pelvis. 2
What is the dip in the top wall of the uterus called?
An arcuate uterus has a slight dip in the top wall, known as the fundus. It is much less pronounced than the dip in a bicornuate uterus.
How to treat fibroids?
Fibroids can be treated using myolysis, a procedure that uses heat, cold, or even ultrasound to kill off or shrink fibroids. If you have severe and recurrent uterine conditions, your doctor might recommend a hysterectomy —the full removal of the uterus. You should speak with your doctor about what uterus procedures you may need, and why the doctor thinks they will be beneficial for you.
How many uterus are there in a septate?
People with a septate uterus have one uterus that is divided by a band of tissue, not unlike the septum that separates your nasal passages. In some people, this tissue runs the entire length of the uterus, but in others, it affects only part of the uterus. 3
What is the name of the double uterus?
Uterus didelphys is also known as double uterus. This can happen along a range: 3
What is a uterus?
Your uterus is a pear-shaped organ in the reproductive system of people assigned female at birth (AFAB). It’s where a fertilized egg implants during pregnancy and where your baby develops until birth. It’s also responsible for your menstrual cycle. It’s commonly referred to as your womb.
What does a uterus do?
Your uterus plays a key role in your reproductive health and function. The three main jobs of your uterus are:
What happens to your uterus during menstruation?
During your menstrual cycle, the lining of your uterus goes through several changes. The lining (called the endometrial lining) gets thicker and rich with blood as you near ovulation (releasing an egg from the ovaries). If an egg is fertilized during that cycle, it implants into the lining of your uterus, and pregnancy begins.
What happens to your uterus during pregnancy?
If conception (when the egg is fertilized by sperm) occurs during your menstrual cycle, the fertilized egg implants into your uterine lining. The fertilized egg (called a blastocyte) burrows into the endometrial lining of your uterus (implantation). This is when pregnancy officially begins, and you miss your menstrual period.
What does a uterus look like?
Your uterus looks like a light bulb. It’s about the size of your fist. It’s also commonly described as an upside-down pear. Your uterus has two horn-like organs at the top (the fallopian tubes). It connects to your cervix at the bottom, which is the part that opens (dilates) during vaginal delivery.
Where is the uterus in your body?
Your uterus is in your pelvis between your bladder and rectum. It’s supported by your pelvic floor muscles and perineal body. Ligaments in your pelvis, lower back and hips also help hold your uterus in place.
What is your uterus made of?
Myometrium: The highly muscular middle layer. This is what expands during pregnancy and contracts to push your baby out.
What happens to the uterus during the menstrual cycle?
During a normal menstrual cycle, the endometrial lining of the uterus goes through a process called vascularization during which tiny blood vessels proliferate, leaving the lining thicker and rich with blood in the event the egg released during that cycle is fertilized. If this does not happen, the uterus sheds the lining as a menstrual period. 3
What is the process of vascularization?
During a normal menstrual cycle, the endometrial lining of the uterus goes through a process called vascularization during which tiny blood vessels proliferate, leaving the lining thicker and rich with blood in the event the egg released during that cycle is fertilized.
What is the contraction of the uterus during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the muscular layer of the uterus begins contracting on-and-off in preparation for childbirth. These "practice" contractions, Braxton-Hicks contractions, resemble menstrual cramps; some women don't even notice them.
Why does the uterus contract after birth?
After a baby is born, the uterus continues to contract in order to expel the placenta. It will continue to contract in the coming weeks to return the uterus to its normal size and to stop the bleeding that occurs in the uterus during childbirth .
What is the condition where the endometrial lining grows outside of the uterus?
Endometriosis. An estimated 11% of women are affected by endometriosis, a condition in which the tissue of the endometrial lining grows outside of the uterus, 4 causing symptoms that include painful cramps, chronic lower back pain, and pain during or after sex.
What is the middle layer of the uterus?
Myometrium: The middle layer made of smooth muscle tissue. Endometrium: The inner lining that builds up over the course of a month and is shed if pregnancy does not occur. Shaped like an inverted pear, the uterus sits behind the bladder and in front of the rectum. It has four main sections: 1 .
What is the uterus called?
She has experience in primary care and hospital medicine. The uterus, also known as the womb, is the hollow, pear-shaped organ in the female pelvis in which fertilization of an ovary (egg), implantation of the resulting embryo, and development of a baby take place. It is a muscular organ that both stretches exponentially to accommodate ...
What is the uterus?
The uterus is a thick-walled muscular organ capable of expansion to accommodate a growing fetus. It is connected distally to the vagina, and laterally to the uterine tubes. The uterus has three parts; Fundus – top of the uterus, above the entry point of the uterine tubes.
What is the peritoneum?
Peritoneum – a double layered membrane, continuous with the abdominal peritoneum. Also known as the perimetrium. Myometrium – thick smooth muscle layer. Cells of this layer undergo hypertrophy and hyperplasia during pregnancy in preparation to expel the fetus at birth.
Where do sympathetic nerve fibres come from?
Sympathetic nerve fibres of the uterus arise from the uterovaginal plexus. This largely comprises the anterior and intermediate parts of the inferior hypogastric plexus.
Where does blood flow to the uterus?
The blood supply to the uterus is via the uterine artery. Venous drainage is via a plexus in the broad ligament that drains into the uterine veins.
What is the surgical removal of the uterus?
A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus, usually as a result of cervical or uterine cancer.
Can a retroflexed uterus cause a prolapse?
Retroflexed and retroverted. These abnormal arrangements do not inherently cause any medical problems. However, the retroverted uterus is positioned directly above the vagina. Thus in instances of increased abdominal pressure, the uterus is more likely to prolapse into the vagina.
Does a retroverted uterus prolapse?
Thus in instances of increased abdominal pressure, the uterus is more likely to prolapse into the vagina. Uterine prolapse is particularly prevalent in those with a history of pelvic floor damage. By Ruksana Begum, TeachMeAnatomy.
What is an ECV for a breech fetus?
If a fetus is in a breech position at 36 weeks, a doctor or midwife may suggest an external cephalic version (ECV). An ECV is a procedure where a doctor or midwife will try to turn the fetus manually. For this procedure, they will first insert a small needle into the woman’s hand to relax the uterus.
What is the position of a fetus before labor?
The ideal position for a fetus just before labor is the anterior position. In this position, the fetus’s head points toward the ground and they are facing the woman’s back. Most fetuses settle into this position by the last month of pregnancy. The anterior position is also known as a vertex, cephalic, or occiput anterior position.
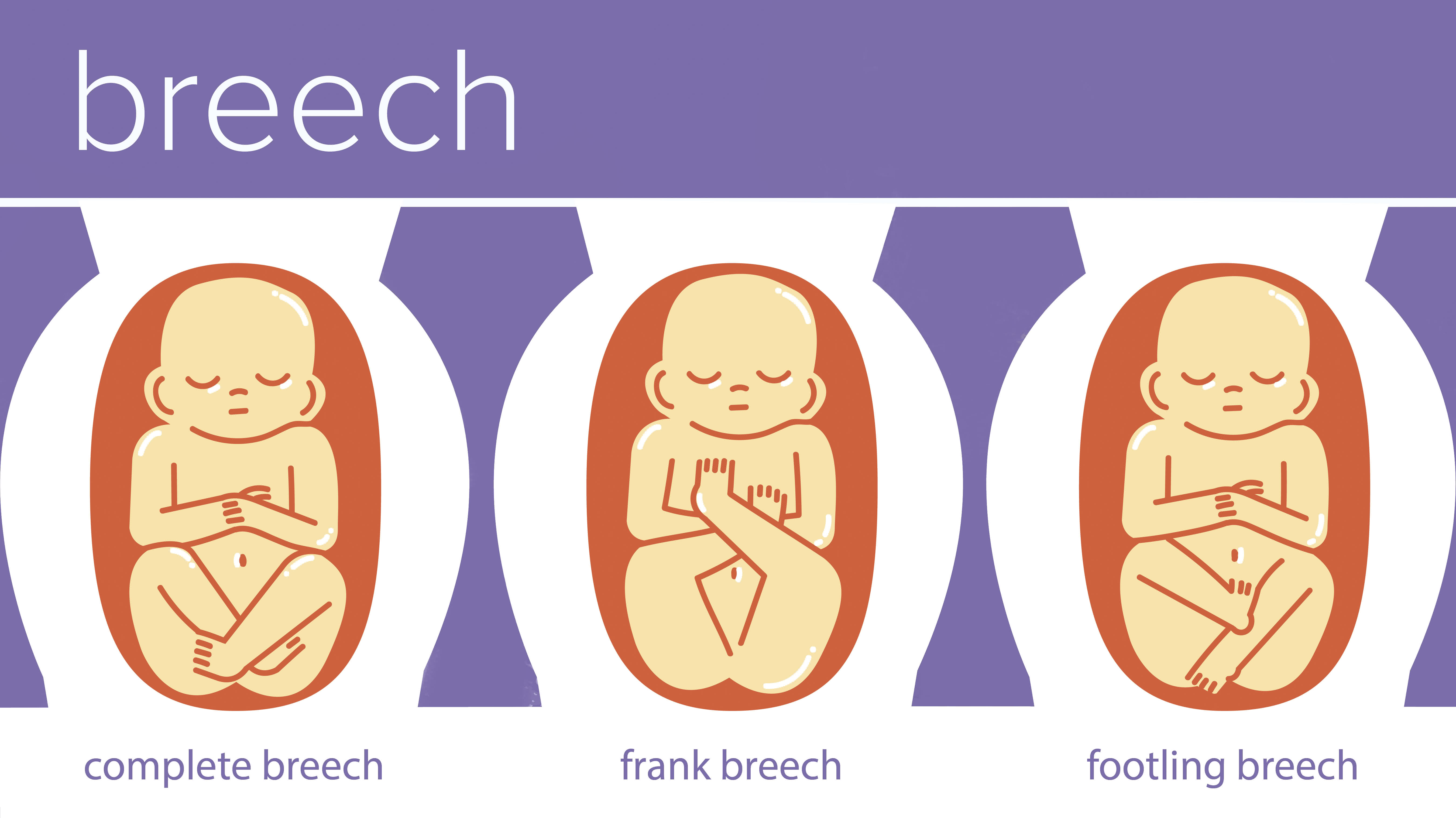
What is the breech position?
Breech position. The breech position is when the fetus remains with the head up instead of down in the woman’s pelvis. There are different types of breech position, including: Frank breech: In this position, the fetus’s legs lie straight upward in front of their body, so the feet are near the face.
What is the anterior position?
The anterior position is also known as a vertex, cephalic, or occiput anterior position. The anterior position may reduce the chances of complications during pregnancy. Learn more about this and other fetal positions in the womb in this article.
How to relax a pregnant woman's uterus?
For this procedure, they will first insert a small needle into the woman’s hand to relax the uterus . Using their hands on the outside of the pregnant woman’s belly, a doctor or midwife will then gently manipulate the fetus from a breech position into a transverse lie position, then into a head-down position.
How to tell what position a baby is in?
How to tell which position the baby is in. The best way of finding out which position the fetus is in is by talking to a doctor or midwife. At each appointment during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, a doctor or midwife should feel the woman’s abdomen to check the position of the fetus.
How to tell if a woman has a bump?
When the fetus is in the back-to-back or posterior position, the pregnancy bump may feel squishy. A woman may also notice kicks around the middle of the belly, and some people may also see an indentation around their belly button.
Why do babies turn their heads down?
This is because there is a small risk of the umbilical cord prolapsing (coming out of the womb before the baby) when your water breaks.
Why does my baby stay in a posterior position during labor?
These tips don’t always work. If your baby stays in a posterior position when labor starts, it may be because of the shape of your pelvis rather than your posture. In some cases, a cesarean delivery will be necessary.
What is the name of the presentation of a baby with a chin?
The baby is able to flex their head and neck, and tuck their chin into their chest. This is usually referred to as occipito-anterior, or the cephalic presentation.
How many babies rotate in the first stage of labor?
In the first stage of labor, about one-tenth to one-third of babies are in this position. Most of these babies will spontaneously rotate themselves to face in the right direction before birth. But a number of cases, the baby doesn’t rotate.
Why does my baby feel like he is kicking?
The position of your baby becomes more important as your due date nears. This is because your baby needs to get into the best position to prepare for delivery.
What is the best position for a baby to be in during delivery?
The narrowest part of the head can press on the cervix and help it to open during delivery. Most babies generally settle in the head-down position around the 33- to 36-week range. This is the ideal and safest position for delivery.
How successful is ECV?
The ECV technique is successful about half of the time.
What (and where) is your cervix?
First things first. If you’ve never really thought about your cervix before - and many of us haven’t - you might not even know where to find it.
What does the cervix do?
Your cervix is a hard-working multi-tasker. It secretes mucus that helps sperm cells travel from the vaginal canal to the uterus, and it also lets menstrual blood flow out. If you become pregnant, it even develops a mucus plug, a build-up of mucus that prevents bacteria and infections from reaching your uterus, protecting your baby.
Why does your cervix change positions?
Changes in your cervix position are related to the different phases of your menstrual cycle, as well as hormonal changes, that are, for example, caused by pregnancy.
Cervix positions during your cycle
So, what are the different positions your cervix moves into throughout your cycle, and what can it tell you?
Track your cycle
Tracking your fertility by cervix position and cervical mucus alone isn’t always an easy task, but when you get to know your cycle, these can be useful indicators to look out for.
