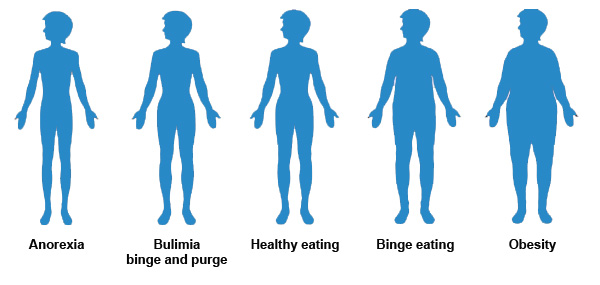
There are four terms used to describe body habitus: Hyperstenic (large to massive). Chest and abdomen are broad and deep, lungs are short, diaphragm is high. Stenic (average). Hypostenic (slender). Asthenic (very slender).
What are the proportions of the body?
What is body size?
What does it mean when your height is below the 3rd percentile?
Where is the mid upper arm measured?
What is the upper to lower segment ratio?
Who owns the copyright to the book Butterworth?
See 3 more
About this website

What is the most common body habitus?
Terms in this set (4)Sthenic. Most common type of body habitus. Organs: ... Hyposthenic. These characteristics are a mix between sthenic and asthenic. This is the most difficult body habitus to classify.Asthenic. Organs: Heart- Nearly vertical, at midline. ... Hypersthenic. Organs: Heart-Axis nearly transverse.
Does body habitus mean fat?
Large body habitus is often used by radiologists as a euphemism for overweight/obese patients in radiology reports, usually in reference to its deleterious effect on image quality, sometimes it maybe expressed as 'large body habitus artifact' 14.
Which body habitus is most difficult to classify?
Hyposthenic (slender) This body habitus is the most difficult to classify.
What does habitus mean in medical terms?
body buildMedical Definition of habitus : habit specifically : body build and constitution especially as related to predisposition to disease an ulcer habitus.
How does fat look on ultrasound?
Fat has classically been described as hyperechoic on sonograms because of its acoustic impedance relative to surrounding tissue, although certain types of fat in certain anatomic locations can be hypoechoic.
Can an ultrasound see through fat?
Fat also absorbs the soundwaves, so the more there is around your abdomen, the less likely it is that the details will be clear. If the sonographer can't get a clear image of your baby via your tummy, she may suggest a vaginal ultrasound scan.
Why is body habitus important in radiography?
Large body habitus can degrade image quality in all medical imaging modalities, sometimes making it difficult to obtain accurate clinical interpretations. In ultrasound imaging, a thick layer of fat can significantly attenuate the beam intensity, especially at high frequencies used for abdominal imaging.
What is the most common body habitus present in about 50% of the population?
According to Cramberry [26], Sthenic type of body habitus accounts for 50% of the total population of human race, followed by hyposthenic and the least hypersthenic body habitus. All the categories of body habitus showed statistically significant relationships between right and left rotations.
Which type of body habitus is likely to have redundant bowel loops?
Positioning Part 1 - Foundation conceptsQuestionAnswerWhich body habitus is likely to have redundant bowel loops?Hyposthenic/AsthenicWhich body habitus is likely to have a high and transverse stomach?HypersthenicWhich body habitus would have their duodenal bulb at the lowest point?Hyposthenic/Asthenic48 more rows
What is an example of habitus?
Through the habitus subjects acquire a world-view and become particular kinds of subjects who act and conduct themselves as such. One example of this is law, which produces subjects who see the world in particular ways, and whose actions come to be conceptualised as such (for example, as lawful or unlawful).
What are the Big 3 in medical terms?
Big Three. The three major tropical infections—HIV/AIDS, malaria, tuberculosis—which receive the bulk of international funding for prevention and treatment.
What is Hyposthenic body habitus?
(hī-pŏs-thĕn′ik) 1. Debilitant. 2. A body habitus characterized by a long, shallow thorax, a long thoracic cavity, a long, narrow abdominal cavity, and a slender build.
Is body mass the same as fat?
Body Mass Index is a measure of body fat based on your height and weight. Physicians widely consider BMI measurements as a simple way to determine if a person is healthy or unhealthy, underweight or overweight.
Which body habitus is average?
1. Sthenic - athletic build, average, similar to hypersthenic but modified by elongation of abdomen and thorax. 3.
What is increased body habitus?
The politically correct term for obesity is “increased body habitus.” Since none of the radiologists worry about “decreased body habitus,” the phrase is often shortened to “body habitus.” A: The expression “increased body habitus” is new to us.
What is considered fat vs chubby?
Rounded features. Someone who's fat, on the other hand, is obese, or significantly overweight, and there's nothing in the least bit healthy about obesity. Below: 25 to 29% body fat is chubby. 30% and above is fat.
Four types of body Habitus Flashcards | Quizlet
Lead has a density of 11.3 g/cm3. If you have 1.0 kg of lead, what is the volume in cubic centimeters (cm3)? Remember to select an answer with the correct number of significant figures.
What is large body habitus? | HealthShare
What are the Reasons and side-effects of amenorrhea? I am a 24 year old female at 1.72m, who has trained quite heavily for triathlons for the past 2 years.
Body Size and Habitus - Clinical Methods - NCBI Bookshelf
Body size and habitus describe the physical characteristics of an individual and include such considerations as physique, general bearing, and body build. Historically, attempts have been made to classify humans into discrete somatotypes (mesomorphic—muscular and athletic; endomorphic—rounded and stout; and ectomorphic—tall and thin), and to relate habitus to propensity to disease (e.g ...
Medical Definition of Body habitus
Body habitus: The physique or body build. For example: "The metabolic complications most commonly reported (with HIV infection) are hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia and altered body habitus.". The term "body habitus" is somewhat redundant, since habitus by itself means "physique or body build."
Body habitus | definition of body habitus by Medical dictionary
body habitus: ( bod'ē hab'i-tŭs ) Build, physique, and general shape of the human body.
Body Habitus | RADTECH 111 - Blogger
1. Sthenic - athletic build, average, similar to hypersthenic but modified by elongation of abdomen and thorax. 2. Hypersthenic - body is large and heavy, bony framework is thick, short and wide, lungs and heart are high, transverse stomach and peripheral colon
What are the proportions of the body?
Body proportionsinclude the trunk to limb ratioand the arm span. The trunk, or "upper segment," is represented by the distance from the symphysis pubis to the crown of the head. The "lower segment" is the distance from the symphysis pubis to the plantar surface of the foot and represents the "limb" contribution to total height. At birth the normal upper to lower segment ratio is 1.7:1. The legs grow more rapidly than the trunk, and by age 10 the segments are equal and remain so in adults. The arm span is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers with the arms fully extended. In adults the arm span should equal the height.
What is body size?
Body size and habitus describe the physical characteristics of an individual and include such considerations as physique, general bearing, and body build. Historically, attempts have been made to classify humans into discrete somatotypes (mesomorphic—muscular and athletic; endomorphic—rounded and st …
What does it mean when your height is below the 3rd percentile?
Heights that fall below the 3rd percentile or above the 97th percentile may require investigation. Weightis the total weight of the body. Weights greater than 120% of "ideal" suggest obesity, while weights less than 70% of "ideal" may indicate severe malnutrition.
Where is the mid upper arm measured?
Mid–upper arm measurementsare taken at the midpoint between the acromial process and the olecranon process. Skinfold thicknessat this site is a measure of subcutaneous fat and is used to estimate total adiposity. Obesity is indicated by a value greater than 23 mm in men and 30 mm in women. Severe depletion of energy stores is indicated by values below the 30th percentile. Mid–upper arm circumferenceis used to calculate mid—upper arm muscle circumference. Muscle circumferences less than the 30th percentile suggest severe depletion of protein stores.
What is the upper to lower segment ratio?
At birth the normal upper to lower segment ratio is 1.7:1 . The legs grow more rapidly than the trunk, and by age 10 the segments are equal and remain so in adults. The arm span is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers with the arms fully extended. In adults the arm span should equal the height.
Who owns the copyright to the book Butterworth?
Copyright © 1990, Butterworth Publishers, a division of Reed Publishing.
What is body size and habitus?
Body size and habitus describe the physical characteristics of an individual and include such considerations as physique, general bearing, and body build. Historically, attempts have been made to classify humans into discrete somatotypes ...
How to measure tricep skinfold?
Triceps skinfold thickness is generally measured at the midpoint, between the acromial process of the scapula and the olecranon process of the ulna of the left arm, using a skinfold caliper. This point is marked on the posterior side with the patient sitting or standing with the arm hanging loosely at the side. Patients unable to sit may be measured supine in bed with the arm folded across the chest. The skin and subcutaneous tissues should be pinched between the thumb and forefinger 1 cm above the mark and gently pulled away from the underlying muscle. While the grasp is maintained, the calipers are placed over the skinfold at the midpoint mark, left in place for 3 seconds and the value is read. The average of three separate readings is recorded in millimeters. Plastic calipers may not be accurate. The subscapular skinfold is similarly measured 1 cm below the right scapula.
Why is skin fold thickness important?
Skin-fold thickness may be used to supplement weight and height measurements. Measurement of body fat is also useful to estimate the duration and severity of inadequate dietary intake as fat is lost slowly in malnutrition.
Why is body weight considered a poor measure of adiposity?
Body weight alone is a poor measure of adiposity because weight is strongly correlated with height. Clinicians have generally relied on height and weight tables to determine the appropriateness of a patient's weight for his or her height. The 1959 Metropolitan Life Desirable Weight Tables in use for the past two decades were based on actuarial data from the 1959 Build and Blood Pressure Study of insured individuals. The term "ideal weight" was coined by Metropolitan Life to encourage people to keep their weight below the average for the insured population. The ideal weight was that associated with the maximum longevity for each height and "frame size." Guidelines for determining frame size were not given and actually represented an arbitrary division of the population into the low (small frame), middle two (medium frame), and highest quartiles (large frame). In fact, there are few studies assessing the contribution of frame size to weight. The "body mass index" (BMI = weight/height2) has been promoted as a superior index of relative weight.
Where is the mid upper arm measured?
Mid–upper arm measurementsare taken at the midpoint between the acromial process and the olecranon process. Skinfold thicknessat this site is a measure of subcutaneous fat and is used to estimate total adiposity. Obesity is indicated by a value greater than 23 mm in men and 30 mm in women. Severe depletion of energy stores is indicated by values below the 30th percentile. Mid–upper arm circumferenceis used to calculate mid—upper arm muscle circumference. Muscle circumferences less than the 30th percentile suggest severe depletion of protein stores.
What are the proportions of the body?
Body proportionsinclude the trunk to limb ratioand the arm span. The trunk, or "upper segment," is represented by the distance from the symphysis pubis to the crown of the head. The "lower segment" is the distance from the symphysis pubis to the plantar surface of the foot and represents the "limb" contribution to total height. At birth the normal upper to lower segment ratio is 1.7:1. The legs grow more rapidly than the trunk, and by age 10 the segments are equal and remain so in adults. The arm span is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers with the arms fully extended. In adults the arm span should equal the height.
Why do insulinacts help?
Insulinacts primarily to preserve the metabolic homeostasis necessary for growth rather than as a direct growth stimulator.
How far away from the midline is the illiac crest?
1-2 inches away from the midline and 2-3 inches above the illiac crest.
Where is the syringe folded in?
It's folded in upon itself and occupies the low median position in he abdominal cavity.
Which body type has a high colon?
The colon is high and extends around the entire periphery of the abdominal cavity in a hyposthenic body type.
Is the heart wide or short?
Heart is short and wide. Diaphragm is high resulting in a long abdominal cavity.
What are the proportions of the body?
Body proportionsinclude the trunk to limb ratioand the arm span. The trunk, or "upper segment," is represented by the distance from the symphysis pubis to the crown of the head. The "lower segment" is the distance from the symphysis pubis to the plantar surface of the foot and represents the "limb" contribution to total height. At birth the normal upper to lower segment ratio is 1.7:1. The legs grow more rapidly than the trunk, and by age 10 the segments are equal and remain so in adults. The arm span is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers with the arms fully extended. In adults the arm span should equal the height.
What is body size?
Body size and habitus describe the physical characteristics of an individual and include such considerations as physique, general bearing, and body build. Historically, attempts have been made to classify humans into discrete somatotypes (mesomorphic—muscular and athletic; endomorphic—rounded and st …
What does it mean when your height is below the 3rd percentile?
Heights that fall below the 3rd percentile or above the 97th percentile may require investigation. Weightis the total weight of the body. Weights greater than 120% of "ideal" suggest obesity, while weights less than 70% of "ideal" may indicate severe malnutrition.
Where is the mid upper arm measured?
Mid–upper arm measurementsare taken at the midpoint between the acromial process and the olecranon process. Skinfold thicknessat this site is a measure of subcutaneous fat and is used to estimate total adiposity. Obesity is indicated by a value greater than 23 mm in men and 30 mm in women. Severe depletion of energy stores is indicated by values below the 30th percentile. Mid–upper arm circumferenceis used to calculate mid—upper arm muscle circumference. Muscle circumferences less than the 30th percentile suggest severe depletion of protein stores.
What is the upper to lower segment ratio?
At birth the normal upper to lower segment ratio is 1.7:1 . The legs grow more rapidly than the trunk, and by age 10 the segments are equal and remain so in adults. The arm span is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers with the arms fully extended. In adults the arm span should equal the height.
Who owns the copyright to the book Butterworth?
Copyright © 1990, Butterworth Publishers, a division of Reed Publishing.