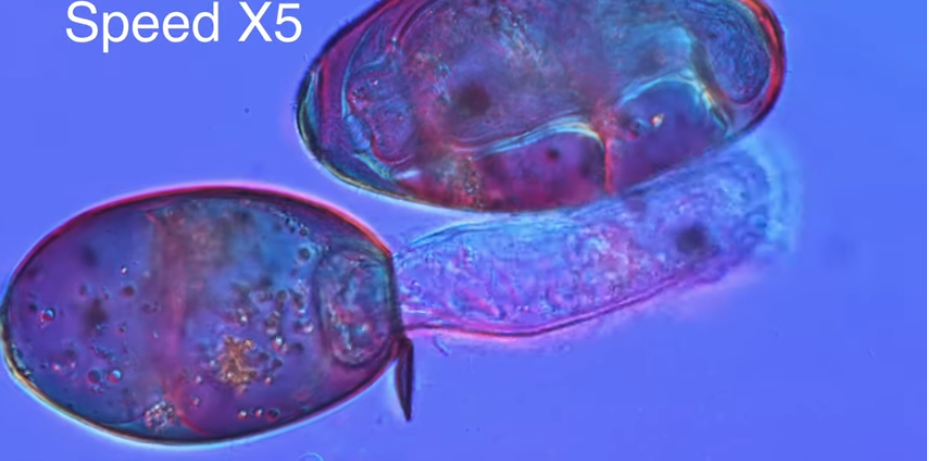
Life Cycle of Liver Fluke
- 1) The Egg – Stage 1 – The adult female liver fluke parasite passes immature eggs in the bile duct and comes out into the environment through the faeces. ...
- 2) The Intermediate Host – Stage 2 – ...
- 3) The Young Fluke – Stage 3 – ...
- 4) The Adult – Stage 4 –
What is the life cycle of liver flukes?
The life cycle of liver flukes is categorized into four stages namely The Egg (stage 1), The Intermediate Host (stage 2), The Young Fluke (stage 3) and The Adult (stage 4). All the four stages are described vividly in the following: 1. The Egg (stage 1): The immature eggs are laid by the adult female liver fluke after fertilization.
What happens to the young Fluke in Stage 3?
The Young Fluke (stage 3): After stage 2 the small intestine wall is penetrated by the fluke parasite and it enters into the peritoneal cavity. Next, it directly comes in contact with the liver and it begins feeding on liver cells. The above phenomenon happens a few days after the host comes in contact with the parasite.
How long does it take for metacercariae to turn into liver fluke?
The metacercariae transform into an adult liver fluke parasite after around three months. An adult liver fluke measures up to 3 cm in length. A gravid adult female liver fluke can produce 20,000 to 25,000 eggs per day.
What is the pathophysiology of liver fluke?
The adult female liver fluke parasite passes immature eggs in the bile duct and comes out into the environment through the faeces. If and when the eggs come in contact with water, the eggs become embryonated and form into a larva called miracidia. A miracidia larva infects a snail and the miracidia larva transforms into cercaria larvae.

What are the larval stages in flukes?
The hatchling is called a miracidium, a free-swimming, ciliated larva. Miracidia will then grow and develop within the intermediate host into a sac-like structure known as a sporocyst or into rediae, either of which may give rise to free-swimming, motile cercariae larvae.
What is the life cycle of liver fluke in cattle?
The lifecycle from initial ingestion at pasture to hosting egg-laying adult liver fluke is around 10 to 12 weeks in cattle, and the time from egg laying to infective cysts being formed is around 12 weeks.
What is the sequence of development in flukes?
So, the correct option is, 'egg, miracidium, sporocyst, cercaria'.
What are the stages in the life cycle of Fasciola hepatica?
In the snail, the parasites progress through several developmental stages (sporocysts, rediae, and cercariae).
What kills all stages of fluke in cattle?
Closantel, Rafoxanide and Nitroxynil will kill any fluke that are over 7-8 weeks of age, depending on the product. So any younger fluke will survive and be able to grow and mature all the while damaging the animal's liver.
Do flukes have a complex life cycle?
Trematodes (Phylum: Platyhelminthes, Subclass: Digenea), also known as flukes or parasitic flatworms, are common in aquatic systems. They have complex life cycles, usually involving a series of three hosts, although life histories vary.
What are the 3 stages in the life cycle of a helminth?
Helminths form three main life-cycle stages: eggs, larvae and adults. Adult worms infect definitive hosts (those in which sexual development occurs) whereas larval stages may be free-living or parasitize invertebrate vectors, intermediate or paratenic hosts.
What is the sequence of development in flukes quizlet?
The correct sequence of development in a typical fluke life cycle is.. -egg, miracidium, cercaria, sporocyst.
What is the life cycle of a lung fluke?
The life cycle of these flukes involves 2 intermediate hosts plus humans. Its complex life cycle involves 7 distinct phases: egg, miracidium, sporocyst, redia, cercaria, metacercaria, and adult. Adult flukes live in human lungs and deposit eggs into the bronchi.
Which of these stages in life cycle of Fasciola hepatica is infective to secondary host?
The adult flukes reside in the large biliary ducts of the mammalian host. By this life cycle, it is known that the infective stage of Fasciola hepatica is metacercaria.
What is the process of reproduction in liver fluke?
Liver flukes reproduce both sexually and asexually. Adults are hermaphroditic, capable of both cross- and self-fertilization. The larvae stage known as sporocyst reproduces asexually with its offspring developing into rediae, which also multiply asexually. Adults live in the bile ducts of their mammalian host.
Which of the following life cycle stage of liver fluke is infectious to the intermediate host?
Miracedium is the larval stage of liver fluke which is released into fresh water when eggs are hatched. These miracedium infects the snail present in that fresh water (intermediate host). So, the correct answer is 'Miracidia'.
What is the general life cycle of a fluke?
The adult flukes deposit fully developed eggs that are passed in the feces . After ingestion by a suitable snail (first intermediate host) , the eggs release miracidia , which undergo in the snail several developmental stages (sporocysts , rediae , cercariae ).
How do you get rid of liver fluke in cattle?
TreatmentValbazen® is approved for the treatment of adult (mature) flukes from F. ... Valbazen®(Albendazole) at 10 mg/kg, the flukes need to be mature (more than 90 days old) for treatment to be effective.Label dose of Valbazen is effective.More items...
How long does a liver fluke live?
Liver flukes infect the liver, gallbladder, and bile duct in humans. While most infected persons do not show any symptoms, infections that last a long time can result in severe symptoms and serious illness. Untreated, infections may persist for up to 25–30 years, the lifespan of the parasite.
How is liver fluke spread in cattle?
Liver fluke infection in cattle The liver fluke life cycle involves a free-living stage which depends on the presence of an intermediate host, a mud snail. The seasonal nature of liver fluke infection results from infective larvae being shed by snails onto pasture primarily during late summer and early autumn.
1. What is fasciolosis?
Liver fluke disease affects the sheep in three different clinical forms – acute, subacute and chronic fasciolosis. The type of clinical forms depen...
2. What is fluke quarantine?
At the time of buying sheep, fluke quarantine treatment strategies must be taken into consideration on the basis of risk posed by the sheep and the...
3. How do snails get infected in the warm seasons?
Snails act as intermediate hosts for liver fluke parasites. Snails can get infected all year round due to the hatching cycles of the parasites as w...
4. Do snails get infected in the winter season as well?
This does not usually happen, however, it is possible that the infection can persist well beyond winter too. In these cases, however, the parasites...
5. Is this disease contagious?
Liver fluke disease is not directly contagious, no. It cannot pass on from skin contact, it must be ingested. The only way the parasites can enter...
6. How can liver fluke disease affect human beings?
In human beings, liver fluke disease can affect the liver, bile duct, and intestines. In fact, it can affect the entire gastrointestinal duct. A lo...
7. How to be certain that the parasites in the body are dying?
Once the person has been diagnosed, he/she can start treatment. In this case, the results can be seen soon in the form of headaches, fainting spell...
How does one know they have liver fluke?
At first, the ingestion of the parasite will not show any symptoms, depending upon the species. However, later when the parasite becomes infective,...
Are liver flukes contagious?
Liver flukes are not contagious and cannot transfer from one person to the other. They spread is from contaminated fish or water that humans consume.
How big are liver flukes?
The liver fluke measures up to 15mm in length and 0.1 mm in width.
Can one see liver fluke in stool?
Eggs of Clonorchis, Opisthorchis or Fasciola are seen in the faeces of the human host. It can also be found in the small intestine.
Can one see liver fluke in stool?
Eggs of Clonorchis, Opisthorchis or Fasciola are seen in the faeces of the human host. It can also be found in the small intestine.
What is the name of the cysts that a snail forms when it is in contact with a miracidia?
A miracidia larva infects a snail and the miracidia larva transforms into cercaria larvae. Here, the snail acts as an intermediate host and the cercaria larvae has a long tail that helps them swim in the water. The cercaria larva grows, leaves the snail host and looks for vegetation, where it forms cysts called metacercariae.
What causes liver fluke?
The liver fluke disease is caused when immature liver fluke parasites migrate through the liver and are sometimes caused by the presence in bile ducts, or sometimes both. Liver fluke infects all grazing animals like sheep, cattle and mammals like human beings. Liver fluke parasites occur in regions around water bodies like river banks, ...
How do flukes get into the liver?
The fluke parasite penetrates the small intestinal wall and enters the peritoneal cavity. After this, it enters the liver and the parasite starts feeding on liver cells. This occurs a few days after the host comes in contact with the parasite. After eating plenty of liver cells, the young flukes migrate to the bile duct and transform into adult liver flukes.
What is the name of the disease caused by a fluke?
Introduction. Liver flukes, also known as Fasciola hepatica, are parasites that cause the liver fluke disease known as Fascioliasis in the liver of human beings. The liver fluke parasite falls under the phylum Platyhelminthes. The liver fluke disease is caused when immature liver fluke parasites migrate through the liver ...
How long does it take for a liver fluke to develop?
The metacercariae transform into an adult liver fluke parasite after around three months. An adult liver fluke measures up to 3 cm in length. A gravid adult female liver fluke can produce 20,000 to 25,000 eggs per day.
What stage of liver fluke is the egg?
1) The Egg – Stage 1 –. The adult female liver fluke parasite passes immature eggs in the bile duct and comes out into the environment through the faeces. If and when the eggs come in contact with water, the eggs become embryonated and form into a larva called miracidia.
How long does it take for a liver fluke to develop?
The infection is patent about 10-12 weeks after the metacercariae are ingested. The whole cycle takes 18-20 weeks.
What is the liver fluke?
Lifecycle. Liver fluke disease (fasciolosis) is caused by the trematode parasite Fasciola hepatica. Disease can result from the migration of large numbers of immature flukes through the liver, or from the presence of adult flukes in the bile ducts, or both. Liver fluke can infect all grazing animals (and man) but mainly affects sheep and cattle.
How do fluke eggs hatch?
Adult fluke lay eggs that are passed out onto pasture in the faeces. At suitable temperatures, a miracidium develops within the egg, hatches and migrates in thin films of moisture, actively seeking the snail host. Miracidia can only survive for a few hours outside the snail. Within the snail they undergo two further developmental stages, including multiplication, eventually becoming infective cercariae, which emerge from the snail when the temperature and moisture levels are suitable.
What is the clinical form of sheep fluke?
Fasciolosis. Liver fluke disease in sheep occurs in three main clinical forms – acute, subacute and chronic fasciolosis. Which form occurs depends on the numbers of infective metaceriae ingested and the period of time over which they are ingested.
When do snails hatch miracidia?
Summer infection of snails: In wet summers, snail populations multiply rapidly and snails are invaded by hatching miracidia from May to July. If wet weather continues, the snails shed massive numbers of cercariae onto pasture during July to October. Conversely, if the climate in May and July is dry or cold, fewer snails appear, fewer fluke eggs hatch and levels of contamination in the autumn are much lower. Clinical fasciolosis resulting from summer infection of snails arises usually from ingestion of large numbers of metacercariae over a short period of time in July to October.
What is the life cycle of a mud snail?
Compared to other helminths, the lifecycle is complex and involves an intermediate host, the mud snail Galba (Lymnaea) truncatula and several free-living stages. The role of the snail, which prefers muddy, slightly acidic conditions, particularly areas associated with poor drainage, means the incidence of liver fluke is far greater in ...
When do liver flukes occur?
Such conditions usually occur from May to October in the UK although patterns have been changing in recent years. The incidence of fasciolosis is highest in years when rainfall is above average during May, June and July. The epidemiology of liver fluke is often viewed as the result of two distinct cycles of snail infection and pasture contamination.
What is the life cycle of a fluke?
Life Cycle: The adult flukes deposit fully developed eggs that are passed in the feces. After ingestion by a suitable snail (first intermediate host) , the eggs release miracidia , which undergo in the snail several developmental stages (sporocysts , rediae , cercariae ).
Where do flukes live?
felineus: 7 mm to 12 mm by 2 mm to 3 mm) reside in the biliary and pancreatic ducts of the mammalian host, where they attach to the mucosa.
