
The three types of density are physiological, arithmetic, and agriculture. Physiological density calculates the amount of people per arable square kilometer of land. Arithmetic density is the amount of people per square kilometer of land.
- Density, mass per unit volume. ...
- Area density or surface density, mass over a (two-dimensional) area.
- Linear density, mass over a (one-dimensional) line.
- Relative density or specific gravity, a measure of density in comparison to the density of something else.
What is a real life example of density?
An example of density is salinity, also known as the amount of salt in an ocean. Salt is heavier than fresh water, so it sinks to the bottom of the ocean. When water is evaporating, the salt stays at the bottom of the ocean and doesn’t evaporate. That is why when it rains, the rain’s not salty.
What are the identify units of density?
Thus, the units of density are defined by the base units of mass and length. The density of a substance is the ratio of the mass of a sample of the substance to its volume. The SI unit for density is the kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m 3 ).
What units are used to measure density?
density, mass of a unit volume of a material substance. The formula for density is d = M/V, where d is density, M is mass, and V is volume. Density is commonly expressed in units of grams per cubic centimetre. How is matter quantified? Mass measures the amount of matter in a substance or an object.
What is the usual unit for density?
The formula for density is d=M/V, where d is density, M is mass, and V is volume. Density is commonly expressed in units of gram per cubic centimeter. For example, the density of water is 1 gram per cubic centimeter.
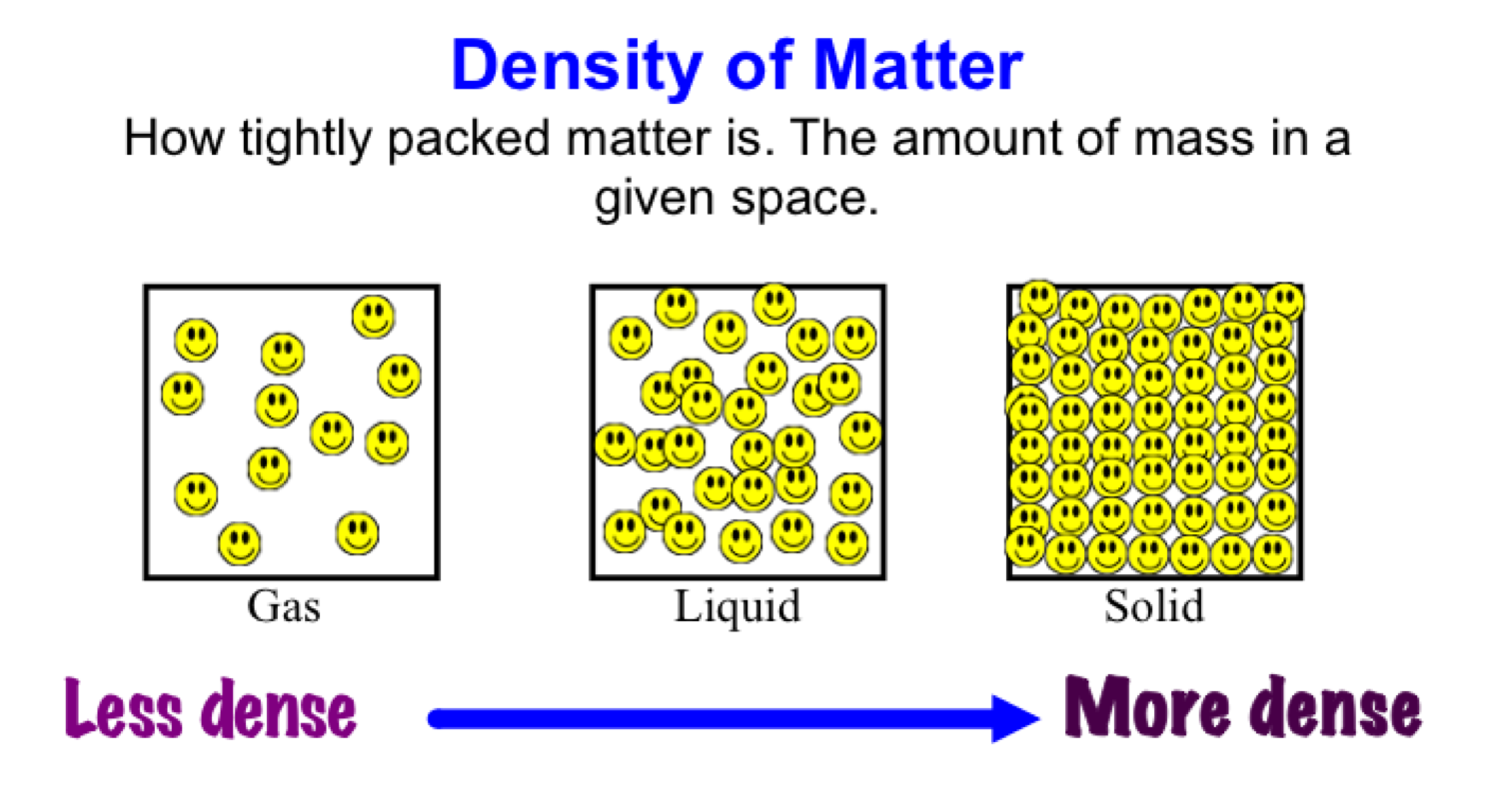
What is density and its type?
The formula for density is d = M/V, where d is density, M is mass, and V is volume. Density is commonly expressed in units of grams per cubic centimetre. For example, the density of water is 1 gram per cubic centimetre, and Earth's density is 5.51 grams per cubic centimetre.
What are 5 examples of density?
Examples of Density:Oil and Water Don't Mix. It's a known fact that oil and water don't mix, but what many people may not know is that the density of oil is what makes it float on top of water. ... Helium Balloons. ... Archimedes and Eureka! ... Icebergs.
What are 3 most commonly used units of density?
Common units for density include g/mL, g/cm3, g/L, kg/L, and even kg/m3.
Why are there different densities?
All types of matter—solids as well as liquids—are made up of many different atoms. Depending on the mass of these atoms, their size and the way they are arranged, different substances will have different densities.
What are 2 examples of density?
Everyday Density Examples A Styrofoam cup is less dense than a ceramic cup, so the Styrofoam cup will float in water and the ceramic cup will sink. Wood generally floats on water because it is less dense than water. Rocks, generally being denser than water, usually sink.
What is density give an example?
Density is the measure of how much “stuff” is in a given amount of space. For example, a block of the heavier element lead (Pb) will be denser than the softer, lighter element gold (Au). A block of Styrofoam is less dense than a brick. It is defined as mass per unit volume.
What is used to measure density?
HydrometerSo, Hydrometer is used for measuring the density or relative density of liquids.
What are the four units of density?
Though the SI unit of density is kg/m³, for convenience we use g/cm³ for solids, g/ml for liquids, and g/L for gases. Density can be explained as the relationship between the mass of the substance and the volume it takes up.
What is material density?
Material density, more often referred to simply as density, is a quantitative expression of the amount of mass contained per unit volume . The standard unit is the kilogram per meter cubed (kg/m 3 or kg · m -3 ). Density is sometimes expressed in grams per centimeter cubed (g/cm 3 or gm · cm-3).
What are the three properties of density?
General Properties of DensityMass of the Object. The mass of the object being measured for density is a part of the calculation. ... Volume. Volume also decides the final density value. ... The Calculation. Putting volume and mass together in a calculation defines density. ... Water. ... Ice.
What is liquid density?
The density of a liquid is a measure of how heavy it is for the amount measured. If you weigh equal amounts or volumes of two different liquids, the liquid that weighs more is more dense. If a liquid that is less dense than water is gently added to the surface of the water, it will float on the water.
What type of property is density?
intensive propertyDensity is an intensive property because there is a narrow range of densities across the samples. No matter what the initial mass was, densities were essentially the same. Since intensive properties do not depend on the amount of material, the data indicate that density is an intensive property of matter.
What has a lot of density?
If something is heavy for its size, it has a high density. If an object is light for its size it has a low density. A pebble is heavy for its size, compared to a piece of popcorn which is light for it's size. Imagine a big bowl of popcorn, compared to a big bowl of pebbles, which would feel heavier?
Where can density be used?
You have probably already encountered one of the important practical applications of density, maybe even without knowing.Ships and Submarines. One well-known application of density is determining whether or not an object will float on water. ... Oil Spills. ... Plumbing Systems. ... Airplane Weight Distribution.
What is the density of an object?
Density is the mass of an object divided by its volume. Density often has units of grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). Remember, grams is a mass and cubic centimeters is a volume (the same volume as 1 milliliter). from edinfomrmatics.
What is the density of water?
997 kg/m³Water / Density
What is density in science?
Put another way, density is the ratio between mass and volume or mass per unit volume. It is a measure of how much "stuff" an object has in a unit volume (cubic meter or cubic centimeter). Density is essentially a measurement of how tightly matter is crammed together.
How to find density of an object?
To calculate the density (usually represented by the Greek letter " ρ ") of an object, take the mass ( m) and divide by the volume ( v ):
What is the difference between specific gravity and density?
An object with a specific gravity less than one will float in water, while a specific gravity greater than one means it will sink.
Is density measured in grams?
Recall that though density is indeed mass divided by volume, it is often measured in units of grams per cubic centimeter because grams represent a standard weight, while cubic centimeters represent the volume of the object.
What is bulk density?
Bulk density, mass of a particulate solid or powder divided by the volume it occupies
What is density estimation?
Density estimation is the construction of an estimate of a probability density function
What is density in chemistry?
Density is the weight per unit volume of a substance. It is expressed in gram per cubic centimeter or pound per cubic foot or mega gram per cubic metre (Mg m -3 ). Two density measurements—particle density and bulk density are common for soils.
What is bulk density?
Bulk density is defined as the mass (weight) per unit volume of a dry soil (volume of solid and pore spaces). It is also expressed in gm./c.c. (G.G.S. system) or lb/cft (F.P.S. system) or mega gram per cubic metre. The bulk density of a soil is always smaller than its particle density. Loose and porous soils have low weights per unit volume and compact soils have high values.
What is the particle density of soil?
Generally in the normal soils the particle density is 2.65 grams per cubic centimetre or mega grams per cubic metre. The particle density is higher if large amounts of heavy minerals such as magnetite, limonite, hematite and zircon are present. With an increase in organic matter of the soil, the particle density decreases.
What is the weight per unit volume of soil called?
The weight per unit volume of the solid portion of soil is called particle density . It is also termed as true density. It is expressed in gm./c.c. (C.G.S. system) or lb/cft (F.P.S. system). It depends upon the accumulative densities of the individual inorganic and organic constituents of the soil. Generally in the normal soils the particle density is 2.65 grams per cubic centimetre or mega grams per cubic metre.
How does soil structure affect bulk density?
Soil structure affects bulk density by influencing the porosity of the soil. More for example, crumb soil structure shows low bulk density than that of platy soil structure. A metal cylinder pushed into a loam soil is removed from the field and the soil it contains is dried in an oven.
Why is bulk density important?
Bulk density is of greater importance than particle density in understanding the physical behaviour of soils. Generally, soils having low and high bulk densities exhibit favourable and poor physical conditions respectively.
How to find bulk density of soil?
2. The bulk density of a soil can be calculated on the basis of dry weight of that soil divided by its volume.
What are dense breasts?
Dense breasts have relatively high amounts of glandular tissue and fibrous connective tissue and relatively low amounts of fatty breast tissue.
How do I know if I have dense breasts?
Only a mammogram can show if a woman has dense breasts. Dense breast tissue cannot be felt in a clinical breast exam or in a breast self-exam. For this reason, dense breasts are sometimes referred to as mammographically dense breasts.
Are breast cancer patients with dense breasts more likely to die from breast cancer?
No. Research has found that breast cancer patients who have dense breasts are no more likely to die from breast cancer than breast cancer patients who have fatty breasts, after accounting for other health factors and tumor characteristics.
Does dense breast tissue affect mammograms?
Does having dense breast tissue affect a woman’s mammogram? Mammograms can be harder to read in women with dense breasts than in women with fatty breasts. That's because dense breast tissue and some abnormal breast changes, such as calcifications and tumors , appear as white areas in the mammogram.
Is breast tissue dense?
Breasts can be almost entirely fatty (A), have scattered areas of dense fibro glandular breast tissue (B), have many areas of glandular and connective tissue (C), or be extremely dense (D). Breasts are classified as “dense” if they fall in the heterogeneously dense (C) or extremely dense (D) categories.
Are dense breasts a risk factor for breast cancer?
Yes, women with dense breasts have a higher risk of breast cancer than women with fatty breasts, and the risk increases with increasing breast density. This increased risk is separate from the effect of dense breasts on the ability to read a mammogram.
